Molecular Formulas - Hatboro
... To the AP Chemistry Student: Welcome to my AP Chemistry class! The Advance Placement Chemistry experience is designed to provide a full year of college-level chemistry, so it places heavy demands on the student, especially in terms of the time commitment required. In fact, the College Board suggests ...
... To the AP Chemistry Student: Welcome to my AP Chemistry class! The Advance Placement Chemistry experience is designed to provide a full year of college-level chemistry, so it places heavy demands on the student, especially in terms of the time commitment required. In fact, the College Board suggests ...
File
... tightly bound to the nucleus (more p+ in the nucleus). Down a group, IE decreases because electrons are farther from the nucleus and not held as tight. Values are found on Table S. ...
... tightly bound to the nucleus (more p+ in the nucleus). Down a group, IE decreases because electrons are farther from the nucleus and not held as tight. Values are found on Table S. ...
Honors Chapter 11 Reactions
... iron sulfide and hydrochloric acid FeS (aq) + HCl (aq) FeCl2 (aq) + H2S (g) hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) NaCl (aq) + H2O (l) potassium iodide and lead (II) nitrate ...
... iron sulfide and hydrochloric acid FeS (aq) + HCl (aq) FeCl2 (aq) + H2S (g) hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) NaCl (aq) + H2O (l) potassium iodide and lead (II) nitrate ...
Synthesis Reactions occur when two of more reactants combine to
... 2. Metallic chlorates and perchlorates decompose into metallic chlorides and oxygen. example A sample of iron(III) chlorate is heated. 2Fe(ClO3)3 2FeCl3 + 9O2 3. Metallic hydroxides (bases) decomposes into metallic oxides and water. example Solid potassium hydroxide is heated. 2KOH K2O + H2O 4. ...
... 2. Metallic chlorates and perchlorates decompose into metallic chlorides and oxygen. example A sample of iron(III) chlorate is heated. 2Fe(ClO3)3 2FeCl3 + 9O2 3. Metallic hydroxides (bases) decomposes into metallic oxides and water. example Solid potassium hydroxide is heated. 2KOH K2O + H2O 4. ...
Summer Assignment Packet
... Sulfur and fluorine form several different compounds including sulfur hexafluoride and sulfur tetrafluoride. Decomposition of a sample of sulfur hexafluoride produces 4.45 g of fluorine and 1.25 g of sulfur, while decomposition of a sample of sulfur tetrafluoride produces 4.43 g of fluorine and 1.87 ...
... Sulfur and fluorine form several different compounds including sulfur hexafluoride and sulfur tetrafluoride. Decomposition of a sample of sulfur hexafluoride produces 4.45 g of fluorine and 1.25 g of sulfur, while decomposition of a sample of sulfur tetrafluoride produces 4.43 g of fluorine and 1.87 ...
AP Chemistry Name: Ch.1 – Matter and Measurement Date: Period:
... Sulfur and fluorine form several different compounds including sulfur hexafluoride and sulfur tetrafluoride. Decomposition of a sample of sulfur hexafluoride produces 4.45 g of fluorine and 1.25 g of sulfur, while decomposition of a sample of sulfur tetrafluoride produces 4.43 g of fluorine and 1.87 ...
... Sulfur and fluorine form several different compounds including sulfur hexafluoride and sulfur tetrafluoride. Decomposition of a sample of sulfur hexafluoride produces 4.45 g of fluorine and 1.25 g of sulfur, while decomposition of a sample of sulfur tetrafluoride produces 4.43 g of fluorine and 1.87 ...
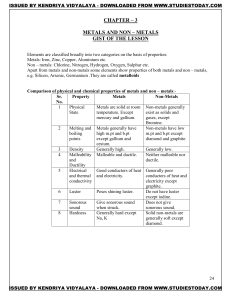
METALS AND NON – METALS Concepts
... Metals: Iron, Zinc, Copper, Aluminium etc. Non – metals: Chlorine, Nitrogen, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Sulphur etc. Apart from metals and non-metals some elements show properties of both metals and non – metals, e.g. Silicon, Arsenic, Germanium .They are called metalloids Comparison of physical and chemical ...
... Metals: Iron, Zinc, Copper, Aluminium etc. Non – metals: Chlorine, Nitrogen, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Sulphur etc. Apart from metals and non-metals some elements show properties of both metals and non – metals, e.g. Silicon, Arsenic, Germanium .They are called metalloids Comparison of physical and chemical ...
Periodic Table
... Harder, denser, stronger, but less reactive than alkali metals E.g. magnesium and calcium ...
... Harder, denser, stronger, but less reactive than alkali metals E.g. magnesium and calcium ...
2014-15 FINAL REVIEW Nomenclature: Chemical Name Chemical
... 1. Using the following equation: 2 NaOH + H2SO4 2 H2O + Na2SO4 How many grams of sodium sulfate will be formed if you start with 200 grams of sodium hydroxide and you have an excess of sulfuric acid (H2SO4)? 2. Using the following equation: Pb(SO4)2 + 4 LiNO3 Pb(NO3)4 + 2 Li2SO4 How many grams o ...
... 1. Using the following equation: 2 NaOH + H2SO4 2 H2O + Na2SO4 How many grams of sodium sulfate will be formed if you start with 200 grams of sodium hydroxide and you have an excess of sulfuric acid (H2SO4)? 2. Using the following equation: Pb(SO4)2 + 4 LiNO3 Pb(NO3)4 + 2 Li2SO4 How many grams o ...
Lecture 2 - Columbia University
... into moles. Obtain relative number of moles of reactants and products independent of the actual chemical amounts. (2) Translate coefficients into molecules. Obtain relative number of molecules of reactants and products independent of the actual chemical amounts. (3) Mass relationships in chemical re ...
... into moles. Obtain relative number of moles of reactants and products independent of the actual chemical amounts. (2) Translate coefficients into molecules. Obtain relative number of molecules of reactants and products independent of the actual chemical amounts. (3) Mass relationships in chemical re ...
balancing chemical equations worksheet
... The following questions relate to these four steps. a. What symbols should we use to describe the physical states? b. Chemists and other scientists always balance chemical equations. Please explain why this is so important. (Hint, refer to the law of conservation of mass) PART B, read the following ...
... The following questions relate to these four steps. a. What symbols should we use to describe the physical states? b. Chemists and other scientists always balance chemical equations. Please explain why this is so important. (Hint, refer to the law of conservation of mass) PART B, read the following ...
10 IB Chemistry Assessment Statements 2009 Revised
... Int, aim 8: Today, we may be starting to experience the consequences of using fossil fuels as our main source of energy. There is a vast range of products that can be derived from fossil fuels as a result of carbon’s rich chemistry. This raises the question “are they too valuable to burn?”. ...
... Int, aim 8: Today, we may be starting to experience the consequences of using fossil fuels as our main source of energy. There is a vast range of products that can be derived from fossil fuels as a result of carbon’s rich chemistry. This raises the question “are they too valuable to burn?”. ...
clean-color-coded-periodic-table_ochoa-edit
... b. Alkaline Earth Metals = brown c. Halogens = pink d. Noble Gases = yellow e. Metalloids = orange (only color the lower portion of Astatine(85)) f. Transition Metals = purple g. Lanthanide Series = red h. Actinide Series = blue 6. Make a color key in the large open region showing all the colored gr ...
... b. Alkaline Earth Metals = brown c. Halogens = pink d. Noble Gases = yellow e. Metalloids = orange (only color the lower portion of Astatine(85)) f. Transition Metals = purple g. Lanthanide Series = red h. Actinide Series = blue 6. Make a color key in the large open region showing all the colored gr ...
AKS Review
... Groups(families)- vertical column on periodic table. Elements in the same family have similar properties because they have the same valence electron configuration Periodic law- “Properties of elements are a Periodic Function of the atomic number.” When elements are arranged by increasing atomic numb ...
... Groups(families)- vertical column on periodic table. Elements in the same family have similar properties because they have the same valence electron configuration Periodic law- “Properties of elements are a Periodic Function of the atomic number.” When elements are arranged by increasing atomic numb ...
Target 3 – Identify the 3 main classes of
... C. Trend 2: Weight loss occurs more when people go out and exercise. (inverse relationship) ...
... C. Trend 2: Weight loss occurs more when people go out and exercise. (inverse relationship) ...
Periodic Table Worksheet
... 8. As you go down a group, the first ionization energy generally (DECREASES / increases). Why? OUTERMOST ELECTRON IS FARTHER AWAY FROM NUCLEUS; SHIELDING EFFECT OF INNER ELECTRONS. 9. Where is the highest electronegativity found? UPPER RIGHT (F) 10. Where is the lowest electronegativity found? LOWER ...
... 8. As you go down a group, the first ionization energy generally (DECREASES / increases). Why? OUTERMOST ELECTRON IS FARTHER AWAY FROM NUCLEUS; SHIELDING EFFECT OF INNER ELECTRONS. 9. Where is the highest electronegativity found? UPPER RIGHT (F) 10. Where is the lowest electronegativity found? LOWER ...
Periodic Table Funsheet (KEY) 1. Where are the most active metals
... 8. As you go down a group, the first ionization energy generally (DECREASES / increases). Why? OUTERMOST ELECTRON IS FARTHER AWAY FROM NUCLEUS; SHIELDING EFFECT OF INNER ELECTRONS. 9. Where is the highest electronegativity found? UPPER RIGHT (F) 10. Where is the lowest electronegativity found? LOWER ...
... 8. As you go down a group, the first ionization energy generally (DECREASES / increases). Why? OUTERMOST ELECTRON IS FARTHER AWAY FROM NUCLEUS; SHIELDING EFFECT OF INNER ELECTRONS. 9. Where is the highest electronegativity found? UPPER RIGHT (F) 10. Where is the lowest electronegativity found? LOWER ...
1 - contentextra
... The position of an element is related to the electron arrangement of its atoms. Magnesium, for example, is in Period 3, as it has three occupied energy levels and in Group 2, as there are two electrons in its outer energy level. Boron is in Period 2, as it has two occupied energy levels and in Group ...
... The position of an element is related to the electron arrangement of its atoms. Magnesium, for example, is in Period 3, as it has three occupied energy levels and in Group 2, as there are two electrons in its outer energy level. Boron is in Period 2, as it has two occupied energy levels and in Group ...
Atoms, Bonding, and the Periodic Table
... 4. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about valence electrons and chemical bonding. a. Most atoms are less stable when they have eight valence electrons. b. Atoms with eight valence electrons easily form compounds. c. Having eight valence electrons makes atoms very reactive. d. Atoms wi ...
... 4. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about valence electrons and chemical bonding. a. Most atoms are less stable when they have eight valence electrons. b. Atoms with eight valence electrons easily form compounds. c. Having eight valence electrons makes atoms very reactive. d. Atoms wi ...
Chapter 6
... -hard, shiny, conduct heat or electricity well, malleable, ductile -have 3 or fewer electrons in outer level (3 or less dots in dot diagram) ...
... -hard, shiny, conduct heat or electricity well, malleable, ductile -have 3 or fewer electrons in outer level (3 or less dots in dot diagram) ...
Chemistry Ch. 5
... have to be stored in kerosene because they react violently with air or moisture. -melting point decreases down the group -have 1 electron in outer energy level ...
... have to be stored in kerosene because they react violently with air or moisture. -melting point decreases down the group -have 1 electron in outer energy level ...
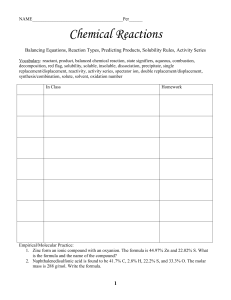
Chemical Reactions
... Don’t forget about the diatomic elements! (Br, I, N, Cl, H, O, F) For example, Oxygen is O2 as an element. In a compound, it can’t be a diatomic element because it’s not an element anymore, it’s a compound! ...
... Don’t forget about the diatomic elements! (Br, I, N, Cl, H, O, F) For example, Oxygen is O2 as an element. In a compound, it can’t be a diatomic element because it’s not an element anymore, it’s a compound! ...
Unit 3.2 Periodic Table Test
... An electron has the same mass as a proton. An electron has much more mass than a neutron. An electron has about the same mass as a neutron. An electron has much less mass than a proton. An electron has much less mass than a neutron. A proton has more mass than an electron. A proton has less mass tha ...
... An electron has the same mass as a proton. An electron has much more mass than a neutron. An electron has about the same mass as a neutron. An electron has much less mass than a proton. An electron has much less mass than a neutron. A proton has more mass than an electron. A proton has less mass tha ...