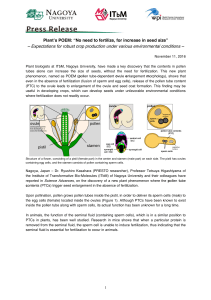
Plant`s POEM: “No need to fertilize, for increase in seed size
... “The most difficult part of this research was to make sure that fertilization does not occur in order to identify the function of PTCs,” says Kasahara. “I was extremely excited when I saw that PTCs alone led to seed development without fertilization.” Reproduction in plants starts from pollination ...
... “The most difficult part of this research was to make sure that fertilization does not occur in order to identify the function of PTCs,” says Kasahara. “I was extremely excited when I saw that PTCs alone led to seed development without fertilization.” Reproduction in plants starts from pollination ...
reproduction - Welcome To Badhan Education
... Semen. It is a fluid containing secretions of accessory glands together with the sperms. Semen also contains enzymes that activate the sperm after ejaculation. Embryo. It is the stage of development between the zygote or fertilized egg and the newly formed offspring. Fertilisation. It is defined as ...
... Semen. It is a fluid containing secretions of accessory glands together with the sperms. Semen also contains enzymes that activate the sperm after ejaculation. Embryo. It is the stage of development between the zygote or fertilized egg and the newly formed offspring. Fertilisation. It is defined as ...
ch 30 seed plants
... • A pollen grain that has landed on a stigma germinates and the pollen tube of the male gametophyte grows down to the ovary • The ovule is entered by a pore called the micropyle • Double fertilization occurs when the pollen tube discharges two sperm into the female gametophyte within an ovule ...
... • A pollen grain that has landed on a stigma germinates and the pollen tube of the male gametophyte grows down to the ovary • The ovule is entered by a pore called the micropyle • Double fertilization occurs when the pollen tube discharges two sperm into the female gametophyte within an ovule ...
Experimental evolution reveals trade
... investment. However, like all Lepidoptera, male P. interpunctella make a substantial reproductive investment at each mating— approximately 4 per cent of the male’s body mass [20]. It may be that the magnitude of male investment in ejaculate provisions transferred to females is sufficient to alter th ...
... investment. However, like all Lepidoptera, male P. interpunctella make a substantial reproductive investment at each mating— approximately 4 per cent of the male’s body mass [20]. It may be that the magnitude of male investment in ejaculate provisions transferred to females is sufficient to alter th ...
NUCLEAR FUSION DEFECTIVE1 Encodes the
... mating of a and a cells in yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae; Rose, 1996). Karyogamy occurs three times during the angiosperm life cycle. Two of these karyogamy events occur during double fertilization. Upon entry of the pollen tube into the ovule, two sperm cells are released into the female gametoph ...
... mating of a and a cells in yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae; Rose, 1996). Karyogamy occurs three times during the angiosperm life cycle. Two of these karyogamy events occur during double fertilization. Upon entry of the pollen tube into the ovule, two sperm cells are released into the female gametoph ...
Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology
... buds, are usually more leafy in appearance than the other floral organs. Petals are typically more brightly colored than sepals and advertise the flower to insects and other pollinators. A stamen consists of a stalk called the filament and a terminal structure called the anther; within the anther are c ...
... buds, are usually more leafy in appearance than the other floral organs. Petals are typically more brightly colored than sepals and advertise the flower to insects and other pollinators. A stamen consists of a stalk called the filament and a terminal structure called the anther; within the anther are c ...
The Land Plants - Del Mar College
... • Most sporophytes have leaves and roots that grow out from rhizomes • Spores are dispersed from clusters of sporangia (sori) on lower surfaces of frond leaves • Many live as epiphytes attached to another plant ...
... • Most sporophytes have leaves and roots that grow out from rhizomes • Spores are dispersed from clusters of sporangia (sori) on lower surfaces of frond leaves • Many live as epiphytes attached to another plant ...
Plant Form and Function
... the claim that a single “Eve” gave rise to the entire kingdom Plantae 450 million years ago. At each subsequent step in evolution, the evidence suggests that only a single family of plants made the transition. The fungi appear to have branched later than the plants and are more closely related to us ...
... the claim that a single “Eve” gave rise to the entire kingdom Plantae 450 million years ago. At each subsequent step in evolution, the evidence suggests that only a single family of plants made the transition. The fungi appear to have branched later than the plants and are more closely related to us ...
9.3 Flowers, pollination, fertilization
... fertilization and seed dispersal • Pollination – pollen is transferred from anther to a stigma • Fertilization- After pollination a zygote is formed by the fusion of a male gamete with a female gamete inside the plants ovule. •Seed Dispersal – Ovaries develop into a fruit. The function of a fruit is ...
... fertilization and seed dispersal • Pollination – pollen is transferred from anther to a stigma • Fertilization- After pollination a zygote is formed by the fusion of a male gamete with a female gamete inside the plants ovule. •Seed Dispersal – Ovaries develop into a fruit. The function of a fruit is ...
1) Pollen sticks to animal or released into wind 2
... 1) Pollen sticks to animal or released into wind 2) Insect flies away covered in pollen 3) Insect comes across another flower and spreads the pollen 4) Pollen tube grows towards ovary 5) Nucleus travels down pollen tube to fertilize egg 6) Zygote hardens into seed…flower starts to die 7) Ovary grows ...
... 1) Pollen sticks to animal or released into wind 2) Insect flies away covered in pollen 3) Insect comes across another flower and spreads the pollen 4) Pollen tube grows towards ovary 5) Nucleus travels down pollen tube to fertilize egg 6) Zygote hardens into seed…flower starts to die 7) Ovary grows ...
BIOLOGY (Theory)
... Now Griffith killed the S strain bacteria by heating them and injected these heat-killed bacteria into the mice. He observed that heat-killed S strain bacteria did not kill the mice. But when a mixture of heat-killed S and live R bacteria was injected into mice, the mice died. It was because when th ...
... Now Griffith killed the S strain bacteria by heating them and injected these heat-killed bacteria into the mice. He observed that heat-killed S strain bacteria did not kill the mice. But when a mixture of heat-killed S and live R bacteria was injected into mice, the mice died. It was because when th ...
PLANT EVOLUTION AND DIVERSITY
... 2. Meiosis in the ovule produces a haploid spore that forms the few cells of the female gametophyte, one of which becomes the egg. 3. Pollination occurs when a pollen grain lands on the stigma. A pollen tube grows from the pollen grain to the ovule. ...
... 2. Meiosis in the ovule produces a haploid spore that forms the few cells of the female gametophyte, one of which becomes the egg. 3. Pollination occurs when a pollen grain lands on the stigma. A pollen tube grows from the pollen grain to the ovule. ...
Expressing the Diphtheria Toxin A Subunit from
... primary endosperm. The mechanisms that control male germline development and gene expression, and ensure that sperm properly fuse with female gametes are just beginning to be understood. Expression of the potent translation inhibitor, diphtheria toxin A subunit, from the Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis tha ...
... primary endosperm. The mechanisms that control male germline development and gene expression, and ensure that sperm properly fuse with female gametes are just beginning to be understood. Expression of the potent translation inhibitor, diphtheria toxin A subunit, from the Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis tha ...
The Producers: The Plant Kingdom An Introduction to
... • Tissue differentiation. Unlike algae, land plants are differentiated into two main parts: a root, usually growing underground and absorbing nutrients, and a shoot, usually growing above ground and absorbing sunlight to perform photosynthesis. Most plants have a variety of specialized tissues withi ...
... • Tissue differentiation. Unlike algae, land plants are differentiated into two main parts: a root, usually growing underground and absorbing nutrients, and a shoot, usually growing above ground and absorbing sunlight to perform photosynthesis. Most plants have a variety of specialized tissues withi ...
Distinguish between the four main groups of land plants
... 14. Describe the adaptations of vascular plants, including modifications of the life cycle and modifications of the sporophyte, that have contributed to their success on land. a. Dominant sporophyte generation b. Modifications i. Branched sporophyte for producing more spores ii. Vascular tissue with ...
... 14. Describe the adaptations of vascular plants, including modifications of the life cycle and modifications of the sporophyte, that have contributed to their success on land. a. Dominant sporophyte generation b. Modifications i. Branched sporophyte for producing more spores ii. Vascular tissue with ...
video slide - Des Moines Area Community College, Iowa
... Transport in Xylem and Phloem • Vascular plants have two types of vascular tissue – Xylem and phloem • Xylem – Conducts most of the water and minerals – Includes dead cells called tracheids. Their cell walls remain to provide the internal ‘pipe system’. – Cell walls are strengthened by the polymer ...
... Transport in Xylem and Phloem • Vascular plants have two types of vascular tissue – Xylem and phloem • Xylem – Conducts most of the water and minerals – Includes dead cells called tracheids. Their cell walls remain to provide the internal ‘pipe system’. – Cell walls are strengthened by the polymer ...
Kingdom Plantae - f
... the sporophyte, a capsule is formed, within which meiosis occurs and the spores are produced. When the spores are mature, the top of the capsule, the operculum, pops off and the spores are then dispersed by the wind. Frequently, an immature capsule is covered by a thin tissue layer called the calypt ...
... the sporophyte, a capsule is formed, within which meiosis occurs and the spores are produced. When the spores are mature, the top of the capsule, the operculum, pops off and the spores are then dispersed by the wind. Frequently, an immature capsule is covered by a thin tissue layer called the calypt ...
A positive signal from the fertilization of the egg cell sets off
... cell divides again so that the mature pollen contains one large vegetative and two small sperm cells (Fig. 2e). In A. thaliana, the two sperm cell nuclei in the mature pollen enter a long S phase, which continues during pollen germination and subsequent pollen tube growth and is completed immediatel ...
... cell divides again so that the mature pollen contains one large vegetative and two small sperm cells (Fig. 2e). In A. thaliana, the two sperm cell nuclei in the mature pollen enter a long S phase, which continues during pollen germination and subsequent pollen tube growth and is completed immediatel ...
Structure of Flower
... All plants have a life cycle in which a diploid sporophyte generation alternates with a haploid gametophyte generation. Gametophyte plants produce male and female gametes—sperm and eggs. When the gametes join, they form a zygote that begins the next sporophyte generation. In some plants, the two sta ...
... All plants have a life cycle in which a diploid sporophyte generation alternates with a haploid gametophyte generation. Gametophyte plants produce male and female gametes—sperm and eggs. When the gametes join, they form a zygote that begins the next sporophyte generation. In some plants, the two sta ...
File
... ICSH- interstitial cell stimulating hormone (same as LH in female) Testosterone functions: 1. Promotes maturation of sperm 2. Maintains accessory organs of male repro. system 3. Secondary sex characteristics 4. Stimulate metabolic operations ( protein synthesis and muscle growth 5. Influen ...
... ICSH- interstitial cell stimulating hormone (same as LH in female) Testosterone functions: 1. Promotes maturation of sperm 2. Maintains accessory organs of male repro. system 3. Secondary sex characteristics 4. Stimulate metabolic operations ( protein synthesis and muscle growth 5. Influen ...
S21:Reproduction in flowering plants
... Dioecious plants. When a species such as willow produces separate male and female plants, it is described as dioecious. Self-pollination is impossible in such species, but the number of dioecious plant species is very few. They are often trees: holly, yew and poplar are examples. Monoecious plants. ...
... Dioecious plants. When a species such as willow produces separate male and female plants, it is described as dioecious. Self-pollination is impossible in such species, but the number of dioecious plant species is very few. They are often trees: holly, yew and poplar are examples. Monoecious plants. ...
video slide
... – If pollination is successful, a pollen grain (花粉粒) produces a structure called a pollen tube (花粉管), which grows down into the ovary (卵房) and discharges sperm near the embryo sac (胚囊) ...
... – If pollination is successful, a pollen grain (花粉粒) produces a structure called a pollen tube (花粉管), which grows down into the ovary (卵房) and discharges sperm near the embryo sac (胚囊) ...
Hormonal
... have sex, etc. Most common is the two dose regimen May inhibit/delay ovulation or altering the transport of sperm/egg; does not affect a fertilized, implanted egg Needs to be taken within 72 hours. Best used within 24 hours ...
... have sex, etc. Most common is the two dose regimen May inhibit/delay ovulation or altering the transport of sperm/egg; does not affect a fertilized, implanted egg Needs to be taken within 72 hours. Best used within 24 hours ...
8 How Do Organisms Reproduce
... 25. Population control involves measures by which fertilisation is prevented. The three common methods are : ...
... 25. Population control involves measures by which fertilisation is prevented. The three common methods are : ...
Introduction to Plants - Trimble County Schools
... and includes dead cells called tracheids • Water-conducting cells are strengthened by lignin and provide structural support • 2. Phloem consists of living cells and distributes sugars, amino acids, and other organic products ...
... and includes dead cells called tracheids • Water-conducting cells are strengthened by lignin and provide structural support • 2. Phloem consists of living cells and distributes sugars, amino acids, and other organic products ...
Fertilisation

Fertilisation (also known as conception, fecundation and syngamy) is the fusion of gametes to initiate the development of a new individual organism. In animals, the process involves the fusion of an ovum with a sperm, which first creates a zygote and then leads to the development of an embryo. Depending on the animal species, the process can occur within the body of the female in internal fertilisation, or outside (external fertilisation). The cycle of fertilisation and development of new individuals is called sexual reproduction.























