Abstract
... Insoluble β-amyloid peptide (Aβ) deposits formed in the synaptic milieu, chronic activation of glial cells and inflammation are consistent features in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and strong candidates for the initiation of this process. S100B is one of the numerous pro-inflammatory molecules produced b ...
... Insoluble β-amyloid peptide (Aβ) deposits formed in the synaptic milieu, chronic activation of glial cells and inflammation are consistent features in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and strong candidates for the initiation of this process. S100B is one of the numerous pro-inflammatory molecules produced b ...
Key concepts_Protein processing and modification
... organelles or to fulfill their physiological function. Such processing may involve covalent cleavage and/ or splicing of the chain, or modification of residue side chains. Much processing and modification occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum or the Golgi apparatus; this requires directed transport ac ...
... organelles or to fulfill their physiological function. Such processing may involve covalent cleavage and/ or splicing of the chain, or modification of residue side chains. Much processing and modification occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum or the Golgi apparatus; this requires directed transport ac ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 9. Nitrosylation is very important for cell cycle progression. 10. Metabolomics and metagenomics are same. III Complete the following ...
... 9. Nitrosylation is very important for cell cycle progression. 10. Metabolomics and metagenomics are same. III Complete the following ...
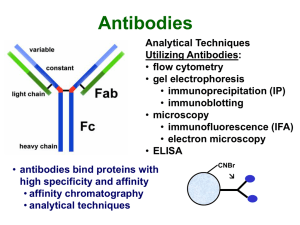
Typical IP Protocol
... Bacterial proteins that bind IgG (Fc): • protein A (Staphylococcus aureus) • protein G (Streptococcus) • binds more species and subclasses ...
... Bacterial proteins that bind IgG (Fc): • protein A (Staphylococcus aureus) • protein G (Streptococcus) • binds more species and subclasses ...
DOC
... CRISPR/Cas9-based methods, represents a central paradigm of modern biology to study protein functions in vivo. However, acting upstream the proteic level is a limiting factor if the turnover of the target protein is slow or the existing pool of the target protein is important (for instance, in insec ...
... CRISPR/Cas9-based methods, represents a central paradigm of modern biology to study protein functions in vivo. However, acting upstream the proteic level is a limiting factor if the turnover of the target protein is slow or the existing pool of the target protein is important (for instance, in insec ...
Document
... Bertrand García Moreno ([email protected]) Monday, Wednesday, & Friday, 1:00 – 5:30 pm Biophysics Lab in the UTL, room G89 Meredith Peck ([email protected]) Lab reports, quizzes, pre-lab, and participation/etiquette ...
... Bertrand García Moreno ([email protected]) Monday, Wednesday, & Friday, 1:00 – 5:30 pm Biophysics Lab in the UTL, room G89 Meredith Peck ([email protected]) Lab reports, quizzes, pre-lab, and participation/etiquette ...
1.Contrast and compare the structure of a saturated fat versus an
... 1. Contrast and compare the structure of a saturated fat versus an unsaturated fat. 2. Identify and describe the four levels of protein structure. 3. Speculate (predict) on why a change in pH or Na+ concentration could cause a protein to lose its secondary or tertiary structure and denature. 4. Disc ...
... 1. Contrast and compare the structure of a saturated fat versus an unsaturated fat. 2. Identify and describe the four levels of protein structure. 3. Speculate (predict) on why a change in pH or Na+ concentration could cause a protein to lose its secondary or tertiary structure and denature. 4. Disc ...
The human kinome and all its associated signaling proteins
... The human kinome and all its associated signaling proteins comprise an important network that is crucial for the regulation of the majority of cellular functions. The NIMA-related kinases (NEKs) are a family of serine/threonine kinases involved largely in cell cycle control in fungi, mammals and oth ...
... The human kinome and all its associated signaling proteins comprise an important network that is crucial for the regulation of the majority of cellular functions. The NIMA-related kinases (NEKs) are a family of serine/threonine kinases involved largely in cell cycle control in fungi, mammals and oth ...
Combinatorial docking approach for structure prediction of large
... for pair-wise docking of smaller molecules or protein domains as well as free-energy calculations to build determine native conformations of larger protein complexes. Such an algorithm is much faster than trying to determine the entire protein or assembly structure through molecular dynamics methods ...
... for pair-wise docking of smaller molecules or protein domains as well as free-energy calculations to build determine native conformations of larger protein complexes. Such an algorithm is much faster than trying to determine the entire protein or assembly structure through molecular dynamics methods ...
Through the Looking Glass a New World of Proteins Enabled
... enantiomorphs, unnatural protein molecules made up entirely of D-amino acids. These D-proteins have a tertiary structure that is the mirror image of the backbone fold of their counterparts found in nature. Such mirror image protein molecules have a variety of uses. More facile crystallization of rac ...
... enantiomorphs, unnatural protein molecules made up entirely of D-amino acids. These D-proteins have a tertiary structure that is the mirror image of the backbone fold of their counterparts found in nature. Such mirror image protein molecules have a variety of uses. More facile crystallization of rac ...
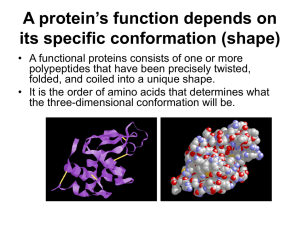
A protein’s function depends on its specific conformation
... • A functional proteins consists of one or more polypeptides that have been precisely twisted, folded, and coiled into a unique shape. • It is the order of amino acids that determines what the three-dimensional conformation will be. ...
... • A functional proteins consists of one or more polypeptides that have been precisely twisted, folded, and coiled into a unique shape. • It is the order of amino acids that determines what the three-dimensional conformation will be. ...
DN: Protein
... Protein There are three major classes of organic components in feeds: • carbohydrates (e.g. fibre and starch); • lipids (fats and oils), and; • proteins. True proteins are composed of long chains of amino acids, each protein distinguishable by its unique sequence of the 20 different amino acids as i ...
... Protein There are three major classes of organic components in feeds: • carbohydrates (e.g. fibre and starch); • lipids (fats and oils), and; • proteins. True proteins are composed of long chains of amino acids, each protein distinguishable by its unique sequence of the 20 different amino acids as i ...
corriganpaperabstract - Workspace
... responses to changing environments. Canonical secondary signalling molecules act through specific receptor proteins by direct binding to alter their activity. Cyclic diadenosine monophosphate (c-di-AMP) is an essential signalling molecule in bacteria that has only recently been discovered. Through o ...
... responses to changing environments. Canonical secondary signalling molecules act through specific receptor proteins by direct binding to alter their activity. Cyclic diadenosine monophosphate (c-di-AMP) is an essential signalling molecule in bacteria that has only recently been discovered. Through o ...
IB2.14.3 Building a protein
... All the basic structural material of the human body is made of proteins. Skin, muscles, bone, cartilage, ligaments and cell membranes all contain a lot of protein. In addition, other proteins do important jobs in cells. All protein molecules contain the elements: Carbon Oxygen Hydrogen Nitro ...
... All the basic structural material of the human body is made of proteins. Skin, muscles, bone, cartilage, ligaments and cell membranes all contain a lot of protein. In addition, other proteins do important jobs in cells. All protein molecules contain the elements: Carbon Oxygen Hydrogen Nitro ...
Theme 1 - NUI Galway
... Project Summary: Protein-protein interactions are central to organisation and function in the living cell. We are interested in understanding the determinants of protein recognition and binding affinity. The aim of this project is to investigate how small molecule modifications of the protein surfac ...
... Project Summary: Protein-protein interactions are central to organisation and function in the living cell. We are interested in understanding the determinants of protein recognition and binding affinity. The aim of this project is to investigate how small molecule modifications of the protein surfac ...
Protein: How Cows and Carrots Become People 1. Your body can
... Protein: How Cows and Carrots Become People 1. Your body can manufacture some amino acids (used as the building blocks of proteins) out of nitrogen. What name is given to this group of amino acids? ...
... Protein: How Cows and Carrots Become People 1. Your body can manufacture some amino acids (used as the building blocks of proteins) out of nitrogen. What name is given to this group of amino acids? ...
Analytical Sciences, Poster AS-101 Kinetics and identification of non
... by pipets is the low reproducibility due to spreading and therefore the dilution of the sample. To overcome this, we developed a protocol to spray trypsin or matrix solution. This works in a short time and preserves the multiplexing SPRi measurements. As a proof of concept we will show an investigat ...
... by pipets is the low reproducibility due to spreading and therefore the dilution of the sample. To overcome this, we developed a protocol to spray trypsin or matrix solution. This works in a short time and preserves the multiplexing SPRi measurements. As a proof of concept we will show an investigat ...
33-6-ET-V1-S1__biomi.. - e-Acharya Integrated E
... called Post-synaptic receptors synaptic membrane vesicles and release their content into recognize them as a synaptic cleft signal and get activated which then transmit the signal on to other signaling components ...
... called Post-synaptic receptors synaptic membrane vesicles and release their content into recognize them as a synaptic cleft signal and get activated which then transmit the signal on to other signaling components ...
About Proteins
... The order of the AAs determines the function If even one AA is out of order by mistake, the protein will not function (work) This is because proteins fold in a specific way ...
... The order of the AAs determines the function If even one AA is out of order by mistake, the protein will not function (work) This is because proteins fold in a specific way ...
Two Rules on Protein-Ligand Interactions Xiaodong Pang1, 2
... ligand is of paramount importance in drug discovery efforts. So far, in finding a real ligand for a given target protein, we are limited to experimental screening from a large number of small molecules, or through free energy calculation of assessing a ligand. However, we still lack a clear molecula ...
... ligand is of paramount importance in drug discovery efforts. So far, in finding a real ligand for a given target protein, we are limited to experimental screening from a large number of small molecules, or through free energy calculation of assessing a ligand. However, we still lack a clear molecula ...
Protein–protein interaction

Protein–protein interactions (PPIs) refer to physical contacts established between two or more proteins as a result of biochemical events and/or electrostatic forces.In fact, proteins are vital macromolecules, at both cellular and systemic levels, but they rarely act alone. Diverse essential molecular processes within a cell are carried out by molecular machines that are built from a large number of protein components organized by their PPIs. Indeed, these interactions are at the core of the entire interactomics system of any living cell and so, unsurprisingly, aberrant PPIs are on the basis of multiple diseases, such as Creutzfeld-Jacob, Alzheimer's disease, and cancer.PPIs have been studied from different perspectives: biochemistry, quantum chemistry, molecular dynamics, signal transduction, among others. All this information enables the creation of large protein interaction networks – similar to metabolic or genetic/epigenetic networks – that empower the current knowledge on biochemical cascades and disease pathogenesis, as well as provide putative new therapeutic targets.