24-1 PowerPoint Notes
... other cell becomes the pollen tube. The pollen tube contains a tube nucleus and the two sperm cells. The pollen tube grows into the style, where it eventually reaches the ovary and enters an ___________. Inside the embryo sac, two distinct fertilizations take place—a process called double __________ ...
... other cell becomes the pollen tube. The pollen tube contains a tube nucleus and the two sperm cells. The pollen tube grows into the style, where it eventually reaches the ovary and enters an ___________. Inside the embryo sac, two distinct fertilizations take place—a process called double __________ ...
Chapter 34
... • One sperm fertilizes the egg while the other sperm fuses with the polar nuclei to form endosperm. • This process of using two sperm cells in fertilization is called double fertilization. ...
... • One sperm fertilizes the egg while the other sperm fuses with the polar nuclei to form endosperm. • This process of using two sperm cells in fertilization is called double fertilization. ...
Lecture 1 Thursday Jan. 4, 2001
... spiral or transverse ridges) cells with connecting pits at their ends, for much more efficient water transport upwards. Enables height growth under drier conditions. (Note that the world’s tallest trees are all gymnosperms that grow in rain-forest conditions) ...
... spiral or transverse ridges) cells with connecting pits at their ends, for much more efficient water transport upwards. Enables height growth under drier conditions. (Note that the world’s tallest trees are all gymnosperms that grow in rain-forest conditions) ...
REPRODUCTION IN SEED PLANTS – CH.24
... INSIDE THE DEVELOPING SEED PERICARP: OUTER WALL OF OVARY THAT WILL ENLARGE WHEN MATURE, FORMING FRUIT CARPELS: SECTIONS W/IN THE OVARY WHERE DEVELOPING SEEDS WILL BE FOUND. THE # OF CARPELS OFTEN EQUALS THE # OF LOBES FOUND MAKING UP THE STIGMA ...
... INSIDE THE DEVELOPING SEED PERICARP: OUTER WALL OF OVARY THAT WILL ENLARGE WHEN MATURE, FORMING FRUIT CARPELS: SECTIONS W/IN THE OVARY WHERE DEVELOPING SEEDS WILL BE FOUND. THE # OF CARPELS OFTEN EQUALS THE # OF LOBES FOUND MAKING UP THE STIGMA ...
Ch35
... An ovary may be formed by various fused carpels. Pistil is another name for the female reproductive structure. A pistil may be formed by a single carpel or by several fused carpels. The ovary contains one or several ovules. The ovule produces contains the embryo sac. The embryo sac produces two pola ...
... An ovary may be formed by various fused carpels. Pistil is another name for the female reproductive structure. A pistil may be formed by a single carpel or by several fused carpels. The ovary contains one or several ovules. The ovule produces contains the embryo sac. The embryo sac produces two pola ...
Vocabulary Review - POTOSI SCHOOL DISTRICT
... of a pistil, supported by the style; the part of the pistil that receives the pollen ...
... of a pistil, supported by the style; the part of the pistil that receives the pollen ...
You Light Up My Life
... – Sperm packed inside a nutritious package – Transferred first by wind currents – Later transferred by insects ...
... – Sperm packed inside a nutritious package – Transferred first by wind currents – Later transferred by insects ...
Revision powerpoint for S1 Reproduction topic
... Take five minutes to do the revision exercise on cells. If you’ve done it already, learn the parts and their functions! ...
... Take five minutes to do the revision exercise on cells. If you’ve done it already, learn the parts and their functions! ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... within tissues of separate haploid male and female gametophytes. Conveyed in a droplet of water, sperm swim to the egg cells. The fertilized egg develops into the diploid sporophyte, which grows a sporangium in which spore mother cells undergo meiosis to produce haploid spores. These grow into haplo ...
... within tissues of separate haploid male and female gametophytes. Conveyed in a droplet of water, sperm swim to the egg cells. The fertilized egg develops into the diploid sporophyte, which grows a sporangium in which spore mother cells undergo meiosis to produce haploid spores. These grow into haplo ...
013368718X_CH24_377-392.indd
... The Angiosperm Life Cycle The life cycle involves alternation of generations. Meiosis in stamens and carpels produces haploid cells (spores) that develop into gametophytes. The haploid cells in a stamen’s anther undergo mitosis and form pollen grains, the male gametophytes, that contain 2 sperm nucl ...
... The Angiosperm Life Cycle The life cycle involves alternation of generations. Meiosis in stamens and carpels produces haploid cells (spores) that develop into gametophytes. The haploid cells in a stamen’s anther undergo mitosis and form pollen grains, the male gametophytes, that contain 2 sperm nucl ...
No Slide Title
... *have no roots, only filamentous rhizoids (so, they are a good example of a NONVASCULAR plant. ). The dominant generation is the 1n gametophyte. The 2n sporophyte is actually parasitic on the gametophyte. * Needs water for sexual reproduction; sperm must swim to egg ...
... *have no roots, only filamentous rhizoids (so, they are a good example of a NONVASCULAR plant. ). The dominant generation is the 1n gametophyte. The 2n sporophyte is actually parasitic on the gametophyte. * Needs water for sexual reproduction; sperm must swim to egg ...
Leaf adaptation and flowers - Miss Jan`s Science Wikispace
... wilts. The cuticle (waxy layer on the top) also stops water loss. ...
... wilts. The cuticle (waxy layer on the top) also stops water loss. ...
Plant Classification
... o Male cones produce (contains sperm) o Wind often blows pollen to female cone ...
... o Male cones produce (contains sperm) o Wind often blows pollen to female cone ...
Mosses-Bryophytes - Crossroads Academy
... The life cycle of a moss alternates between a green leafy gametophyte and a stalked sporophyte that grows on the gametophyte. The sporophyte is 2n and produces 1n spores through a process called meiosis. Protonema. Spores with n chromosomes germinate and produce two kinds of protonema. The protonem ...
... The life cycle of a moss alternates between a green leafy gametophyte and a stalked sporophyte that grows on the gametophyte. The sporophyte is 2n and produces 1n spores through a process called meiosis. Protonema. Spores with n chromosomes germinate and produce two kinds of protonema. The protonem ...
Reproduction - Cleveden Secondary School
... The embryo is surrounded by the amnion which is full of amniotic fluid. This acts as a shock absorber. This can be demonstrated by placing an egg into a beaker of water and giving it a shake. The embryo is connected to the placenta by the umbilical cord. The placenta allows exchange of materials bet ...
... The embryo is surrounded by the amnion which is full of amniotic fluid. This acts as a shock absorber. This can be demonstrated by placing an egg into a beaker of water and giving it a shake. The embryo is connected to the placenta by the umbilical cord. The placenta allows exchange of materials bet ...
begins during female`s embryonic development Ovaries
... 1) when blastomeres are separated & each one can complete normal development it’s called indeterminate cleavage 2) when blastomeres are separated the individuals CAN’T complete development it’s called determinate cleavage (each cell has ...
... 1) when blastomeres are separated & each one can complete normal development it’s called indeterminate cleavage 2) when blastomeres are separated the individuals CAN’T complete development it’s called determinate cleavage (each cell has ...
Ovary
... DIFFERENTIATION – When cells begin to become different from one another & specialize their functions ...
... DIFFERENTIATION – When cells begin to become different from one another & specialize their functions ...
Reproduction in Flowering Plants
... producing a pollen tube. The pollen tube grows down through the tissue of the style. At some point during its journey, the generative cell of the pollen grain divides by mitosis to form two sperm nuclei, or male gametes. The pollen tube continues to grow until it reaches the ovary. It then enters an ...
... producing a pollen tube. The pollen tube grows down through the tissue of the style. At some point during its journey, the generative cell of the pollen grain divides by mitosis to form two sperm nuclei, or male gametes. The pollen tube continues to grow until it reaches the ovary. It then enters an ...
The Reproductive System
... What is the difference between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction? Many organisms can carry out both at some point in their life. ...
... What is the difference between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction? Many organisms can carry out both at some point in their life. ...
Document
... • Only one megaspore survives and divides by mitosis 3 times to make 8 haploid nuclei. ...
... • Only one megaspore survives and divides by mitosis 3 times to make 8 haploid nuclei. ...
BY 124 Worksheet 3 Which of the following adaptations is common
... central cell, forming a triploid nucleus called the endosperm c. union of the two sperm nuclei, forming a zygote d. formation of a gametophyte e. fusion of both sperm nuclei with the egg nucleus and the formation of a triploid zygote 25. Of the following, which is a difference in how reproduction oc ...
... central cell, forming a triploid nucleus called the endosperm c. union of the two sperm nuclei, forming a zygote d. formation of a gametophyte e. fusion of both sperm nuclei with the egg nucleus and the formation of a triploid zygote 25. Of the following, which is a difference in how reproduction oc ...
Angiosperms
... In seedless plants (moss, fern) the sperms swims through a thin film of water on the plant to reach the egg in the arachegonium. 2. What features not present in seedless plants, have contributed to the great success of seed plants on land? (list, describe, state evolutionary advantage) 1. Reduced ga ...
... In seedless plants (moss, fern) the sperms swims through a thin film of water on the plant to reach the egg in the arachegonium. 2. What features not present in seedless plants, have contributed to the great success of seed plants on land? (list, describe, state evolutionary advantage) 1. Reduced ga ...
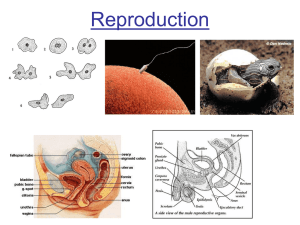
Reproduction
... pollen sticks to it. 2. style supports stigma aids pollination 3. ovary creates eggs, becomes fruit 4. Ovules – turn into seeds if fertilized 5. Receptacle Point where flower joins stem ...
... pollen sticks to it. 2. style supports stigma aids pollination 3. ovary creates eggs, becomes fruit 4. Ovules – turn into seeds if fertilized 5. Receptacle Point where flower joins stem ...
Fertilisation

Fertilisation (also known as conception, fecundation and syngamy) is the fusion of gametes to initiate the development of a new individual organism. In animals, the process involves the fusion of an ovum with a sperm, which first creates a zygote and then leads to the development of an embryo. Depending on the animal species, the process can occur within the body of the female in internal fertilisation, or outside (external fertilisation). The cycle of fertilisation and development of new individuals is called sexual reproduction.