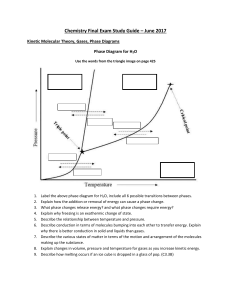
AS Chemistry - Crawshaw Academy
... When chlorine is passed through a solution of potassium bromide, bromine and potassium chloride are formed. ...
... When chlorine is passed through a solution of potassium bromide, bromine and potassium chloride are formed. ...
Summary of 5.4
... amino compound and name one more example of each. 5.4.2b Reactions of amines describe and carry out, where appropriate (using butylamine and phenylamine), reactions to investigate the typical behaviour of primary amines. This will be limited to: i characteristic smell ii miscibility with water as a ...
... amino compound and name one more example of each. 5.4.2b Reactions of amines describe and carry out, where appropriate (using butylamine and phenylamine), reactions to investigate the typical behaviour of primary amines. This will be limited to: i characteristic smell ii miscibility with water as a ...
Trends in The Periodic Table OL Page 1 of 3 G. Galvin Name
... All Halogens are very reactive because they only need 1 extra electron to fill their outer energy level. Trend: The reactivity of the Halogens increases going up the group. Reason: 1. The Halogens are the most electronegative of all elements. The values of their electronegativities increase go ...
... All Halogens are very reactive because they only need 1 extra electron to fill their outer energy level. Trend: The reactivity of the Halogens increases going up the group. Reason: 1. The Halogens are the most electronegative of all elements. The values of their electronegativities increase go ...
Chemistry-5th-Edition-Brady-Solution-Manual
... To test the law of conservation of mass, a reaction would have to be carried out in which the mass of the reactants and the mass of the products are weighed and shown to be the same. The law of definite proportions could be shown by demonstrating that no matter how a compound is made, the same propo ...
... To test the law of conservation of mass, a reaction would have to be carried out in which the mass of the reactants and the mass of the products are weighed and shown to be the same. The law of definite proportions could be shown by demonstrating that no matter how a compound is made, the same propo ...
Atomic
... nonmetals and are known as ____________________. C) The rows on the periodic table are also called _______________ D) The columns on the periodic table are called ____________ or _____________ E) The elements in a column on the periodic table have similar chemical and physical properties because all ...
... nonmetals and are known as ____________________. C) The rows on the periodic table are also called _______________ D) The columns on the periodic table are called ____________ or _____________ E) The elements in a column on the periodic table have similar chemical and physical properties because all ...
ionization energy
... particle) it becomes positively charged because it now has less negative charges than it originally had. When they lose these electrons they will end up with a smaller radius than when they were atoms. Group I or all those elements in the first column, except hydrogen, will all have similar properti ...
... particle) it becomes positively charged because it now has less negative charges than it originally had. When they lose these electrons they will end up with a smaller radius than when they were atoms. Group I or all those elements in the first column, except hydrogen, will all have similar properti ...
Chapter 5 Review Game Questions
... 14) Where are the p block elements on the periodic table? (right) 15) Where is the d-block on the periodic table? (middle) 16) Where is the s block on the periodic table? (left) 17) Half the distance between the nuclei of identical atoms that are bonded together? (atomic radius) 18) Elements on the ...
... 14) Where are the p block elements on the periodic table? (right) 15) Where is the d-block on the periodic table? (middle) 16) Where is the s block on the periodic table? (left) 17) Half the distance between the nuclei of identical atoms that are bonded together? (atomic radius) 18) Elements on the ...
Honors Chemistry Unit 4 Student Packet: Honors Chemistry Problem
... 1. If 90.0 g of sodium is dropped into 80.0 g of water, how many grams of hydrogen would be produced? 2. What is the mass of the excess reactant left form the reaction in problem #1? 3. How many grams of calcium hydroxide would be formed if 100. g of calcium were added to 100.mL of water. (Remember ...
... 1. If 90.0 g of sodium is dropped into 80.0 g of water, how many grams of hydrogen would be produced? 2. What is the mass of the excess reactant left form the reaction in problem #1? 3. How many grams of calcium hydroxide would be formed if 100. g of calcium were added to 100.mL of water. (Remember ...
Unit 2 PPT
... formed molecules. F2 and Cl2 are gases at room temperature, Br2 is a liquid, and I2 is a dark purple solid. Astatine is a synthetic element. ...
... formed molecules. F2 and Cl2 are gases at room temperature, Br2 is a liquid, and I2 is a dark purple solid. Astatine is a synthetic element. ...
The 7 Secrets of the Periodic Table
... Valence electrons are the electrons occupying the highest energy levels. It is important to master this concept because the valence electrons are the electrons involved in bonding. You determine the valence electrons by counting the "s" and "p" electrons in that period. You can determine that fluori ...
... Valence electrons are the electrons occupying the highest energy levels. It is important to master this concept because the valence electrons are the electrons involved in bonding. You determine the valence electrons by counting the "s" and "p" electrons in that period. You can determine that fluori ...
Chapter 11 Chemical Reactions
... gaseous hydrogen chloride to form iron (III) chloride and hydrogen sulfide gas. Nitric acid dissolved in water reacts with solid sodium carbonate to form liquid water and carbon dioxide gas and sodium nitrate dissolved in water. ...
... gaseous hydrogen chloride to form iron (III) chloride and hydrogen sulfide gas. Nitric acid dissolved in water reacts with solid sodium carbonate to form liquid water and carbon dioxide gas and sodium nitrate dissolved in water. ...
Unit 3 Revision Notes 213.00KB 2017-03-01 18
... 2. Like metals, a more reactive halogen will displace a less reactive one: e.g. chlorine + potassium bromide = bromine + potassium chloride Cl2 + 2KI = Br2 + 2KCl or bromine + sodium iodide = iodine + sodium bromide Br2 + 2NaI = I2 + 2KBr THE TRANSITION METALS This is the block which appears in the ...
... 2. Like metals, a more reactive halogen will displace a less reactive one: e.g. chlorine + potassium bromide = bromine + potassium chloride Cl2 + 2KI = Br2 + 2KCl or bromine + sodium iodide = iodine + sodium bromide Br2 + 2NaI = I2 + 2KBr THE TRANSITION METALS This is the block which appears in the ...
REACTION PREDICTION
... PRE-AP CHEMISTRY Complete the word equation, write the formula equation, balance it and identify the type of reaction. You many abbreviate as S, D, SR, DR, and C. ...
... PRE-AP CHEMISTRY Complete the word equation, write the formula equation, balance it and identify the type of reaction. You many abbreviate as S, D, SR, DR, and C. ...
CHAPTER 9 HYDROGEN Position of Hydrogen in Periodic Table
... [c] Electron rich hydrides:-The hydrides which have excess electrons as required to form normal covalent bonds is called electron rich hydride. For example, hydrides of group 15 to 17 (NH3, PH3, H2O, H2S, H2Se, H2Te, HF etc.) (iii) Metallic or non-stoichiometric hydrides: These are formed by many d ...
... [c] Electron rich hydrides:-The hydrides which have excess electrons as required to form normal covalent bonds is called electron rich hydride. For example, hydrides of group 15 to 17 (NH3, PH3, H2O, H2S, H2Se, H2Te, HF etc.) (iii) Metallic or non-stoichiometric hydrides: These are formed by many d ...
Language of chemistry
... H2O. That means there are 2 hydrogen atoms combining with 1 oxygen atom. Why is this? It is because oxygen has a valency of 2 while hydrogen has a valency of 1. How do we remember this? For now it will help to remember a few valencies. Monovalent Divalent Trivalent Tetra valent H - hydrogen Ca - cal ...
... H2O. That means there are 2 hydrogen atoms combining with 1 oxygen atom. Why is this? It is because oxygen has a valency of 2 while hydrogen has a valency of 1. How do we remember this? For now it will help to remember a few valencies. Monovalent Divalent Trivalent Tetra valent H - hydrogen Ca - cal ...
Chapter 4- The Periodic Table Section 1
... nucleus and its outermost electrons due to the cancellation of some of the positive charge by the negative charges of the inner electrons ...
... nucleus and its outermost electrons due to the cancellation of some of the positive charge by the negative charges of the inner electrons ...
How many grams of oxygen are made if 3.75 moles of KClO 3
... 16. Plants are equipped with a mitochondria that is able to store energy in the bonds of a chemical. Plants and animals depend on this chemical (glucose) as an energy source. What is the chemical formula for glucose? How many molecules of glucose are there in 1.3 g of glucose that were extracted fro ...
... 16. Plants are equipped with a mitochondria that is able to store energy in the bonds of a chemical. Plants and animals depend on this chemical (glucose) as an energy source. What is the chemical formula for glucose? How many molecules of glucose are there in 1.3 g of glucose that were extracted fro ...
Chapter 11 Chemical Reactions
... Example (needs to be a double replacement reaction) AgNO3 + NaCl AgCl + NaNO3 1. this is the full balanced equation 2. next, write it as an ionic equation by splitting the compounds into their ions: Ag1+ + NO31- + Na1+ + Cl1- AgCl + Na1+ + NO31Note that the AgCl did not ionize, because it is a “ ...
... Example (needs to be a double replacement reaction) AgNO3 + NaCl AgCl + NaNO3 1. this is the full balanced equation 2. next, write it as an ionic equation by splitting the compounds into their ions: Ag1+ + NO31- + Na1+ + Cl1- AgCl + Na1+ + NO31Note that the AgCl did not ionize, because it is a “ ...
File
... the table below. a. The word grid below will help you assess your understanding of the terms involved with the Periodic Table. b. Rate your understanding of each word with either a “+” (understand well), a “” (limited understanding or unsure), or a “-” (don’t know at all). c. Continue to revisit th ...
... the table below. a. The word grid below will help you assess your understanding of the terms involved with the Periodic Table. b. Rate your understanding of each word with either a “+” (understand well), a “” (limited understanding or unsure), or a “-” (don’t know at all). c. Continue to revisit th ...
Chapter 11 Chemical Reactions
... Example (needs to be a double replacement reaction) AgNO3 + NaCl AgCl + NaNO3 1. this is the full balanced equation 2. next, write it as an ionic equation by splitting the compounds into their ions: Ag1+ + NO31- + Na1+ + Cl1- AgCl + Na1+ + NO31Note that the AgCl did not ionize, because it is a “ ...
... Example (needs to be a double replacement reaction) AgNO3 + NaCl AgCl + NaNO3 1. this is the full balanced equation 2. next, write it as an ionic equation by splitting the compounds into their ions: Ag1+ + NO31- + Na1+ + Cl1- AgCl + Na1+ + NO31Note that the AgCl did not ionize, because it is a “ ...
Chemistry of CHLORINE
... Reduce tooth decay when added in small amounts/equations in tooth paste. Note: large small quantities of fluorine /fluoride ions in water cause browning of teeth/flourosis. Hydrogen fluoride is used to engrave word pictures in glass. (ii) ...
... Reduce tooth decay when added in small amounts/equations in tooth paste. Note: large small quantities of fluorine /fluoride ions in water cause browning of teeth/flourosis. Hydrogen fluoride is used to engrave word pictures in glass. (ii) ...
Unit 1 PowerPoint Complete Notes
... describe the millions of known compounds. This communication depends on a standard system of naming and writing the formulas for compounds. Chemists formed a group to standardize the system of naming and called themselves the International Union of Physical and Applied Chemists, or IUPAC. A chemical ...
... describe the millions of known compounds. This communication depends on a standard system of naming and writing the formulas for compounds. Chemists formed a group to standardize the system of naming and called themselves the International Union of Physical and Applied Chemists, or IUPAC. A chemical ...
Midterm 2 from Summer 2012
... 45.7 mL of 0.500 M H2SO4 is required to completely neutralize an NaOH solution. How many grams of NaOH were required to carry-out this neutralization? ...
... 45.7 mL of 0.500 M H2SO4 is required to completely neutralize an NaOH solution. How many grams of NaOH were required to carry-out this neutralization? ...