Gymnosperms
... Cycads- look like palm trees with cones. Grow in tropical areas Conifers- cone-bearing plants. Most diverse group. “evergreens” Ginkgoes- only one species Ginkgo biloba. Gnetophytes- trees, shrubs or vines. Grow in deserts and tropical rain forests ...
... Cycads- look like palm trees with cones. Grow in tropical areas Conifers- cone-bearing plants. Most diverse group. “evergreens” Ginkgoes- only one species Ginkgo biloba. Gnetophytes- trees, shrubs or vines. Grow in deserts and tropical rain forests ...
Biology Notes: Seeded Vascular Plants Gymnosperms
... 1) Name three advantages of seeds: _______________________________________________________________________________________ 2) Which structure will protect gymnosperm seeds? ______________________________________________ 3) What do male cones produce? ______________________________________________ ...
... 1) Name three advantages of seeds: _______________________________________________________________________________________ 2) Which structure will protect gymnosperm seeds? ______________________________________________ 3) What do male cones produce? ______________________________________________ ...
Earthworm Dissection
... • Seminal receptaclespaired organs that store sperm received from another worm during copulation ...
... • Seminal receptaclespaired organs that store sperm received from another worm during copulation ...
Kingdom Plantae : “Plants”... - nonmotile eukaryotic, multicellular
... female parts. Each pollen grain contains two sperm. One fertilizes an ovum, while the other joins with another cell in the ovary to form endosperm ( a tissue rich in starch and / or fats) which serves as a food source for any new germinating sprout until its leaves are ready for photosynthesis. 2 ty ...
... female parts. Each pollen grain contains two sperm. One fertilizes an ovum, while the other joins with another cell in the ovary to form endosperm ( a tissue rich in starch and / or fats) which serves as a food source for any new germinating sprout until its leaves are ready for photosynthesis. 2 ty ...
Sexual Asexual Reproduction
... tube grows down through the style to the ovary. • The nucleus of the pollen grain passes down the tube. It fertilizes the egg cell inside the ovule. • The fertilized egg cell develops into an embryo. The ovary becomes the fruit and the ovule becomes a seed - from which (once dispersed) the offspring ...
... tube grows down through the style to the ovary. • The nucleus of the pollen grain passes down the tube. It fertilizes the egg cell inside the ovule. • The fertilized egg cell develops into an embryo. The ovary becomes the fruit and the ovule becomes a seed - from which (once dispersed) the offspring ...
Unit XVII: Reproduction
... Fallopian Tubes / Oviducts – tube leading from the ovary to the uterus the Fallopian tubes are the normal site fertilization Uterus – thick muscular walled organ where implantation of the egg takes place the fertilized egg will grow and develop here Birth Canal = Vagina – site where sperm are depos ...
... Fallopian Tubes / Oviducts – tube leading from the ovary to the uterus the Fallopian tubes are the normal site fertilization Uterus – thick muscular walled organ where implantation of the egg takes place the fertilized egg will grow and develop here Birth Canal = Vagina – site where sperm are depos ...
Reproduction in Animals Learning Outcomes Reproduction
... place. Gametes are haploid which means that they only have one set of chromosomes. During fertilisation, the nucleus of the male gamete and the nucleus of the female gamete fuse together to form a Zygote. Since the zygote has two sets of chromosomes it is said to be diploid. In animals the male game ...
... place. Gametes are haploid which means that they only have one set of chromosomes. During fertilisation, the nucleus of the male gamete and the nucleus of the female gamete fuse together to form a Zygote. Since the zygote has two sets of chromosomes it is said to be diploid. In animals the male game ...
Angiosperms and course summary
... Characters of angiosperms • Carpel encloses the seeds • Double integument for seed • Flowers – determinate stem tip with leaves and modified leaves that bear the pollen and seeds • 7-celled, 8 nucleate megagametophyte (= embryo sac) 3 antipodals, 2 synergids, 1 egg, large central cell with 2 nuclei ...
... Characters of angiosperms • Carpel encloses the seeds • Double integument for seed • Flowers – determinate stem tip with leaves and modified leaves that bear the pollen and seeds • 7-celled, 8 nucleate megagametophyte (= embryo sac) 3 antipodals, 2 synergids, 1 egg, large central cell with 2 nuclei ...
Chapter 20 and 21
... sperm during reproduction; allows menstrual flow to exit body; also the birth canal through which baby is delivered 2. _____ Hormone that causes pubic and underarm hair growth, strengthens bones, regulate monthly release of an egg and prepare body for pregnancy 3. _____ Produces egg and estrogen and ...
... sperm during reproduction; allows menstrual flow to exit body; also the birth canal through which baby is delivered 2. _____ Hormone that causes pubic and underarm hair growth, strengthens bones, regulate monthly release of an egg and prepare body for pregnancy 3. _____ Produces egg and estrogen and ...
Chapter 46: Animal Reproduction
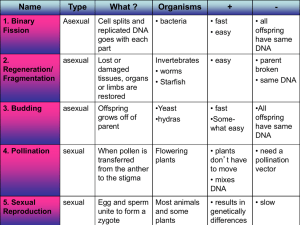
... - Sexual reproduction: the fusion of haploid gametes to form a diploid cell (zygote). - The egg - The sperm - Asexual reproduction: generation of new individuals without the fusion of egg and sperm - Fission - Budding ...
... - Sexual reproduction: the fusion of haploid gametes to form a diploid cell (zygote). - The egg - The sperm - Asexual reproduction: generation of new individuals without the fusion of egg and sperm - Fission - Budding ...
Angiosperm Reproduction Student Notes File
... b) The surviving megaspore undergoes mitosis producing 8 haploid nuclei. c) 3 nuclei migrate to each end of the cell and 2 move to the center and are called the ______________________. d) Cell walls form around each group of nuclei forming the ________________ ...
... b) The surviving megaspore undergoes mitosis producing 8 haploid nuclei. c) 3 nuclei migrate to each end of the cell and 2 move to the center and are called the ______________________. d) Cell walls form around each group of nuclei forming the ________________ ...
Aim # 6: How do some plants and animals pass on
... the new individual. The female parent produces sex cells called eggs. The male parent produces sex cells called sperm. The male and female sex cells join together during fertilization. The resulting cell is called a zygote. Because the zygote contains genetic material from each parent, it is a total ...
... the new individual. The female parent produces sex cells called eggs. The male parent produces sex cells called sperm. The male and female sex cells join together during fertilization. The resulting cell is called a zygote. Because the zygote contains genetic material from each parent, it is a total ...
Ch 30 Evolution Seed Plants
... Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers or completions. Select one that is best in each case and write, using capital letters, the letter of the answer in the blank provided. ___1. Which of the following is an ongoing trend in the evolut ...
... Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers or completions. Select one that is best in each case and write, using capital letters, the letter of the answer in the blank provided. ___1. Which of the following is an ongoing trend in the evolut ...
Angiosperm Review Sheet
... four haploid cells (n), but only one of them will survive. The cell that survives is called a megaspore (n) and it will go through mitosis three times to create 8 cells. Two of them will fuse together to form the central cell (2n) so we now have 7 cells. One of these cells is the female egg. Thi ...
... four haploid cells (n), but only one of them will survive. The cell that survives is called a megaspore (n) and it will go through mitosis three times to create 8 cells. Two of them will fuse together to form the central cell (2n) so we now have 7 cells. One of these cells is the female egg. Thi ...
Alternation of generations: a review
... two sperm cells with two cells of the embryo sac Pollen grain germinates and extends pollen tube Generative cell undergoes mitosis, forming two sperm Pollen tube enters through micropyle and discharges sperm One sperm unites with egg Other sperm unites with polar nuclei forming endosperm (3n) ...
... two sperm cells with two cells of the embryo sac Pollen grain germinates and extends pollen tube Generative cell undergoes mitosis, forming two sperm Pollen tube enters through micropyle and discharges sperm One sperm unites with egg Other sperm unites with polar nuclei forming endosperm (3n) ...
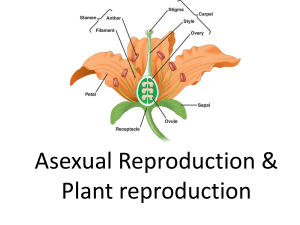
PlantReproduction
... Anther: The part of the stamen where pollen is produced. Filament: thread-like part that holds up the anther Pollen: the male gamete (i.e. sperm) ...
... Anther: The part of the stamen where pollen is produced. Filament: thread-like part that holds up the anther Pollen: the male gamete (i.e. sperm) ...
Male and Female Reproductive Systems
... CMT correlation C26. Describe the structure and function of the male and female human reproductive systems, including the process of egg and sperm production. A. Sex Cells (gametes) 1. Ovum (Ova)-Egg(s) is the female sex cell. 2. Sperm is the male sex cell. 3. The joining of the female and male sex ...
... CMT correlation C26. Describe the structure and function of the male and female human reproductive systems, including the process of egg and sperm production. A. Sex Cells (gametes) 1. Ovum (Ova)-Egg(s) is the female sex cell. 2. Sperm is the male sex cell. 3. The joining of the female and male sex ...
Warm-Up
... 1. Tube nucleus (forms pollen tube) 2. Generative nucleus (divides to form 2 sperm cells) ...
... 1. Tube nucleus (forms pollen tube) 2. Generative nucleus (divides to form 2 sperm cells) ...
6.2 Sexual Reproduction
... The embryo and fetus develops an umbilical cord attached to an organ called the placenta. The placenta is attached to the inside of a mother’s womb (uterus) and transfers food and oxygen to the fetus as well as taking wastes away like carbon dioxide and ammonia. The mother supplies the placenta with ...
... The embryo and fetus develops an umbilical cord attached to an organ called the placenta. The placenta is attached to the inside of a mother’s womb (uterus) and transfers food and oxygen to the fetus as well as taking wastes away like carbon dioxide and ammonia. The mother supplies the placenta with ...
Plant Reproduction and Development
... When pollen is Flowering transferred plants from the anther to the stigma ...
... When pollen is Flowering transferred plants from the anther to the stigma ...
Fertilisation

Fertilisation (also known as conception, fecundation and syngamy) is the fusion of gametes to initiate the development of a new individual organism. In animals, the process involves the fusion of an ovum with a sperm, which first creates a zygote and then leads to the development of an embryo. Depending on the animal species, the process can occur within the body of the female in internal fertilisation, or outside (external fertilisation). The cycle of fertilisation and development of new individuals is called sexual reproduction.