* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reproduction and Domestication of Flowering Plants
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
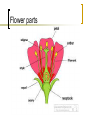
Reproduction and Domestication of Flowering Plants Pollination - wind, insects birds transfer of pollen from an anther to the stigma of a carpel Pollen tube is formed when pollen lands on stigma Double fertilization – 1 sperm nucleus unites with the egg nucleus 2n zygote mitosis to form embryo Other sperm nucleus unties with polar nuclei of central cell and forms 3n endosperm cell Endosperm nourishes embryo and seedling during development Mutualism and Coevolution Many species of flowering plants have evolved with specific animal pollinators – mutualism The joint evolution of two interacting species, each in response to selection imposed by the other – coevolution! Flower parts Flower parts sepal – green, protects bud Petal – specific to pollinator, wind pollination may not have flowers Stamen – male anther -pollen grains produced here from microspores filament Carpel – female Stigma – sticky knob Style - stalk Ovary – base, contains ovules Ovary = Fruit Contains ovules, which develops into seeds. Fruit protects the seeds and aids in their dispersal by wind and animals. Seeds As seed matures, it enters dormancy Low metabolic rate, growth and development suspended Resumes growth under good conditions, fire, rain temperature can break dormancy Seed Germination Imbibing water causes seed to expand and rupture seed coat and triggers growth Timing and coordination of breaking seed dormancy and initiation of germination is important. Environmental cues and cell signaling Flowering plants reproduce sexually or asexually or both Asexual reproduction is called vegetative reproduction – clones Self fertilization Grafting, cuttings, test tube cloning For genetic variation, plants can have self – incompatibility – rejects own pollen Genetic Engineering with plants Artificial selection Conversion of plant material to sugars to make alcohols and distilled to yield biofuels. GMO’s – golden rice