Chapter 31 Plant Reproduction
... expanded lower chamber (ovary), slender column (style) and upper surface (stigma) for pollen landing. In ovary eggs develop, fertilization occurs and seeds mature. ...
... expanded lower chamber (ovary), slender column (style) and upper surface (stigma) for pollen landing. In ovary eggs develop, fertilization occurs and seeds mature. ...
Reproduction and Domestication of Flowering Plants
... transfer of pollen from an anther to the stigma of a carpel Pollen tube is formed when pollen lands on stigma Double fertilization – 1 sperm nucleus unites with the egg nucleus 2n zygote mitosis to form embryo ...
... transfer of pollen from an anther to the stigma of a carpel Pollen tube is formed when pollen lands on stigma Double fertilization – 1 sperm nucleus unites with the egg nucleus 2n zygote mitosis to form embryo ...
Reproduction in Flowering Plants
... • Self-pollination reduces genetic variation and may concentrate ‘bad’ genes • Incomplete flowers – separate male and female flowers • Timing variation – pollen is shed at a time when stigma is not receptive • Self-incompatibility – a plant has the ability to identify and reject its own pollen ...
... • Self-pollination reduces genetic variation and may concentrate ‘bad’ genes • Incomplete flowers – separate male and female flowers • Timing variation – pollen is shed at a time when stigma is not receptive • Self-incompatibility – a plant has the ability to identify and reject its own pollen ...
Lecture #17 Date
... Female gametophyte: megasporocyte (in ovule) divides by meiosis to 4 cells, only 1 survives to a 1-N megaspore; 3 mitotic divisions forms the embryo sac; includes: 1 egg cell (female gamete) and 2 polar nuclei (synergids) ...
... Female gametophyte: megasporocyte (in ovule) divides by meiosis to 4 cells, only 1 survives to a 1-N megaspore; 3 mitotic divisions forms the embryo sac; includes: 1 egg cell (female gamete) and 2 polar nuclei (synergids) ...
Angiosperm Reproduction
... OVULES form with diploid cell that undergoes MEIOSIS to make 4 haploid MEGASPORES ONLY ONE megaspore survives; divides by mitosis to make FEMALE GAMETOPHYTE Female gametophyte (=EMBRYO SAC) is inside ovule; reduced to seven cells with 8 nuclei DOUBLE FERTILIZATION ONE nucleus = EGG; will join with s ...
... OVULES form with diploid cell that undergoes MEIOSIS to make 4 haploid MEGASPORES ONLY ONE megaspore survives; divides by mitosis to make FEMALE GAMETOPHYTE Female gametophyte (=EMBRYO SAC) is inside ovule; reduced to seven cells with 8 nuclei DOUBLE FERTILIZATION ONE nucleus = EGG; will join with s ...
Meiosis in Flowering Plants
... The zygote grows by mitosis to form an embryo. The 3N cell divides by mitosis and becomes endosperm, a food-containing material for the developing embryo. The ovary, sometimes with other floral parts, develops into a fruit. It usually contains seeds. ...
... The zygote grows by mitosis to form an embryo. The 3N cell divides by mitosis and becomes endosperm, a food-containing material for the developing embryo. The ovary, sometimes with other floral parts, develops into a fruit. It usually contains seeds. ...
N5- Unit 1 MO4- Reproduction, variation, inheritance Sexual
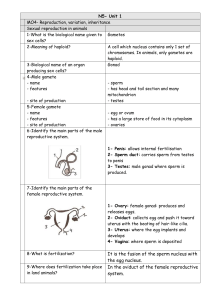
... 7-Identify the main parts of the female reproductive system. 1- Ovary: female gonad: produces and releases eggs. 2- Oviduct: collects egg and push it toward uterus with the beating of hair-like cilia. 3- Uterus: where the egg implants and ...
... 7-Identify the main parts of the female reproductive system. 1- Ovary: female gonad: produces and releases eggs. 2- Oviduct: collects egg and push it toward uterus with the beating of hair-like cilia. 3- Uterus: where the egg implants and ...
Fertilisation

Fertilisation (also known as conception, fecundation and syngamy) is the fusion of gametes to initiate the development of a new individual organism. In animals, the process involves the fusion of an ovum with a sperm, which first creates a zygote and then leads to the development of an embryo. Depending on the animal species, the process can occur within the body of the female in internal fertilisation, or outside (external fertilisation). The cycle of fertilisation and development of new individuals is called sexual reproduction.