Neuro Objectives 17
... dopamine, and serotonin are all pumped back into the presynaptic cell against a concentration gradient b. metabolism: acetylcholine (acetylcholinesterase), norepinephrine (MAO, COMT to form MHPG), dopamine (MAO, COMT to form HVA), and serotonin (MAO to form 5-HIAA) are metabolized by the body and le ...
... dopamine, and serotonin are all pumped back into the presynaptic cell against a concentration gradient b. metabolism: acetylcholine (acetylcholinesterase), norepinephrine (MAO, COMT to form MHPG), dopamine (MAO, COMT to form HVA), and serotonin (MAO to form 5-HIAA) are metabolized by the body and le ...
Acetylcholine
... Stress tends to deplete our store of adrenalin, while exercise tends to increase it. Amphetamines ("speed") work by causing the release of norepinephrine, as well as other neurotransmitters called dopamine and seratonin.. ...
... Stress tends to deplete our store of adrenalin, while exercise tends to increase it. Amphetamines ("speed") work by causing the release of norepinephrine, as well as other neurotransmitters called dopamine and seratonin.. ...
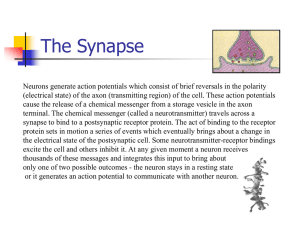
The Synapse
... thousands of these messages and integrates this input to bring about only one of two possible outcomes - the neuron stays in a resting state or it generates an action potential to communicate with another neuron. ...
... thousands of these messages and integrates this input to bring about only one of two possible outcomes - the neuron stays in a resting state or it generates an action potential to communicate with another neuron. ...
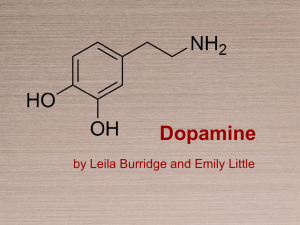
Dopamine 2013
... ● Found in the regions of the brain that regulate movement, emotion, motivation and the feeling of ...
... ● Found in the regions of the brain that regulate movement, emotion, motivation and the feeling of ...
Binding
... hepatocytes rupture and release thousands of merozoites each of which can invade an erythrocyte, thus initiating the asexual erythrocytic stage of the parasite’s life cycle. ...
... hepatocytes rupture and release thousands of merozoites each of which can invade an erythrocyte, thus initiating the asexual erythrocytic stage of the parasite’s life cycle. ...
Drug Addiction - Perelman School of Medicine at the
... junctions through which cells of the nervous system signal to one another and to nonneuronal cells such as muscles ...
... junctions through which cells of the nervous system signal to one another and to nonneuronal cells such as muscles ...
Neurotransmitters & Synapses - IB
... • Block re-uptake proteins (e.g. cocaine) • Mimic or block NTs, binding to the receptors ...
... • Block re-uptake proteins (e.g. cocaine) • Mimic or block NTs, binding to the receptors ...
Neurotransmitter - Pamoja Education Blogs
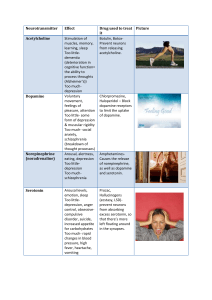
... process throughts (Alzheimer’s)) Too muchdepression Voluntary movement, feelings of pleasure, attention Too little- some form of depression & muscular rigidity Too much- social anxiety, schizophrenia (breakdown of thought processes) Arousal, alertness, eating, depression Too littledepression Too muc ...
... process throughts (Alzheimer’s)) Too muchdepression Voluntary movement, feelings of pleasure, attention Too little- some form of depression & muscular rigidity Too much- social anxiety, schizophrenia (breakdown of thought processes) Arousal, alertness, eating, depression Too littledepression Too muc ...
Biochemistry of neurotransmitters
... Glutamate is released (1) and acts on NMDA receptors located on the postsynaptic neuron (2) Ca2+ enters the postsynaptic neuron and binds with calmodulin activating NOS (3) resulting in formation of NO and citrulline from L-arginine (4). ...
... Glutamate is released (1) and acts on NMDA receptors located on the postsynaptic neuron (2) Ca2+ enters the postsynaptic neuron and binds with calmodulin activating NOS (3) resulting in formation of NO and citrulline from L-arginine (4). ...
Poster
... and the blue hydrophobic. When αsynuclein takes its helical form, it causes the hydrophobic amino acids to line up on one side of the molecule. This allows it to bind to the membranes. ...
... and the blue hydrophobic. When αsynuclein takes its helical form, it causes the hydrophobic amino acids to line up on one side of the molecule. This allows it to bind to the membranes. ...
Word
... pharmacokinetics and pharmacological effects of drugs. It is one of the most important areas of investigation in drug pharmacokinetics research. Drug binding to plasma proteins was first considered to be a nonspecific physical phenomenon, similar to the adsorption of small molecules to charcoal. Acc ...
... pharmacokinetics and pharmacological effects of drugs. It is one of the most important areas of investigation in drug pharmacokinetics research. Drug binding to plasma proteins was first considered to be a nonspecific physical phenomenon, similar to the adsorption of small molecules to charcoal. Acc ...
glutamate - Dental Decks
... on the postsynaptic membrane of the dendrite accept only certain neurotransmitters. In the brain, 30 different neurotransmitters have been classified as amino acids, amines, and neuropeptides. • Amino acid neurotransmitters: - Glutamate, GABA, and glycine. Glutamate is an excitatory neurotransmitter ...
... on the postsynaptic membrane of the dendrite accept only certain neurotransmitters. In the brain, 30 different neurotransmitters have been classified as amino acids, amines, and neuropeptides. • Amino acid neurotransmitters: - Glutamate, GABA, and glycine. Glutamate is an excitatory neurotransmitter ...
Lecture
... Model of kinesin-based vesicle transport • Kinesins bind via their motor domain to microtubules while the tail (cargo) domain is connected to the vesicle • The vesicle connection is mediated by kinesin receptor proteins (linker proteins) ...
... Model of kinesin-based vesicle transport • Kinesins bind via their motor domain to microtubules while the tail (cargo) domain is connected to the vesicle • The vesicle connection is mediated by kinesin receptor proteins (linker proteins) ...
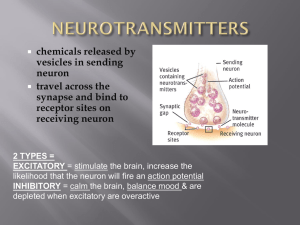
5-2_NeurotransmRelease_BenseM
... 6. By diffusion, neurotransmitters are able to cross the synaptic cleft and attach to the receptors located at the surface of the pos-synaptic membrane of the target cell Quantal neurotransmitter release: 1. Neurotransmitters are synthesized in the axon terminal and are stored in vesicles 2. These n ...
... 6. By diffusion, neurotransmitters are able to cross the synaptic cleft and attach to the receptors located at the surface of the pos-synaptic membrane of the target cell Quantal neurotransmitter release: 1. Neurotransmitters are synthesized in the axon terminal and are stored in vesicles 2. These n ...
Curriculum Vitae
... Mooslehner-Allen K, Pask D, Diekmann H, Fleming A, Goldsmith P, Rubinsztein D, Roach A (2008) An Alzheimer’s disease model of rod cell loss in zebrafish. Manuscript in preparation. Yap D, Walker D, McKinney S, Turashvili G, Mooslehner-Allen K, Ruiz de Algara T, Prentice L , Fee J, d’Anglemont de Tas ...
... Mooslehner-Allen K, Pask D, Diekmann H, Fleming A, Goldsmith P, Rubinsztein D, Roach A (2008) An Alzheimer’s disease model of rod cell loss in zebrafish. Manuscript in preparation. Yap D, Walker D, McKinney S, Turashvili G, Mooslehner-Allen K, Ruiz de Algara T, Prentice L , Fee J, d’Anglemont de Tas ...
Presynaptic Questions
... Neurons can contain more than on NT; they frequently contain a peptide and one of the other types of NTs What ion is critical in vesicular release of NT? How might the role of this ion explain the proposed mechanism of the Lambert-Eaton Syndrome? Vesicular release of NTs is a Ca-dependent process o ...
... Neurons can contain more than on NT; they frequently contain a peptide and one of the other types of NTs What ion is critical in vesicular release of NT? How might the role of this ion explain the proposed mechanism of the Lambert-Eaton Syndrome? Vesicular release of NTs is a Ca-dependent process o ...
EASTERN MICHIGAN UNIVERSITY Chemistry Department Seminar Wednesday December 3, 2014 2:00 p.m.
... Neurotransmitter Sodium Symporter Family Neurotransmitter sodium symporters (NSS) including human dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine transporters harness sodium and chloride gradients to facilitate reuptake of neurotransmitters from the synapse into presynaptic neurons. This function is vital f ...
... Neurotransmitter Sodium Symporter Family Neurotransmitter sodium symporters (NSS) including human dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine transporters harness sodium and chloride gradients to facilitate reuptake of neurotransmitters from the synapse into presynaptic neurons. This function is vital f ...
In the brain, most excitatory communication in synapses occurs by
... In the brain, most excitatory communication in synapses occurs by way of glutamate and most inhibitory communication occurs by way of gamma-aminobutyric acid. In general terms, describe what the other neurotransmitters do. ...
... In the brain, most excitatory communication in synapses occurs by way of glutamate and most inhibitory communication occurs by way of gamma-aminobutyric acid. In general terms, describe what the other neurotransmitters do. ...
Chapter 2 - Biological Basis of Behavior
... schizophrenia Stimulants (ex: cocaine, meds for ADD/ADHD, caffeine) cause dopamine to be pushed into the synapse so that focus is improved BUT cause a depletion over time Acetylcholine triggers muscle contraction important role in arousal and attention Loss = linked to Alzheimer’s Disease ...
... schizophrenia Stimulants (ex: cocaine, meds for ADD/ADHD, caffeine) cause dopamine to be pushed into the synapse so that focus is improved BUT cause a depletion over time Acetylcholine triggers muscle contraction important role in arousal and attention Loss = linked to Alzheimer’s Disease ...
Drugs Change the way Neurons communicate
... 2. Meth passes directly through the neuronal cell membrane and is carried into the axon terminals where it enters the vesicles that contain dopamine. This triggers the vesicles to be released, even without an action potential. Combined, this causes a surge of dopamine to be present in the synaptic ...
... 2. Meth passes directly through the neuronal cell membrane and is carried into the axon terminals where it enters the vesicles that contain dopamine. This triggers the vesicles to be released, even without an action potential. Combined, this causes a surge of dopamine to be present in the synaptic ...
Neurotransmitter receptors and reuptake
... There are two families of transporters: o One co-transports noradrenaline, dopamine, GABA, glycine etc- co-transport with Na+ and Clo ...
... There are two families of transporters: o One co-transports noradrenaline, dopamine, GABA, glycine etc- co-transport with Na+ and Clo ...