lecture1
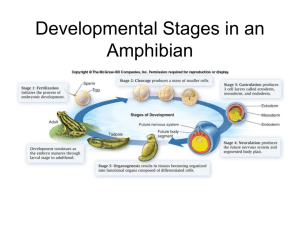
... CLEAVAGE- The partition of the egg cell into several cells is known as cleavage. It is a period of rapid, synchronized cell division as hundreds and sometimes thousand of cells are produced within a matter of hours. The cell becomes smaller with each cleavage. There are different types of cleavage p ...
... CLEAVAGE- The partition of the egg cell into several cells is known as cleavage. It is a period of rapid, synchronized cell division as hundreds and sometimes thousand of cells are produced within a matter of hours. The cell becomes smaller with each cleavage. There are different types of cleavage p ...
Paraaxial mesoderm
... rules. Formation of new pairs of somites and their number are under the control of molecular clock. Their nature is the periodic expression of specific genes (FGF and Wnt). FGF and Wnt stimulate proliferation of mesenchymal cells. Other signal molecules - Notch (it prevents differentiation of neighb ...
... rules. Formation of new pairs of somites and their number are under the control of molecular clock. Their nature is the periodic expression of specific genes (FGF and Wnt). FGF and Wnt stimulate proliferation of mesenchymal cells. Other signal molecules - Notch (it prevents differentiation of neighb ...
Embryonic Development of Animals
... Lots of ribosomes, mitochondria and tubulin, usually pigment ...
... Lots of ribosomes, mitochondria and tubulin, usually pigment ...
PDF
... Mediator, a complex that allows transcription factors to activate RNA polymerase II. The researchers suggest, therefore, that GCT/MED13 and CCT/MED12 regulate pattern formation during Arabidopsis embryogenesis by transiently repressing the transcription of genes that would otherwise interfere with r ...
... Mediator, a complex that allows transcription factors to activate RNA polymerase II. The researchers suggest, therefore, that GCT/MED13 and CCT/MED12 regulate pattern formation during Arabidopsis embryogenesis by transiently repressing the transcription of genes that would otherwise interfere with r ...
Questions, chapter 18
... Asymmetric mRNA distribution takes place in conjunction with cell division. In this case, a regulatory mRNA is unevenly distributed within a cell along the same axis as that used for division. In this way, the two daughter cells produced when the cell divides inherit different amounts of the mRNA, a ...
... Asymmetric mRNA distribution takes place in conjunction with cell division. In this case, a regulatory mRNA is unevenly distributed within a cell along the same axis as that used for division. In this way, the two daughter cells produced when the cell divides inherit different amounts of the mRNA, a ...
Apical Ectodermal Ridge (AER)
... of a limb bud is attached to the body; required for proper pattern formation along the anterior-posterior axis of the limb. • Positoinal Infortmation-Molecular cues that control pattern formation in an animal or plant embryonic structure by indicating a cell’s location relative to the organism’s bod ...
... of a limb bud is attached to the body; required for proper pattern formation along the anterior-posterior axis of the limb. • Positoinal Infortmation-Molecular cues that control pattern formation in an animal or plant embryonic structure by indicating a cell’s location relative to the organism’s bod ...
Premedical XXI
... Different types of cells have the same genetic information, create different proteins as result of regulatin of transcription. ...
... Different types of cells have the same genetic information, create different proteins as result of regulatin of transcription. ...
bicoid target genes
... Peer group pressure: The story of the epidermal versus neural decision in the fruit fly ...
... Peer group pressure: The story of the epidermal versus neural decision in the fruit fly ...
Development of the embryo - Hyndland Secondary School
... of their female offspring exposed to DES in utero are characterized by anatomic abnormalities. Here we show that DES administered to mice in utero produces changes in the expression pattern of several Hox genes that are involved in patterning of the reproductive tract. DES produces posterior shifts ...
... of their female offspring exposed to DES in utero are characterized by anatomic abnormalities. Here we show that DES administered to mice in utero produces changes in the expression pattern of several Hox genes that are involved in patterning of the reproductive tract. DES produces posterior shifts ...
Chapter 19 Notes
... establishes anterior end of embryo if injected into posterior end of normal embryos, head and thorax will develop at that end • Within three hours after fertilization, orchestrated ________________ gene activity produces fly ____________________. – Gene activation depends on free diffusion of __ ...
... establishes anterior end of embryo if injected into posterior end of normal embryos, head and thorax will develop at that end • Within three hours after fertilization, orchestrated ________________ gene activity produces fly ____________________. – Gene activation depends on free diffusion of __ ...
Concept Check Questions with answers
... During animal development, movement of cells and tissues is a major mechanism, which is not the case in plants. In plants, growth and morphogenesis continue throughout the life of the plant. This is true only of a few types of ...
... During animal development, movement of cells and tissues is a major mechanism, which is not the case in plants. In plants, growth and morphogenesis continue throughout the life of the plant. This is true only of a few types of ...
chapter16
... Polytenes form when the DNA replicate many times without mitosis or cytokinesis. It may consist of 1000 or more DNA double helices with its associated histones. Bands are formed when the region associated with an active gene uncoils and forms a “puff”, the region of active RNA synthesis. The life c ...
... Polytenes form when the DNA replicate many times without mitosis or cytokinesis. It may consist of 1000 or more DNA double helices with its associated histones. Bands are formed when the region associated with an active gene uncoils and forms a “puff”, the region of active RNA synthesis. The life c ...
Premedical XXI
... chemical signals. Signals (molecules) have target cells (with receptors) and cell-cell surface interactions results in a change of transcription /regulation of gene expression. Target cell has an ability to respond to signals ...
... chemical signals. Signals (molecules) have target cells (with receptors) and cell-cell surface interactions results in a change of transcription /regulation of gene expression. Target cell has an ability to respond to signals ...
Lecture 24
... Female flies possessing mutations in maternal effect genes appear phenotypically normal, but produce offspring with mutant phenotypes ...
... Female flies possessing mutations in maternal effect genes appear phenotypically normal, but produce offspring with mutant phenotypes ...
An Overview of Insect Hormones
... Egg Membranes Chorion卵殼: synthesized within the ovariole by the follicular epithelium – Vitelline envelope卵黃膜: an inner noncellular membrane with a thickness of about 0.3 mm – Wax layer腊層: 5 nm to 2 mm; to provide ...
... Egg Membranes Chorion卵殼: synthesized within the ovariole by the follicular epithelium – Vitelline envelope卵黃膜: an inner noncellular membrane with a thickness of about 0.3 mm – Wax layer腊層: 5 nm to 2 mm; to provide ...
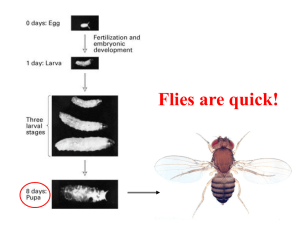
Drosophila embryogenesis

Drosophila embryogenesis, the process by which Drosophila (fruit fly) embryos form, is a favorite model system for geneticists and developmental biologists studying embryogenesis. The small size, short generation time, and large brood size make it ideal for genetic studies. Transparent embryos facilitate developmental studies. Drosophila melanogaster was introduced into the field of genetic experiments by Thomas Hunt Morgan in 1909.