* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Taxonomy and Classification Powerpoint
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
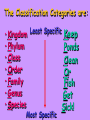
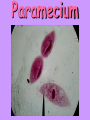
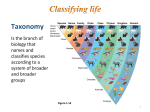
Do Now: • Think back to the Jones Beach lab where you classified and sorted organisms. • What do scientists sort organisms based on? Spider crab vs. green crab What is taxonomy? • The way in which organisms are sorted based on physical characteristics and DNA code. Initially all organisms, were broken down into only 2 major groups or Kingdoms: •Plants •Animals Taxonomy: • However, as more organisms were discovered there was a need to divide the groups even further. • The classification of living organisms is called Taxonomy and is primarily based on structure of the organism. Classification Categories: • The 5 kingdoms are very broad and general categories. • To help organize the wide variety of animals, plants etc, the 5 kingdoms were subdivided into more specific categories. The Classification Categories are: Least Specific • Kingdom • Phylum • Class • Order • Family • Genus • Species Most Specific Keep Ponds Clean Or Fish Get Sick! The Five Kingdoms… • There are now 5 kingdoms or major groups. • They are: – Monerans (bacteria, algae) – Protists (ameba, paramecium) – Fungi (lichens, yeast, mold) – Plants(grasses, trees, flowers) – Animals (fish, birds, dogs, humans) A. Kingdom Monera • Microscopic • Unicellular (single cell) • Prokaryotic (no nucleus) • Lack most cell organelles • Ingest food by absorption • Ex: Blue-green algae, bacteria Blue-green Algae B. Kingdom Protista • Unicellular (single cell) • Eukaryotic (has nucleus) • Some are motile (able to move) • Ex: Amoeba, paramecium Ameba Paramecium C. Kingdom Fungi • Multicellular (has many cells) • Eukaryotic (has nucleus) • Have cell walls but CANNOT make own food • Ex: lichens, yeast, mold, mushrooms Marine Fungi • Rarely heard of • Important role in decomposing (breaking down cellulose in plant material) • Coral reefs, estuaries, mangroves, etc. Lichens Mold Moldy Room Yeast D. Plant Kingdom Kelp can grow half a meter a day! • Multicellular • Eukaryotic • Make food by photosynthesis • Sessile (does not move) Phytoplankton Sea grass • The only flowering plant in the ocean! E. Animal Kingdom • Multicellular • Eukaryotic • Obtain food mostly by ingestion • Motile 1. Kingdom • This is the largest and most general unit of classification • What kingdom do dolphins belong to? Animalia Bottle Nose Dolphin Taxonomy • KingdomAnimalia Phylum:Chordata Class:Mammalia Order:Cetacea Family:Delphinidae Genus:Tursiops Species: truncatus 2. Phylum • The grouping of organisms based on general body plan and structure • What phylum do dolphins belong to? Chordata • All chordates have a dorsal (back) nerve cord and cranium that protects the brain. • Ex: Humans, dolphins, sharks, dogs, frogs 3. Class • Share common characteristics • What class do dolphins belong to? Mammalia (mammals) • Ex: Characteristics: – Hair on body – Give birth to live young – Warm blooded 4. Order • These organisms are more similar than those of the same class • What to? order do dolphins belong Cetaceans Dolphins, whales & porpoises Sub order: Odontocetes • Toothed whales • Carnivores 5. Family • They are similar in appearance, and have the same feeding habits, behaviors, and general functions • What family do Dolphins belong to? Delphinidae • Ex: orca, pilot whales; fast, use echolocation, do not dive as deep as other cetaceans 6. Genus • They are more similar in appearance and may breed with each other • What genus do dolphins belong to? Tursiops • Ex:Rounded forehead, pronounced “beak” Slight, almost un-noticable genetic differences • • • • Common bottle nose Indopacific bottle nose (T. aduncus ) Pacific bottle nose (T. gillii) Black sea bottle nose (T. truncatus ponticus ) 7. Species • This is the most specific unit of classification • These individuals can interbreed freely and are most similar to each other • What species do bottle nose dolphins belong to? truncatus Bottle Nose Dolphin Taxonomy • KingdomAnimalia Phylum:Chordata Class:Mammalia Order:Cetacea Family:Delphinidae Genus:Tursiops Species: truncatus Binomial Nomenclature • Every organism has 2 names • The first name is the Genus (always Capitalized) • The second name is the species (lower case) • The scientific name for humans therefore is Homo sapiens which means “wise man” What is the scientific name for a dog? • The Genus is Canis • House pet = Canis familiaris • Wolf = Canis lupus What is the scientific name for a cat? • The genus is Felis • House pet = Felis domestica • Bobcat = Felis rufa