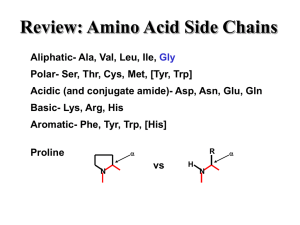
The instructions for how to create and run a living organism are
... Weissman and colleagues at the University of California, San Francisco, developed a technique, called ribosome profiling, in which they sequenced the mRNA chunks that ribosomes were latched onto and being decoded in a yeast cell. That gave them a snapshot of the genes being translated within a cell. ...
... Weissman and colleagues at the University of California, San Francisco, developed a technique, called ribosome profiling, in which they sequenced the mRNA chunks that ribosomes were latched onto and being decoded in a yeast cell. That gave them a snapshot of the genes being translated within a cell. ...
Center for Structural Biology
... Tertiary- organization of a complete chain Quaternary- organization of multiple chains ...
... Tertiary- organization of a complete chain Quaternary- organization of multiple chains ...
Estimation of the protein secondary structure in aqueous solutions
... N.M.Romanov The secondary structure of proteins is very important for their proper functioning. The investigation of the secondary structure gives us an insight into the mechanisms of protein functioning in the living cell. IR absorption spectroscopy provides the opportunity to identify a large numb ...
... N.M.Romanov The secondary structure of proteins is very important for their proper functioning. The investigation of the secondary structure gives us an insight into the mechanisms of protein functioning in the living cell. IR absorption spectroscopy provides the opportunity to identify a large numb ...
Daniel Kaganovich Molecular Mechanism of
... folding quality control system, which includes chaperones that enhance protein folding and regulate protein aggregation. From basic findings in simple cellular models, we develop animal models of neural function and neurodegenerative disease. Our goal is to understand some of the ways in which neuro ...
... folding quality control system, which includes chaperones that enhance protein folding and regulate protein aggregation. From basic findings in simple cellular models, we develop animal models of neural function and neurodegenerative disease. Our goal is to understand some of the ways in which neuro ...
Proteins - Wesleyan College Faculty
... http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/dna/transcribe/ ...
... http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/dna/transcribe/ ...
Introduction Methods Procedure Conclusion and Future Work
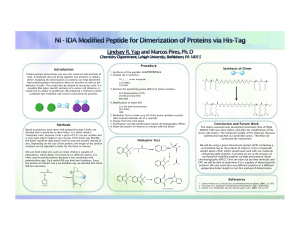
... cells. A molecule that can bring together two proteins is called a dimer. Studying the dimerization or proteins can help determine how protein-protein interactions alters its function as well as the behavior of cells. This could also be related to cancerous cells. It is possible that when specific p ...
... cells. A molecule that can bring together two proteins is called a dimer. Studying the dimerization or proteins can help determine how protein-protein interactions alters its function as well as the behavior of cells. This could also be related to cancerous cells. It is possible that when specific p ...
intracellular protein synthesis, post
... Changes in the functioning of proteins during ageing can be due to inefficient and inaccurate protein synthesis, altered pattern of post-translational modifications, and defective pathways of protein turnover. Slowing-down of bulk protein synthesis is a widely recognized biochemical change with age. ...
... Changes in the functioning of proteins during ageing can be due to inefficient and inaccurate protein synthesis, altered pattern of post-translational modifications, and defective pathways of protein turnover. Slowing-down of bulk protein synthesis is a widely recognized biochemical change with age. ...
Cartoon modeling of proteins
... How does this ordered soup of proteins maintain a such a large number of tightly synchronised feedback control systems? ...
... How does this ordered soup of proteins maintain a such a large number of tightly synchronised feedback control systems? ...
Cartoon modeling of proteins
... How does this ordered soup of proteins maintain a such a large number of tightly synchronised feedback control systems? ...
... How does this ordered soup of proteins maintain a such a large number of tightly synchronised feedback control systems? ...
Coevolution in protein families: a functional correlation study.
... In this study we restrict our goal to the prediction of the set of residues in physical contacts (i.e. the set of residue pairs at distance lower than 8Å in the native 3-D structure). Local correlation based analysis (e.g. mutual information) are attractive measures because they explicitly show the ...
... In this study we restrict our goal to the prediction of the set of residues in physical contacts (i.e. the set of residue pairs at distance lower than 8Å in the native 3-D structure). Local correlation based analysis (e.g. mutual information) are attractive measures because they explicitly show the ...
Supplementary Table 1: A complete list of proteins identified with
... Supplementary Table 1: A complete list of proteins identified with two or more peptides using MaxQuant (version 1.2.2.5) from experiments using anti-acetyl-lysine immunoprecipitation and SILAC (stable isotope labeling with amino acids in cell culture) analysis of MOLM-13 cells treated with nutlin-3 ...
... Supplementary Table 1: A complete list of proteins identified with two or more peptides using MaxQuant (version 1.2.2.5) from experiments using anti-acetyl-lysine immunoprecipitation and SILAC (stable isotope labeling with amino acids in cell culture) analysis of MOLM-13 cells treated with nutlin-3 ...
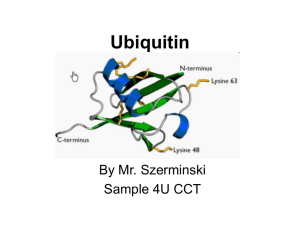
Ubiquitin
... Topics to be discussed • General info: - it is a regulatory protein that has been found in almost all tissues of eukaryotes - one of its functions: it directs protein recycling - can attach to proteins and label them for destruction. - discovery won the Nobel Prize for chemistry in 2004 ...
... Topics to be discussed • General info: - it is a regulatory protein that has been found in almost all tissues of eukaryotes - one of its functions: it directs protein recycling - can attach to proteins and label them for destruction. - discovery won the Nobel Prize for chemistry in 2004 ...
Key Points Folding
... • Proteins have many possible conformations (ways to fold up into a 3D structure) • Proteins can spontaneously fold into the correct (biologically functional) 3D structure demonstrated by Christian Anfinsen in the 1950’s • -helix and -sheet are forms of secondary structure (repeating patterns of h ...
... • Proteins have many possible conformations (ways to fold up into a 3D structure) • Proteins can spontaneously fold into the correct (biologically functional) 3D structure demonstrated by Christian Anfinsen in the 1950’s • -helix and -sheet are forms of secondary structure (repeating patterns of h ...
Proteins for Growth and Repair
... oats. Threonine can be found in lenses, cereal, herbs and grasses. To avoid shortage it is easier if you drink milk, otherwise you must make sure that you eat various kinds of beans, lentils etc. ...
... oats. Threonine can be found in lenses, cereal, herbs and grasses. To avoid shortage it is easier if you drink milk, otherwise you must make sure that you eat various kinds of beans, lentils etc. ...
Proteomics techniques used to identify proteins
... Identification of regulatory proteins from human cells using 2D-GE and LC-MS/MS Victor Paromov Christian Muenyi William L. Stone ...
... Identification of regulatory proteins from human cells using 2D-GE and LC-MS/MS Victor Paromov Christian Muenyi William L. Stone ...
Proteins - CasimiroSBI4U
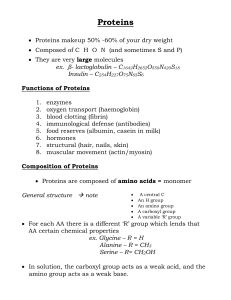
... Peptide bond = covalent bond formed by condensation reaction that links carboxyl group of one amino acid to amino group of another. ...
... Peptide bond = covalent bond formed by condensation reaction that links carboxyl group of one amino acid to amino group of another. ...
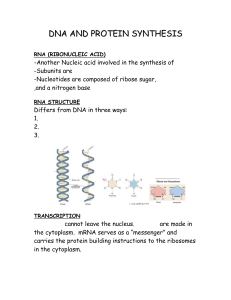
DNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... bases in mRNA into the amino acids of a protein. 1 Codon = 3 nucleotides on mRNA 1 Codon = Some codons are redundant (can be used again to give the same amino acid) RESULT OF TRANSLATION ...
... bases in mRNA into the amino acids of a protein. 1 Codon = 3 nucleotides on mRNA 1 Codon = Some codons are redundant (can be used again to give the same amino acid) RESULT OF TRANSLATION ...
Knuffke Prezi- Macromolecules
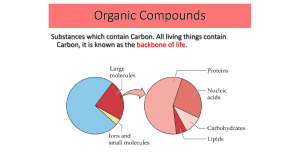
... Organic Compounds Substances which contain Carbon. All living things contain Carbon, it is known as the backbone of life. ...
... Organic Compounds Substances which contain Carbon. All living things contain Carbon, it is known as the backbone of life. ...
Final Report
... Department of Chemistry and Physics This proposal aimed to create expression vectors for two forms of a protein: Noxo1 and Noxo1. Noxo1 (NOX Organizer 1) is a protein that serves as an “organizer” in a multiprotein enzyme complex that is involved in a wide range of cellular functions. Aberrant fun ...
... Department of Chemistry and Physics This proposal aimed to create expression vectors for two forms of a protein: Noxo1 and Noxo1. Noxo1 (NOX Organizer 1) is a protein that serves as an “organizer” in a multiprotein enzyme complex that is involved in a wide range of cellular functions. Aberrant fun ...
Bioinformatik - Brigham Young University
... •Low coverage •Does not include results from high throughput experiments •Gene names may not be consistent ...
... •Low coverage •Does not include results from high throughput experiments •Gene names may not be consistent ...
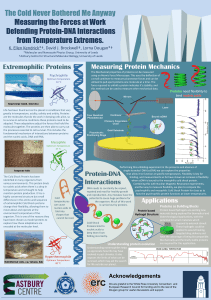
The Cold Never Bothered Me Anyway Measuring the Forces at Work
... adapted. These adaptations adjust the forces that hold the molecules together. The proteins are then able to carry out the processes essential to cell survival. This includes the fundamental mechanism of interactions between proteins and the nucleic acids, DNA and RNA. ...
... adapted. These adaptations adjust the forces that hold the molecules together. The proteins are then able to carry out the processes essential to cell survival. This includes the fundamental mechanism of interactions between proteins and the nucleic acids, DNA and RNA. ...
Protein–protein interaction

Protein–protein interactions (PPIs) refer to physical contacts established between two or more proteins as a result of biochemical events and/or electrostatic forces.In fact, proteins are vital macromolecules, at both cellular and systemic levels, but they rarely act alone. Diverse essential molecular processes within a cell are carried out by molecular machines that are built from a large number of protein components organized by their PPIs. Indeed, these interactions are at the core of the entire interactomics system of any living cell and so, unsurprisingly, aberrant PPIs are on the basis of multiple diseases, such as Creutzfeld-Jacob, Alzheimer's disease, and cancer.PPIs have been studied from different perspectives: biochemistry, quantum chemistry, molecular dynamics, signal transduction, among others. All this information enables the creation of large protein interaction networks – similar to metabolic or genetic/epigenetic networks – that empower the current knowledge on biochemical cascades and disease pathogenesis, as well as provide putative new therapeutic targets.