Diapositiva 1 - Holy Family Catholic Regional Division No. 37
... tubules consist of diploid spermatogonia, stem cells that are the precursors of sperm. divide by mitosis to produce more spermatogonia The Meiosis of each spermatocyte produces 4 haploid spermatids. These then differentiate into sperm, losing most of their cytoplasm and gaining motility in the proce ...
... tubules consist of diploid spermatogonia, stem cells that are the precursors of sperm. divide by mitosis to produce more spermatogonia The Meiosis of each spermatocyte produces 4 haploid spermatids. These then differentiate into sperm, losing most of their cytoplasm and gaining motility in the proce ...
File - thebiotutor.com
... In plants: o Male gametes = Pollen cells o Female gametes = Ova or egg cells Gametes are formed in Anther and ovaries from the meiosis of reproductive cells Process of Meiosis: 1. Chromosomes of the reproductive cell fatten and become visible 2. Each chromosome makes an exact cop of itself 3. Ch ...
... In plants: o Male gametes = Pollen cells o Female gametes = Ova or egg cells Gametes are formed in Anther and ovaries from the meiosis of reproductive cells Process of Meiosis: 1. Chromosomes of the reproductive cell fatten and become visible 2. Each chromosome makes an exact cop of itself 3. Ch ...
BSCI 442
... fertilization can begin. The sperm in the pollen grain must get to the egg, located at the base of the pistil in the ovary. When the pollen grain germinates, its tube nucleus grows a tube from the stigma, through the style, and down to the ovary. The two sperm from the pollen travel down this tube t ...
... fertilization can begin. The sperm in the pollen grain must get to the egg, located at the base of the pistil in the ovary. When the pollen grain germinates, its tube nucleus grows a tube from the stigma, through the style, and down to the ovary. The two sperm from the pollen travel down this tube t ...
Plant Diversity I
... Antheridium (male gametangium) produces flagellated sperm cells Archegonium (female gametangium) produces egg fertilisation/embryo development occur within female organ ...
... Antheridium (male gametangium) produces flagellated sperm cells Archegonium (female gametangium) produces egg fertilisation/embryo development occur within female organ ...
Topic 3 - Science 9 Jones
... anthers, which are supported by the filaments, produce and store pollen grains containing sperm nuclei. Each stamen is composed of an anther and a filament. B When a pollen grain lands on the stigma, a pollen tube is formed. A sperm nucleus then travels down the tube to fertilize one egg. C Prior to ...
... anthers, which are supported by the filaments, produce and store pollen grains containing sperm nuclei. Each stamen is composed of an anther and a filament. B When a pollen grain lands on the stigma, a pollen tube is formed. A sperm nucleus then travels down the tube to fertilize one egg. C Prior to ...
Unit 1 Topic 3 - Holy Cross Collegiate
... anthers, which are supported by the filaments, produce and store pollen grains containing sperm nuclei. Each stamen is composed of an anther and a filament. B When a pollen grain lands on the stigma, a pollen tube is formed. A sperm nucleus then travels down the tube to fertilize one egg. C Prior to ...
... anthers, which are supported by the filaments, produce and store pollen grains containing sperm nuclei. Each stamen is composed of an anther and a filament. B When a pollen grain lands on the stigma, a pollen tube is formed. A sperm nucleus then travels down the tube to fertilize one egg. C Prior to ...
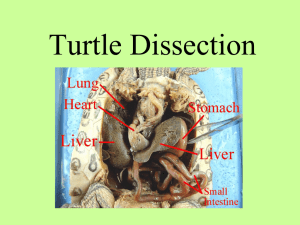
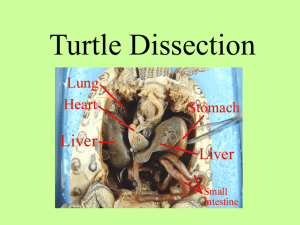
Frog Dissection
... but kept in body until just before hatching or can hatch inside female Nourishment comes from egg not mother Ex: Some reptiles (snakes) ...
... but kept in body until just before hatching or can hatch inside female Nourishment comes from egg not mother Ex: Some reptiles (snakes) ...
Pollination & Fertilization
... The ovary also ripens and becomes a fruit. If an ovary contains several ovules, each ovule can form a seed. The petals and stamens of the flower are no longer necessary, and they often wither. In many plants, however, the receptacle and the calyx become part of the fruit. ...
... The ovary also ripens and becomes a fruit. If an ovary contains several ovules, each ovule can form a seed. The petals and stamens of the flower are no longer necessary, and they often wither. In many plants, however, the receptacle and the calyx become part of the fruit. ...
Plant Phylogeny Notes
... Integument protects the megasporangium within the parent plant. Ovule is formed by the megasporangium, megaspore, and integument Pollen is the microspore of the plant which consists of the male gametophyte enclosed in the pollen wall Seeds are considered an evolutionary advantage because it contains ...
... Integument protects the megasporangium within the parent plant. Ovule is formed by the megasporangium, megaspore, and integument Pollen is the microspore of the plant which consists of the male gametophyte enclosed in the pollen wall Seeds are considered an evolutionary advantage because it contains ...
You Light Up My Life
... Nonvascular Plants Bryophytes are nonvascular plants with flagellated sperm that require liquid water to reach and fertilize the eggs. A sporophyte of these plants develops within gametophyte tissues. It remains attached to the gametophyte and receives some nutritional support from it. ...
... Nonvascular Plants Bryophytes are nonvascular plants with flagellated sperm that require liquid water to reach and fertilize the eggs. A sporophyte of these plants develops within gametophyte tissues. It remains attached to the gametophyte and receives some nutritional support from it. ...
29 Origin of Plants
... • Adapted to higher light intensities – Leads to common chloroplast structure? ...
... • Adapted to higher light intensities – Leads to common chloroplast structure? ...
Frog Dissection
... but kept in body until just before hatching or can hatch inside female Nourishment comes from egg not mother Ex: Some reptiles (snakes) ...
... but kept in body until just before hatching or can hatch inside female Nourishment comes from egg not mother Ex: Some reptiles (snakes) ...
Gymnosperms - OpenStax CNX
... generative cell in the pollen grain divides into two haploid sperm cells by mitosis. At fertilization, one of the sperm cells will nally unite its haploid nucleus with the haploid nucleus of a haploid egg cell. Female cones contain two ovules per scale. ...
... generative cell in the pollen grain divides into two haploid sperm cells by mitosis. At fertilization, one of the sperm cells will nally unite its haploid nucleus with the haploid nucleus of a haploid egg cell. Female cones contain two ovules per scale. ...
Plant Diversity I: Colonization by Land Plants
... and produces a pollen tube – allows for the discharge of two sperm (gametes) into the ovule – unites with the egg developing within female gametophyte (within the ovule) in non-vascular plants (bryophytes) and seedless vascular plants (ferns) – the sperm is flagellated and swims to the female gameto ...
... and produces a pollen tube – allows for the discharge of two sperm (gametes) into the ovule – unites with the egg developing within female gametophyte (within the ovule) in non-vascular plants (bryophytes) and seedless vascular plants (ferns) – the sperm is flagellated and swims to the female gameto ...
cotyledon - ScienceToGo
... On sperm fertilizes the egg, forming the zygote. The other sperm combines with the two polar nuclei of the embyoso sac’s large central cell, forming a triploid cell that develops into the nutritive tissue called endosperm. This ensures that endosperm will develop only in ovules where the egg has bee ...
... On sperm fertilizes the egg, forming the zygote. The other sperm combines with the two polar nuclei of the embyoso sac’s large central cell, forming a triploid cell that develops into the nutritive tissue called endosperm. This ensures that endosperm will develop only in ovules where the egg has bee ...
Microsoft Word 97
... 1. timing in the formation and release of eggs and sperm and 2. having the gametes placed as closely together as possible. Both of these conditions are necessary because of the gamete cells' short life spans, which may average only several days. It is therefore important that females and males find ...
... 1. timing in the formation and release of eggs and sperm and 2. having the gametes placed as closely together as possible. Both of these conditions are necessary because of the gamete cells' short life spans, which may average only several days. It is therefore important that females and males find ...
Section 24.3 Summary – pages 646-657
... that attaches to them can be carried to another flower, resulting in pollination. ...
... that attaches to them can be carried to another flower, resulting in pollination. ...
REPTILE REVIEW
... 1. Male reptiles have a __ __ __ __ __ to transfer sperm inside the female’s body. 2. In an amniotic egg the fat rich food supply (yolk) is surrounded by a membrane called the __ __ __ __ sac. 3. In reptiles the sperm and egg join inside the female’s body. This is called __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ fert ...
... 1. Male reptiles have a __ __ __ __ __ to transfer sperm inside the female’s body. 2. In an amniotic egg the fat rich food supply (yolk) is surrounded by a membrane called the __ __ __ __ sac. 3. In reptiles the sperm and egg join inside the female’s body. This is called __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ fert ...
Seeds and pollen are reproductive adaptations.
... Some plants reproduce with seeds. In most places, plants that reproduce with seeds are common and easy to see. Trees, bushes, flowers, and grasses are all seed plants. It’s a bit harder to find plants that reproduce with spores, such as mosses or ferns. Why are there so many more seed plants in the ...
... Some plants reproduce with seeds. In most places, plants that reproduce with seeds are common and easy to see. Trees, bushes, flowers, and grasses are all seed plants. It’s a bit harder to find plants that reproduce with spores, such as mosses or ferns. Why are there so many more seed plants in the ...
1) Pollen sticks to animal or released into wind
... • Seeds enclosed in cones – Male cones: produce pollen (sperm) – Female cones: produce eggs • Zygote hardens into seed (protected inside cones) ...
... • Seeds enclosed in cones – Male cones: produce pollen (sperm) – Female cones: produce eggs • Zygote hardens into seed (protected inside cones) ...
Reproduction
... a protective shell. Mammal females, except monotremes, develop a new embryo inside their body. This extra protection increases an organism's chances of survival. ...
... a protective shell. Mammal females, except monotremes, develop a new embryo inside their body. This extra protection increases an organism's chances of survival. ...
LAND ENVIRONMENT: PLANTS AND FUNGI
... d. mature ovule that contains a sporophyte with stored food enclosed by a protective coat _______________________ e. fern, gymnosperms, and angiosperms _______________________ f. woody seed plant; seeds usually borne in cones _______________________ g. haploid generation of the alternation of genera ...
... d. mature ovule that contains a sporophyte with stored food enclosed by a protective coat _______________________ e. fern, gymnosperms, and angiosperms _______________________ f. woody seed plant; seeds usually borne in cones _______________________ g. haploid generation of the alternation of genera ...
137 CHAPTER 10 – REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS
... Inside each ovule, a large, diploid, spore mother cell develops. This cell divides by meiosis to produce four haploid cells. All but one of these degenerates and the one surviving haploid cell then develops into an embryo sac. The embryo sac absorbs nutrients from the nucleus and grows larger. Its n ...
... Inside each ovule, a large, diploid, spore mother cell develops. This cell divides by meiosis to produce four haploid cells. All but one of these degenerates and the one surviving haploid cell then develops into an embryo sac. The embryo sac absorbs nutrients from the nucleus and grows larger. Its n ...
Euglenophyta (Euglenids, trypanosoma
... grain then germinates, forming a pollen tube that slowly digests its way through the megasporangium. 5. While the pollen tube develops, the megasporocyte undergoes meiosis, producing four haploid cells. One survives as a megaspore. 6. The megasore develops into a female gametophyte that contains two ...
... grain then germinates, forming a pollen tube that slowly digests its way through the megasporangium. 5. While the pollen tube develops, the megasporocyte undergoes meiosis, producing four haploid cells. One survives as a megaspore. 6. The megasore develops into a female gametophyte that contains two ...
CHAPTER 37: EVOLUTIONARY HISTORY OF PLANTS
... within the ovules and are pollinated when contacted by pollen grains. Pollination and fertilization may be separated by long periods of time. This group is divided into two broad categories, plants that produce naked seeds and those that have seeds enclosed within fruit. The former, commonly called ...
... within the ovules and are pollinated when contacted by pollen grains. Pollination and fertilization may be separated by long periods of time. This group is divided into two broad categories, plants that produce naked seeds and those that have seeds enclosed within fruit. The former, commonly called ...
Fertilisation

Fertilisation (also known as conception, fecundation and syngamy) is the fusion of gametes to initiate the development of a new individual organism. In animals, the process involves the fusion of an ovum with a sperm, which first creates a zygote and then leads to the development of an embryo. Depending on the animal species, the process can occur within the body of the female in internal fertilisation, or outside (external fertilisation). The cycle of fertilisation and development of new individuals is called sexual reproduction.