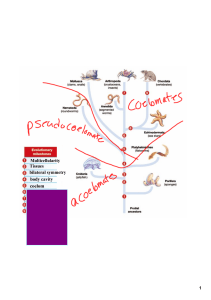
Multicellularity Tissues bilateral symmetry body cavity coelom
... Multicellularity Tissues bilateral symmetry body cavity coelom segmentation jointed appendaes deuterostomes notochord ...
... Multicellularity Tissues bilateral symmetry body cavity coelom segmentation jointed appendaes deuterostomes notochord ...
Taxonomy and Classification Powerpoint
... • Think back to the Jones Beach lab where you classified and sorted organisms. • What do scientists sort organisms based on? ...
... • Think back to the Jones Beach lab where you classified and sorted organisms. • What do scientists sort organisms based on? ...
02 Chapter
... advantageous for survival and reproduction. • Other variations keep an organism from surviving or reproducing. • Advantageous mutations are passed to future generations, and new species can be produced. ...
... advantageous for survival and reproduction. • Other variations keep an organism from surviving or reproducing. • Advantageous mutations are passed to future generations, and new species can be produced. ...
Creating a Venn diagram and list for unique genes from RAST
... Go to rast.nmpdr.org Login to RAST (username: newmanlab password: 16srrna1) In the Jobs Overview window, find the organism you wish to focus on by searching the Name column and click View Details under Annotation Progress In the Job Details window, click Browse annotated genome in the SEED View ...
... Go to rast.nmpdr.org Login to RAST (username: newmanlab password: 16srrna1) In the Jobs Overview window, find the organism you wish to focus on by searching the Name column and click View Details under Annotation Progress In the Job Details window, click Browse annotated genome in the SEED View ...
Lecture PPT - Carol Eunmi LEE
... • Pleiotropy: phenomenon where a gene affects several different traits • Antagonistic Pleiotropy: where a gene has a positive effect on one trait but a negative effect on another trait (example: a gene that increases heat tolerance but reduces cold tolerance) • Antagonistic Pleiotropy Theory of Agin ...
... • Pleiotropy: phenomenon where a gene affects several different traits • Antagonistic Pleiotropy: where a gene has a positive effect on one trait but a negative effect on another trait (example: a gene that increases heat tolerance but reduces cold tolerance) • Antagonistic Pleiotropy Theory of Agin ...
B2_learning_outcomes_Foundation
... Animals – feed on other organisms, no cell walls Fungi – make spores instead of seeds, cell wall made of chitin Protoctista – made up of one cell Prokaryotes – no nucleus, cell wall but not made of cellulose Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus and species Continually evolving and new organi ...
... Animals – feed on other organisms, no cell walls Fungi – make spores instead of seeds, cell wall made of chitin Protoctista – made up of one cell Prokaryotes – no nucleus, cell wall but not made of cellulose Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus and species Continually evolving and new organi ...
MOLLUSK VOCAB ONLY
... Type of development in which offspring hatch as an immature larva and must change into indirect their adult form _____________ Joining of an egg and sperm inside the female’s body _________________ Internal fertilization Organism that lives in the ocean (salt water) ________________ ...
... Type of development in which offspring hatch as an immature larva and must change into indirect their adult form _____________ Joining of an egg and sperm inside the female’s body _________________ Internal fertilization Organism that lives in the ocean (salt water) ________________ ...
MOLLUSK VOCAB ONLY
... Type of development in which offspring hatch as an immature larva and must indirect change into their adult form _____________ Joining of an egg and sperm inside the female’s body _________________ Internal fertilization Organism that lives in the ocean (salt water) ________________ ...
... Type of development in which offspring hatch as an immature larva and must indirect change into their adult form _____________ Joining of an egg and sperm inside the female’s body _________________ Internal fertilization Organism that lives in the ocean (salt water) ________________ ...
Feeding young through mammary glands
... Interspecies relationships: A relationship between two different animal species. Examples include a lion hunting a zebra, fighting between two different animals, etc. ...
... Interspecies relationships: A relationship between two different animal species. Examples include a lion hunting a zebra, fighting between two different animals, etc. ...
eoi review packet
... How would you determine which species are most closely related? How would you determine which species are not closely related? When determining relatedness, what type of evidence is better to use? 2. Species acquire many of their unique characteristics through biological adaptation, which involves t ...
... How would you determine which species are most closely related? How would you determine which species are not closely related? When determining relatedness, what type of evidence is better to use? 2. Species acquire many of their unique characteristics through biological adaptation, which involves t ...
Feature
... recombination. This is the reason why all humans may have trichromatic vision but still there are some colour-blind individuals. An adaptive trait may cease to be useful and eventually be lost when the environment in response to which it was formed changes. Loss of eyes of cave crustaceans is one su ...
... recombination. This is the reason why all humans may have trichromatic vision but still there are some colour-blind individuals. An adaptive trait may cease to be useful and eventually be lost when the environment in response to which it was formed changes. Loss of eyes of cave crustaceans is one su ...
Genetics PPT - Ms. George`s Science Class
... • Traits are “characteristics that can be used to identify or describe an organism.” • This passing on of traits from parents to their offspring is called “heredity.” • Think of 3 physical traits you received from your parents: ____________, _____________, _____________. ...
... • Traits are “characteristics that can be used to identify or describe an organism.” • This passing on of traits from parents to their offspring is called “heredity.” • Think of 3 physical traits you received from your parents: ____________, _____________, _____________. ...
Appendices: Cluster 1 Reproduction
... Types of Asexual Reproduction 1. Binary fission: This is the process by which a unicellular organism ...
... Types of Asexual Reproduction 1. Binary fission: This is the process by which a unicellular organism ...
Classification Chapter 18 - Ms. Dooley`s Science Class
... All of the classification methods discussed so far are based on physical similarities and differences. Even organisms with very different anatomies can share common traits. EX: All living things use ______________to pass on DNA and RNA information and control growth. http://sbchem.sunysb.edu/msl/dn ...
... All of the classification methods discussed so far are based on physical similarities and differences. Even organisms with very different anatomies can share common traits. EX: All living things use ______________to pass on DNA and RNA information and control growth. http://sbchem.sunysb.edu/msl/dn ...
Grade 7 Model Science Unit 6: Inheritance and Variation
... Each chromosome consists of a single, very long DNA molecule, and each gene on the chromosome is a particular segment of that DNA. The instructions for forming species’ characteristics are carried in DNA. All cells in an organism have the same genetic content, but the genes used (expressed) by the c ...
... Each chromosome consists of a single, very long DNA molecule, and each gene on the chromosome is a particular segment of that DNA. The instructions for forming species’ characteristics are carried in DNA. All cells in an organism have the same genetic content, but the genes used (expressed) by the c ...
16.4 Evidence of Evolution - Since Darwin`s work, every scientific
... different, but closely related species that are separated by some structure (like islands) Distantly Related but Similar - Similar habitats around the world are home to distantly related animals and plants, but the similarities among those animals and plants provide evidence that similar selection p ...
... different, but closely related species that are separated by some structure (like islands) Distantly Related but Similar - Similar habitats around the world are home to distantly related animals and plants, but the similarities among those animals and plants provide evidence that similar selection p ...
Dihybrid Crosses Worksheet
... 3. What fraction of the offspring will be rough and green? Remember to express this as -/16. 4. What fraction of the offspring will be AAbb? 5. What fraction of the offspring will be homozygous dominant for both traits? 6. What fraction of the offspring will be heterozygous for both traits? ...
... 3. What fraction of the offspring will be rough and green? Remember to express this as -/16. 4. What fraction of the offspring will be AAbb? 5. What fraction of the offspring will be homozygous dominant for both traits? 6. What fraction of the offspring will be heterozygous for both traits? ...
Student Packet 18 Laws of Segregation and Independent
... you think the hawk would then most likely try to catch? Why? _________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Gizmo Warm-up How long could a parrot survive in Antarctica? It would probably not survive lo ...
... you think the hawk would then most likely try to catch? Why? _________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Gizmo Warm-up How long could a parrot survive in Antarctica? It would probably not survive lo ...
Chapter 6 and 9 - Wando High School
... 25. What are polygenic traits? Give an example. Polygenic traits are traits that are controlled by two or more genes. These traits often show a great variety of phenotypes, e.g. skin color. 26. What is a pedigree? A pedigree is a chart to show an inheritance pattern (trait, disease, disorder) within ...
... 25. What are polygenic traits? Give an example. Polygenic traits are traits that are controlled by two or more genes. These traits often show a great variety of phenotypes, e.g. skin color. 26. What is a pedigree? A pedigree is a chart to show an inheritance pattern (trait, disease, disorder) within ...
chapter 1 ppt
... reproduce among themselves to produce offspring of the same type that can also reproduce successfully. ex. Moose, caribou, trout, salmon, fox, pine marten ...
... reproduce among themselves to produce offspring of the same type that can also reproduce successfully. ex. Moose, caribou, trout, salmon, fox, pine marten ...
Adaptation as organism design
... was developed into the modern theory of kin selection, by W. D. Hamilton (figure 1d ) in the 1960s. Hamilton (1964) showed that the ultimate criterion for a trait to be favoured by natural selection is for it to increase the overall reproductive success of all the individual’s relatives (including i ...
... was developed into the modern theory of kin selection, by W. D. Hamilton (figure 1d ) in the 1960s. Hamilton (1964) showed that the ultimate criterion for a trait to be favoured by natural selection is for it to increase the overall reproductive success of all the individual’s relatives (including i ...
A Multi-level Selection Theory of Evolutionary Transitions in
... may fuse with other propagules as in the case of sex or other forms of aggregation) or by direct fragmentation. The functioning of the groups and their group fitness (number of propagules or offspring groups produced) depends upon their composition of mutant and non-mutant cells at the end of develo ...
... may fuse with other propagules as in the case of sex or other forms of aggregation) or by direct fragmentation. The functioning of the groups and their group fitness (number of propagules or offspring groups produced) depends upon their composition of mutant and non-mutant cells at the end of develo ...
Reproduction: Cetaceans.
... implantation capability; Lactation 4-6 months; First reproduction at 3-4 yrs; Breeding life of 10-12 yrs; Males territorial during breeding season, with slight sexual dimorphism in size (males larger) ...
... implantation capability; Lactation 4-6 months; First reproduction at 3-4 yrs; Breeding life of 10-12 yrs; Males territorial during breeding season, with slight sexual dimorphism in size (males larger) ...
do not open the examination paper until you are told by the
... Candidates are expected to be thoroughly familiar with all regulations pertaining to their conduct during the examinations. These were explained by the chief supervisor prior to the first session, and have been posted for further reference near the entrance to the examination room. Candidates shoul ...
... Candidates are expected to be thoroughly familiar with all regulations pertaining to their conduct during the examinations. These were explained by the chief supervisor prior to the first session, and have been posted for further reference near the entrance to the examination room. Candidates shoul ...























