* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chordata - De Anza College
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
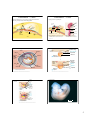
Chordata Phylum Chordata • Embryonic development: – Triploblastic Phylum Chordata — subphylum Protochordata • Special features: – No cephalization – Bilateral symmetry – Eucoelomate – pharyngeal arches and slits → ciliated atrium • Filter feeding & gas exchange – Deuterostome • Special features: – Notochord – Dorsal hollow nerve tube – Post-anal tail – Segmentation → – Open circulatory system – Metanephridia-type excretory system (misidentified as protonephridia in most texts) and/or secretion into atrium • Classes: • mesodermal blocs • pharyngeal arches and slits – Urochordata – Larvacea – Cephalochordata Pelagic colonial salp Solitary sea squirt Urochordates – tunicates (sea squirts) Wild convergence! • Vertebrate like early development • Mollusk-like bauplan • Plant-like tunic • Sponge-like or gelatinous final morphology Colonial tunicate Larvaceans Cephalochordates - lancelets • External suspension feeding • Mucus “house” • Reduced pharynx Heyer 1 Chordata Phylum Chordata — subphylum Vertebrata (Craniata) • Special features: Axial skeleton of a bony fish Axial skeleton: Cranium & vertebral column – Prolonged embryonic development – Strong cephalization • Brain in cranium – mesodermal blocs → • Myomeres & vertebrae – Closed circulatory system Vertebra • Agnathans — jawless vertebrates • Gnathostomes — jawed vertebrates • Fishes — axial skeleton only • Tetrapods — axial + appendicular skelton Axial & appendicular skeleton of a bipedal tetrapod key Axial skeleton Appendicular skeleton Cranium Figure 3.02 Phylum Chordata — subphylum Vertebrata (Craniata) • Classes: Pectoral girdle – Agnatha — jawless fishes Vertebra – Chondrichthyes — cartilaginous fishes Pelvic girdle – Osteichthyes — bony fishes – Amphibia – Reptilia – Aves — birds – Mammalia Figure 49.26 Heyer 2 clades Chordate Systematics ⇐TET classes Both systems have valid uses Fertilization of a mammalian egg Vertebrate Development Follicle cell Sperm Cortical basal ganules body Sperm nucleus Zona pellucida Egg plasma membrane Acrosomal vesicle From EGG CYTOPLASM M.K. Richardson (1997) Anatomy & Embryology Radial Cleavage & Blastulation — Frog Point of sperm entry 47-8: Frog body polarity — established during oogenesis & fertilization • Large yolk content necessitates asymmetrical blastulation Animal hemisphere Vegetal hemisphere Vegetal pole Point of sperm entry Future dorsal side of tadpole Anterior Gray crescent Right Ventral Animal pole First cleavage Dorsal Left Posterior Body axes Establishing the axes CROSS SECTION SURFACE VIEW 47-9: Frog body polarity — Animal pole Zygote 47-12: frog gastrulation Cleavage planes Blastocoel 0.25 mm 2-cell stage forming Vegetal pole 4-cell stage forming Dorsal lip of blastopore Dorsal tip of blastopore Blastula Blastocoel shrinking Archenteron Eight-cell stage (viewed from the animal pole) 8-cell stage 0.25 mm Ectoderm Animal pole Blastula (cross section) Blastocoel Mesoderm Endoderm Blastocoel remnant Key Vegetal pole Blastula (at least 128 cells) Future ectoderm Future mesoderm Future endoderm Yolk plug Yolk plug Gastrula 3 Neurulation Neural fold — unique to chordates 47-23a: frog fate map Neural plate Epidermis Neural folds Central nervous system Epidermis Notochord Neural crest LM 1 mm Neural fold Mesoderm Neural plate Outer layer of ectoderm Endoderm Neural crest Notochord Ectoderm Mesoderm Formation of the neural tube Fate map of a frog embryo Archenteron 47-14: frog Neural tube stage (transverse section) Blastula Neural tube Endoderm Neural plate formation neurulation Somites Eye Fish Development Tail bud chordate segmentation Mesoderm lateral to the notochord forms blocks called somites Lateral to the somites, the mesoderm splits to form the coelom SEM Neural tube Notochord 1 mm Neural crest Coelom Somite Archenteron (digestive cavity) Somites 47-14c: frog segmentation Source: http://www.ucalgary.ca/UofC/eduweb/virtualembryo/why_fish.html Another way — asymmetric blastulation in many vertebrates • Large, yolk-rich eggs • Cleavage forms the blastoderm. • Separation of the epiblast from the hypoblast forms the blastocoel. Fertilized egg Fertilized egg Disk of cytoplasm Zygote 47-10: Chick cleavage Figure 47.10 Disk of cytoplasm Four-cell stage 1 Zygote. Most of the cell’s volume is yolk, with a small disk of cytoplasm located at the animal pole. 2 Four-cell stage. Blastoderm Cutaway view of the blastoderm 3 Blastoderm. The many cleavage divisions produce the blastoderm, a mass of cells that rests on top of the yolk mass. BLASTODERM YOLK MASS Epiblast Blastocoel Hypoblast Cutaway view of the blastoderm. The cells of the blastoderm are arranged in two layers, the epiblast and hypoblast, that enclose a fluidfilled cavity, the blastocoel. Blastocoel BLASTODERM YOLK MASS Epiblast Hypoblast 4 Gastrulation — Chick Gastrulation — Chick • Instead of blastopore, groove (primitive streak) forms in blastoderm. • All three germ layers form from infolding epiblast. epiblast. • Organogenesis from germ layers. Eye Epiblast Forebrain Neural tube Notochord Somite Heart Coelom Future ectoderm Archenteron Primitive streak Endoderm Mesoderm Lateral fold Blood vessels Ectoderm Yolk stalk Migrating cells (mesoderm) Form extraembryonic membranes Endoderm Hypoblast Somites Yolk sac YOLK (a) Early organogenesis. The archenteron forms when lateral folds pinch the embryo away from the yolk. YOLK Figure 47.13 Neural tube (b) Late organogenesis. 56 hours old chick embryo, about 2–3 mm long (LM). Figure 47.15 chick extra-embryonic membranes (amniote) Amnion Endometrium (uterine lining) Allantois 47-18a: mammalian blastulation Inner cell mass Trophoblast Embryo Blastocoel Amniotic cavity with amniotic fluid Albumen Blastocyst reaches uterus. Maternal blood vessel Shell Yolk (nutrients) Chorion Yolk sac 47-17: chick extra-embryonic membranes Expanding region of trophoblast 47-18b : mammalian gastrulation Expanding region of trophoblast Epiblast Hypoblast Trophoblast Blastocyst implants. 6-week human embryo Amniotic cavity Amnion Epiblast Hypoblast Chorion (from trophoblast Yolk sac (from hypoblast) Extraembryonic membranes start to form and gastrulation begins. Extraembryonic mesoderm cells (from epiblast) Allantois Amnion Chorion Ectoderm Mesoderm Endoderm Yolk sac Extraembryonic mesoderm Gastrulation has produced a three-layered embryo with four extraembryonic membranes. 1 mm 5