Protein Structure 2 - Interactions - Hydrolysis
... Tend to form α-helix sections: Ala, Cys, Leu Met, Glu, Gln, His, Lys Tend to form β-sheet sections: Val, Ser, Asp, Asn, Pro, Arg Triple Helix – 3 strands. Collagen has this structure. (Collagen is the most abundant protein. Found in skin, connective tissue, blood vessels, tendons, ligaments, cartila ...
... Tend to form α-helix sections: Ala, Cys, Leu Met, Glu, Gln, His, Lys Tend to form β-sheet sections: Val, Ser, Asp, Asn, Pro, Arg Triple Helix – 3 strands. Collagen has this structure. (Collagen is the most abundant protein. Found in skin, connective tissue, blood vessels, tendons, ligaments, cartila ...
D6- Bulletin Board Powerful Protein
... What are Proteins? • Proteins are made up of chains of amino acids. Proteins are part of every cell in our bodies, especially muscles, bones, skin, and blood! • Foods that are high in protein are also usually high in B vitamins, Iron, magnesium, zinc, and other vitamins and minerals. ...
... What are Proteins? • Proteins are made up of chains of amino acids. Proteins are part of every cell in our bodies, especially muscles, bones, skin, and blood! • Foods that are high in protein are also usually high in B vitamins, Iron, magnesium, zinc, and other vitamins and minerals. ...
distinct format
... proteins of which 714 proteins were identified in asexual blood stages (left panel), 931 in gametocytes (right panel) and 645 in gametes. The last two groups provide insights into the biology of the sexual stages of the parasite, and include conserved, stage-specific, secreted and membrane-associate ...
... proteins of which 714 proteins were identified in asexual blood stages (left panel), 931 in gametocytes (right panel) and 645 in gametes. The last two groups provide insights into the biology of the sexual stages of the parasite, and include conserved, stage-specific, secreted and membrane-associate ...
2016 N1 Week 4
... Warm UP Identify the following properties as either a carbohydrate or a lipid: 1. Does not dissolve in water. 2. The monomer is monosaccharide. 3. This molecule is not a true polymer. 4. The ratio of hydrogen to oxygen is 2:1. 5. Identify the following as a carb or lipid. B A ...
... Warm UP Identify the following properties as either a carbohydrate or a lipid: 1. Does not dissolve in water. 2. The monomer is monosaccharide. 3. This molecule is not a true polymer. 4. The ratio of hydrogen to oxygen is 2:1. 5. Identify the following as a carb or lipid. B A ...
Chemistry 160 Protein Structure Homework
... 1. Give three roles of proteins in an organism. 2. What are prosthetic groups? 3. What are glycoproteins and lipoproteins? 4. Describe the 4 levels of protein structure. 5. Describe 3 types of interactions that stabilize protein structure. 6. What drives protein folding? 7. Give two ways amino acid ...
... 1. Give three roles of proteins in an organism. 2. What are prosthetic groups? 3. What are glycoproteins and lipoproteins? 4. Describe the 4 levels of protein structure. 5. Describe 3 types of interactions that stabilize protein structure. 6. What drives protein folding? 7. Give two ways amino acid ...
3.2 Proteins - Biology with Radjewski
... • Polypeptides or proteins range in size from insulin, which has 51 amino acids, to huge molecules such as the muscle protein titin, with 34,350 amino acids. ...
... • Polypeptides or proteins range in size from insulin, which has 51 amino acids, to huge molecules such as the muscle protein titin, with 34,350 amino acids. ...
(Biological) networks
... Many real-world networks exhibit “scale-free” behavior: characterized by many low-degree nodes and a small number of high-degree nodes. Similarly, many real-world networks exhibit “small-world” behavior, where the longest shortest path is objectively small (see: the “Kevin Bacon game”). Identifying ...
... Many real-world networks exhibit “scale-free” behavior: characterized by many low-degree nodes and a small number of high-degree nodes. Similarly, many real-world networks exhibit “small-world” behavior, where the longest shortest path is objectively small (see: the “Kevin Bacon game”). Identifying ...
Medical Informatics Group
... Medical Informatics Group Mingjie Chen Gil Alterovitz’s lab Harvard Medical School ...
... Medical Informatics Group Mingjie Chen Gil Alterovitz’s lab Harvard Medical School ...
Genetic Engineering - USF :: Biological Sciences
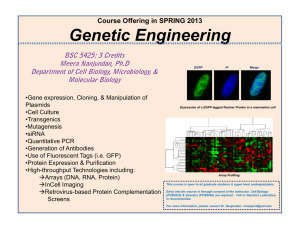
... Department of Cell Biology, Microbiology, & Molecular Biology •Gene expression, Cloning, & Manipulation of Plasmids •Cell Culture •Transgenics •Mutagenesis •siRNA •Quantitative PCR •Generation of Antibodies •Use of Fluorescent Tags (i.e. GFP) •Protein Expression & Purification •High-throughput Techn ...
... Department of Cell Biology, Microbiology, & Molecular Biology •Gene expression, Cloning, & Manipulation of Plasmids •Cell Culture •Transgenics •Mutagenesis •siRNA •Quantitative PCR •Generation of Antibodies •Use of Fluorescent Tags (i.e. GFP) •Protein Expression & Purification •High-throughput Techn ...
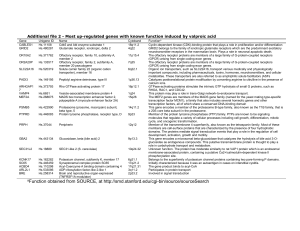
Table - BioMed Central
... This protein may play a role in trans-Golgi network-to-endosome transport. The MEF2 genes are members of the MADS gene family (named for the yeast mating type-specific transcription factor MCM1), a family that also includes several homeotic genes and other transcription factors, all of which share a ...
... This protein may play a role in trans-Golgi network-to-endosome transport. The MEF2 genes are members of the MADS gene family (named for the yeast mating type-specific transcription factor MCM1), a family that also includes several homeotic genes and other transcription factors, all of which share a ...
The measurement of the biological inventory of proteins within an
... *Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution ...
... *Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution ...
Ch. 5. Protein Purification and Characterization Techniques
... Chapter Five Protein Purification and Characterization Techniques ...
... Chapter Five Protein Purification and Characterization Techniques ...
Crash Course in Biochemistry
... • Sequence determines structure • Structure determines function • Structure VERY important – Gives insights to how protein works ...
... • Sequence determines structure • Structure determines function • Structure VERY important – Gives insights to how protein works ...
Organelles and Cellular Function
... Relate cellular metabolism and transport to homeostasis and cellular reproduction. ► e. Describe how structure and function are related in terms of cell and tissue types. ...
... Relate cellular metabolism and transport to homeostasis and cellular reproduction. ► e. Describe how structure and function are related in terms of cell and tissue types. ...
VIRTUAL COUNTER SCREENING: KINASE INHIBITOR STUDY
... In virtual counter screening (VCS), or inverse docking, a small molecule of interest is docked against a database containing structures of multiple proteins. The VCS approach is potentially useful for measuring (A) drug re-positioning, (B) toxicity, (C) metabolic degradation, (D) lead optimization, ...
... In virtual counter screening (VCS), or inverse docking, a small molecule of interest is docked against a database containing structures of multiple proteins. The VCS approach is potentially useful for measuring (A) drug re-positioning, (B) toxicity, (C) metabolic degradation, (D) lead optimization, ...
Elise Young: Animal & Range Sciences
... Linking common factors in the phenomenon of protein clumping observed in several diseases Proteins perform many important functions at the cellular level. However, if proteins do not fold properly, they are prone to aggregating and sticking together, preventing them from performing their functions, ...
... Linking common factors in the phenomenon of protein clumping observed in several diseases Proteins perform many important functions at the cellular level. However, if proteins do not fold properly, they are prone to aggregating and sticking together, preventing them from performing their functions, ...
Protein Engineering
... Usually found in extracellular proteins, not intracellular Cross link between chains or in chains formed by oxidation of cysteine residues ...
... Usually found in extracellular proteins, not intracellular Cross link between chains or in chains formed by oxidation of cysteine residues ...
R032 Publication Only Basic Science: Biofilm Key proteins of
... processed using the Protein Pilot and the sequences were found in the Swiss databank. Results: The proteomic analysis revealed that the samples exhibited different protein profiles, with an increased protein expression of the strain in biofilm compared to planktonic fungal growth, being approximatel ...
... processed using the Protein Pilot and the sequences were found in the Swiss databank. Results: The proteomic analysis revealed that the samples exhibited different protein profiles, with an increased protein expression of the strain in biofilm compared to planktonic fungal growth, being approximatel ...
Interdisciplinary Data Science Faculty Candidate
... Computational Methods for Data-Driven Study of Protein Structure and Function High-throughput sequencing has been producing a large amount of protein sequences, but many of them are missing solved structures and functional annotations, which are essential to the understanding of life process and dis ...
... Computational Methods for Data-Driven Study of Protein Structure and Function High-throughput sequencing has been producing a large amount of protein sequences, but many of them are missing solved structures and functional annotations, which are essential to the understanding of life process and dis ...
College 5
... bonding between two atoms in which both electrons shared in the bond come from the same atom. Once such a bond has been formed, its strength and description is no different from that of other polar covalent bonds. They may involve metal ions. In such complexes, a molecule "donates" its"free" pairs o ...
... bonding between two atoms in which both electrons shared in the bond come from the same atom. Once such a bond has been formed, its strength and description is no different from that of other polar covalent bonds. They may involve metal ions. In such complexes, a molecule "donates" its"free" pairs o ...
Protein–protein interaction

Protein–protein interactions (PPIs) refer to physical contacts established between two or more proteins as a result of biochemical events and/or electrostatic forces.In fact, proteins are vital macromolecules, at both cellular and systemic levels, but they rarely act alone. Diverse essential molecular processes within a cell are carried out by molecular machines that are built from a large number of protein components organized by their PPIs. Indeed, these interactions are at the core of the entire interactomics system of any living cell and so, unsurprisingly, aberrant PPIs are on the basis of multiple diseases, such as Creutzfeld-Jacob, Alzheimer's disease, and cancer.PPIs have been studied from different perspectives: biochemistry, quantum chemistry, molecular dynamics, signal transduction, among others. All this information enables the creation of large protein interaction networks – similar to metabolic or genetic/epigenetic networks – that empower the current knowledge on biochemical cascades and disease pathogenesis, as well as provide putative new therapeutic targets.