* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download bicoid target genes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
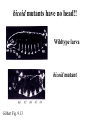
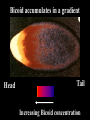
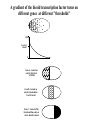
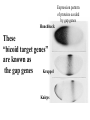
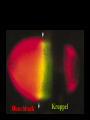
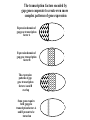
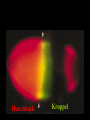
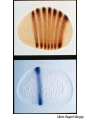
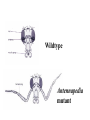
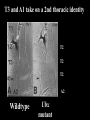
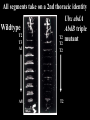
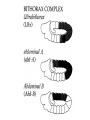
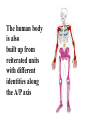
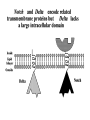
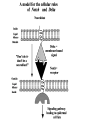
I can’t wait to grow up! Laugh now The fruit fly body plan is self-assembled in 24 hours How is the body plan specified? Egg ---> animal in 24 hours! Eric Wieschaus and Christiane Nüsslein-Volhard used genetics to identify proteins that set up the embryonic body plan The molecular genetics of pattern formation in candy corn Anterior Posterior The wild-type pattern We collected a series of mutants affecting the body plan Wild-type Posterior group Anterior group Morphogenesis defects Gap gene The wild-type body is segmented and each segment has a unique identity and thus produces distinctive structures Wieschaus and Nüsslein-Volhard removed single genes and looked for effects on the body plan bicoid mutants have no head!! Wildtype larva bicoid mutant Gilbert Fig. 9.13 Remember that cleavage starts without cell division in Drosophila Nurse cells synthesize macromolecules and pump them into the oocyte through the cytoplasmic bridges oocyte Molecules synthesized by the nurse cells and specifically localized in the oocyte determine the anterior/posterior axis of the embryo Oocyte Anterior determinant = bicoid mRNA Posterior determinant = nanos mRNA bicoid protein becomes distributed in a graded fashion 100 Level of bicoid 0 Bicoid accumulates in a gradient Head Tail Increasing Bicoid concentration gradient of the bicoid transcription factor turns on A gradientAof the bicoid transcription factor turns on different genes different genes at "thresholds" different "thresholds" at different 100 Level of bicoid 0 Gene A- turned on only by high level of bicoid Gene B- turned on only by intermediate level of bicoid Gene C- turned off by bicoid and thus only on where bicoid is absent Hunchback These “bicoid target genes” are known as the gap genes Kruppel Knirps Expression pattern of proteins ecoded by gap genes Hunchback Kruppel Gap gene mutants are missing different regions of the body Wildtype Krüppel hunchback knirps The transcription factors encoded by gap genes cooperate to create even more complex patterns of gene expression Expression domain of gap gene transcription factor A Expression domain of gap gene transcription factor B The expression patterns of gap gene transcription factors A and B overlap Some genes require both gap gene transcription factors A and B present to be turned on Hunchback Kruppel Alberts Chapter 8 title page So, in summary so far… Maternal Determinants Zygotic Gap Genes Zygotic Pair-rule Genes Figure 9.8(1) Model of Drosophila Anterior-Posterior Pattern Formation Isn’t life wonderful, beautiful and incredible! Ed Lewis was far ahead of his time who’s Wildtype Antennapedia mutant T3 and A1 take on a 2nd thoracic identity T2 T2 T2 A2 Wildtype Ubx mutant All segments take on a 2nd thoracic identity Wildtype T2 T3 A1 T2 T2 T2 A8 T2 Ubx abdA AbdB triple mutant Is Ubx is expressed at the right time and place to make in T3 different from T2? Yes! Ubx is expressed in T3 and A1 Figure 9.28 Homeotic Gene Expression in Drosophila The homeotic genes encode transcription factors that act as master regulators of segmental identity Ultrabithorax is expressed in the region of the embryo that will become the 3rd thoracic and 1st abdominal segments In these segments, Ultrabithorax protein acts as a transcription factor that turns on genes specific for the 3rd thoracic and 1st abdominal segments ON OFF T1 specific gene A1 specific gene ON A1 specific gene OFF A5 specific gene Ultrabithorax, abdA, and AbdB normally repress expression of the“leg gene” Distalless in the abdominal segments Distalless in wild-type T1 T2 T3 Distalless in triple mutant abdomen Lewis hypothesized that the duplication and diversification of homeotic master regulators underlies the evolution of an increasingly complex body plan The human body is also built up from reiterated units with different identities along the A/P axis Mouse homeotic genes also encode transcription factors that act as master regulators of segmental identity Hox 3.1 is expressed in the region of the embryo that will become the 12th and 13th ribs In these segments, Hox 3.1 protein acts as a transcription factor that turns on genes specific for the 12th and 13th ribs. ON 12th rib specific gene OFF 4th rib specific gene OFF 15th rib specific gene ON 13th rib specific gene As we’ll see later, mammals also have homeotic genes expressed at different places along the A/P axis Peer group pressure: The story of the epidermal versus neural decision in the fruit fly They started as one big happy ectodermal epithelium I feel a need to be a neuroblast Then one of their number got some big ideas and started to migrate inside You guys stay here and keep up the good work As it left, it sent a message to its neighbors, telling them to stick with the epidermal fate The failure of peer group pressure: Neurogenic mutants in the fruit fly Some cells become neuroblasts and signal their neighbors to remain epidermis If signal is missing... All cells eventually invaginate and become neuroblasts Nervous system Epidermis Extra nervous system No epidermis Cells lacking signal or lacking receptor behave differently + + + + + + + + + Thanks, I needed that! + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + mutant mutant mutant + What? I can't hear you! + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + mutant mutant mutant If mutant cells lack signal, they can be rescued by wild type neighbors which make signal. If mutant cells lack receptor, they cannot be rescued by wild type neighbors which make signal. Cells lacking signal or lacking receptor behave differently + + + + + + + + + Thanks, I needed that! + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + mutant mutant mutant + What? I can't hear you! + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + mutant mutant mutant If mutant cells lack signal, DELTA mutant cells can be rescued they can be rescued by by wild type neighbors. wild type neighbors which make signal. Therefore, DELTA must be the SIGNAL. If mutantmutant cells NOTCH cells cannot be rescued lack receptor, by wild neighbors. they cannottype be rescued by wild type neighbors Therefore, NOTCH must be the which make signal. Receptor.