* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5 Section 3:
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Monocotyledon wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
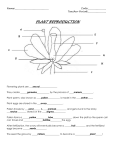
Chapter 5 Section 3: Angiosperms 1. What is an angiosperm? Flowering Plant 2. What two characteristics do angiosperms have in common? Produce flowers and seeds are enclosed by a fruit 3. What is the one function that all angiosperms complete? Reproduction 4. Define Sepals – Leaf like structures that enclose a bud 5. Define Petals – Colorful part of plant 6. Define Stamen – The male reproductive structure inside of the leaves 7. Define Pistil – The female reproductive structure 8. Define Pollinators – Animals or insects that ensure pollination occurs; they are attracted by their colors, shape, or scent 9. What is pollination? Pollen falls from anther into stigma, pollen falls after an animal brushes against anther, pollen can travel with insects of animals as they pass by 10. What is fertilization? Once pollen is on stigma, it travels down the style to the ovary where pollen meets the egg (ovule) and form the zygote that will develop into an embryo 11. What is fruit development and seed dispersal? As the seed develops the ovary changes into a fruit. The fruit disperses the seeds, animals help by eating the fruit 12. What are the two major groups of angiosperms? Monocots and Dicots 13. Define Monocots – One seed leaf, vascular tissue scattered, patallel veins, flower in three parts (grasses, corn, wheat, rice, lilies, tulips) 14. Define Dicots – Two seed leaves, vascular tissue in a ring, branching veins, flour in fours and fives (roses, violets, oak/maple trees, beans, apples) 15. How are angiosperms used in everyday life? Food, clothing, medicine 16. Label the Angiosperm A. Stamen D. Petal B. Anther E. Stigma C. Filament F. Style G. Pistal H. Ovary I. Sepal