chapter32
... nervous system. They have muscular and nervous tissues. 6. Most reproduce sexually, with large non-motile eggs and small flagellated sperms. 7. The diploid zygote produced by fertilization divides by mitotic divisions, resulting in a ball of cells that usually hollows out to become a blastula. Spong ...
... nervous system. They have muscular and nervous tissues. 6. Most reproduce sexually, with large non-motile eggs and small flagellated sperms. 7. The diploid zygote produced by fertilization divides by mitotic divisions, resulting in a ball of cells that usually hollows out to become a blastula. Spong ...
I. Concept 32.1: What is an Animal?
... -Characterized by a body form with a central longitudinal plane dividing the body into two equal but opposite halves -A dorsal (top) and ventral (bottom) sides -Anterior (head) and posterior (tail) ends -Left and right sides -Exhibit cephalization (concentration of nerves and sense organs on anterio ...
... -Characterized by a body form with a central longitudinal plane dividing the body into two equal but opposite halves -A dorsal (top) and ventral (bottom) sides -Anterior (head) and posterior (tail) ends -Left and right sides -Exhibit cephalization (concentration of nerves and sense organs on anterio ...
Fertilization and Development
... Where do stem cells come from? • Stem cells are the body’s master cells, they are undifferentiated and can become any cell in your body. • Early stem cells are found in the inner cell mass of the blastocyst. Once the inner cell mass is removed from the blastocyst, the stem cells are placed in a cu ...
... Where do stem cells come from? • Stem cells are the body’s master cells, they are undifferentiated and can become any cell in your body. • Early stem cells are found in the inner cell mass of the blastocyst. Once the inner cell mass is removed from the blastocyst, the stem cells are placed in a cu ...
Development
... Most plants transfer male gametes as pollen. Pollen can be carried by wind or other organisms. ...
... Most plants transfer male gametes as pollen. Pollen can be carried by wind or other organisms. ...
Diencephalon - Study Windsor
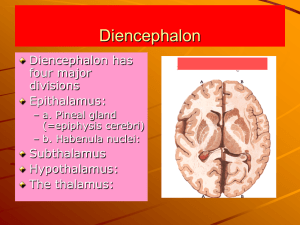
... Diencephalon Diencephalon has four major divisions Epithalamus: – a. Pineal gland (=epiphysis cerebri) – b. Habenula nuclei: ...
... Diencephalon Diencephalon has four major divisions Epithalamus: – a. Pineal gland (=epiphysis cerebri) – b. Habenula nuclei: ...
1 Sample Reading Comprehension Test Time Limit: 15
... head region, and a similar one called proctodeum at the posterior end. In later embryonic life these break through to join the endoderm of the digestive tract, the stomodeum becoming the mouth cavity and the proctodeum becoming the anal canal, both lined by ectoderm. During larval life a ventral out ...
... head region, and a similar one called proctodeum at the posterior end. In later embryonic life these break through to join the endoderm of the digestive tract, the stomodeum becoming the mouth cavity and the proctodeum becoming the anal canal, both lined by ectoderm. During larval life a ventral out ...
The Language of Anatomy - Doral Academy High School
... Stand erect, feet parallel, eyes forward ...
... Stand erect, feet parallel, eyes forward ...
phases of embryonic development 4
... • The head fold also affects the arrangement of the embryonic coelom (primordium of body cavities). • Before folding, the coelom consists of a flattened, horseshoeshaped cavity. • After folding, the pericardial coelom lies ventral to the heart and cranial to the septum transversum. ...
... • The head fold also affects the arrangement of the embryonic coelom (primordium of body cavities). • Before folding, the coelom consists of a flattened, horseshoeshaped cavity. • After folding, the pericardial coelom lies ventral to the heart and cranial to the septum transversum. ...
Gastrulation
... epiblast forms all three germ layers (plus extraembryonic membrane) hypoblast forms extraembryonic endoderm does not form any embryonic endoderm or mesoderm forms primordial germ cells Figure 5.16 ...
... epiblast forms all three germ layers (plus extraembryonic membrane) hypoblast forms extraembryonic endoderm does not form any embryonic endoderm or mesoderm forms primordial germ cells Figure 5.16 ...
Section 15.2 Reproductive Control
... During the first week of its development, an embryo’s cells are identical to each other. However, during the second week the cells begin to differentiate or specialize. ...
... During the first week of its development, an embryo’s cells are identical to each other. However, during the second week the cells begin to differentiate or specialize. ...
Animal cells lack cell walls
... Embryonic development Consist of 3 basic stages: 1. Cleavage-After fertilization the zygote undergoes cleavage, a succession mitotic cell divisions, leading to the formation of a multicellular, hollow ball of cells called the blastula 2. Gastrulation 3. Organogenesis ...
... Embryonic development Consist of 3 basic stages: 1. Cleavage-After fertilization the zygote undergoes cleavage, a succession mitotic cell divisions, leading to the formation of a multicellular, hollow ball of cells called the blastula 2. Gastrulation 3. Organogenesis ...
PPT 1 MB embryology skeletal system
... extremity in smaller bones, such as the phalanges; it is found only at one extremity and in irregular bones such as the vertebrae one or more primary centers of ossification. ...
... extremity in smaller bones, such as the phalanges; it is found only at one extremity and in irregular bones such as the vertebrae one or more primary centers of ossification. ...
Intro to Animals
... Eggs released to water, eggs held internally, development internal or external, typically direct development ...
... Eggs released to water, eggs held internally, development internal or external, typically direct development ...
S1 NRB
... and is oriented medially in the transverse plane as it comes back toward the spinal canal (almost perpendicular to the posterior S1 neuroforamen). ...
... and is oriented medially in the transverse plane as it comes back toward the spinal canal (almost perpendicular to the posterior S1 neuroforamen). ...
Chapter 28 - apsubiology.org
... The Primary Germ Layers form populations of stem cells from which all body tissues and organs are derived Ectoderm – forms structures of the nervous system and skin epidermis ...
... The Primary Germ Layers form populations of stem cells from which all body tissues and organs are derived Ectoderm – forms structures of the nervous system and skin epidermis ...
honors biology ch. 18 notes “the evolution of invertebrate diversity”
... *obtain nutrients by ingestion (*includes some exceptions) lack cell walls collagen extracellular structural protein unique to animals *muscle for movement nerves Describe the general animal life cycle and the basic animal body plan. 1. Male and female adult animals make haploid gametes by meiosis 2 ...
... *obtain nutrients by ingestion (*includes some exceptions) lack cell walls collagen extracellular structural protein unique to animals *muscle for movement nerves Describe the general animal life cycle and the basic animal body plan. 1. Male and female adult animals make haploid gametes by meiosis 2 ...
Document
... expression on the left side. These genes upregulate PITX2, a transcription factor responsible for left sidedness. Epiblast cells moving through the node and streak are predetermined by their position to become specific types of mesoderm and endoderm. Thus, it is possible to construct a fate map of t ...
... expression on the left side. These genes upregulate PITX2, a transcription factor responsible for left sidedness. Epiblast cells moving through the node and streak are predetermined by their position to become specific types of mesoderm and endoderm. Thus, it is possible to construct a fate map of t ...
Animal Evolution and Diversity - Mrs. Loyd`s Biology
... *obtain nutrients by ingestion (*includes some exceptions) ✍ lack cell walls ✍ collagen extracellular structural protein unique to animals ✍ *muscle for movement ✍ nerves ...
... *obtain nutrients by ingestion (*includes some exceptions) ✍ lack cell walls ✍ collagen extracellular structural protein unique to animals ✍ *muscle for movement ✍ nerves ...
Animals - WordPress.com
... a. Usually sexual with diploid stage dominating life cycle b. Meiosis produces haploid sperm and egg c. Fertilization small flagellated sperm fertilizes larger, nonmotlile egg zygote (n) 2. Devlpemt: early/late a. Early embryonic development: i. Cleavage: zygote undergo series of mitotic divisions ...
... a. Usually sexual with diploid stage dominating life cycle b. Meiosis produces haploid sperm and egg c. Fertilization small flagellated sperm fertilizes larger, nonmotlile egg zygote (n) 2. Devlpemt: early/late a. Early embryonic development: i. Cleavage: zygote undergo series of mitotic divisions ...
anatomical terminology
... 2. posterior (caudal) = toward the tail or rear, behind 3. dorsal (superior) = toward the backbone 4. ventral (inferior) = toward the stomach, opposite of dorsal 5. lateral = toward the side, away from the midline of the body 6. medial = the midline of the body extending from anterior to posterior, ...
... 2. posterior (caudal) = toward the tail or rear, behind 3. dorsal (superior) = toward the backbone 4. ventral (inferior) = toward the stomach, opposite of dorsal 5. lateral = toward the side, away from the midline of the body 6. medial = the midline of the body extending from anterior to posterior, ...
The Animal Kingdom
... Benefits of Cephalization • The anterior end of the animal became most likely to first encounter food, predators, and other important features of the external environment. • Flatworms (platyhelminthes) are the most primitive organisms to show cephalization ...
... Benefits of Cephalization • The anterior end of the animal became most likely to first encounter food, predators, and other important features of the external environment. • Flatworms (platyhelminthes) are the most primitive organisms to show cephalization ...
Chordata - De Anza College
... blastulation in many vertebrates • Large, yolk-rich eggs • Cleavage forms the blastoderm. • Separation of the epiblast from the hypoblast forms the blastocoel. ...
... blastulation in many vertebrates • Large, yolk-rich eggs • Cleavage forms the blastoderm. • Separation of the epiblast from the hypoblast forms the blastocoel. ...
Anatomical dissection vocab File
... ANATOMICAL DISSECTION TERMS The body can be broken into planes i.e. top and bottom, left and right, middle and outside, front and back etc. These words can be used to help determine the placement of body parts. ...
... ANATOMICAL DISSECTION TERMS The body can be broken into planes i.e. top and bottom, left and right, middle and outside, front and back etc. These words can be used to help determine the placement of body parts. ...
B 406 C V A
... explain how human conjoined twins form. At which developmental stage does the process that forms conjoined twins begin? (6%) Conjoined twins can form when two primitive streaks (regions of gastrulation) occur somewhat closely together in the same human embryo. They occur on the same blastodisc (flat ...
... explain how human conjoined twins form. At which developmental stage does the process that forms conjoined twins begin? (6%) Conjoined twins can form when two primitive streaks (regions of gastrulation) occur somewhat closely together in the same human embryo. They occur on the same blastodisc (flat ...
Drosophila embryogenesis

Drosophila embryogenesis, the process by which Drosophila (fruit fly) embryos form, is a favorite model system for geneticists and developmental biologists studying embryogenesis. The small size, short generation time, and large brood size make it ideal for genetic studies. Transparent embryos facilitate developmental studies. Drosophila melanogaster was introduced into the field of genetic experiments by Thomas Hunt Morgan in 1909.