Figure 47.0 Human embryo
... • A true body cavity is called a coelom and is derived from mesoderm; these animals are called coelomates Coelom ...
... • A true body cavity is called a coelom and is derived from mesoderm; these animals are called coelomates Coelom ...
1 2 - VCOMcc
... o Chorion = gives rise to chorionic villi that invade the endometrium and promote transfer of nutrients from maternal blood to fetal blood o Yolk sac = functions as circulatory system for first few weeks; observed in prenatal ultrasound; later attaches to the hindgut via vitelline duct External Mo ...
... o Chorion = gives rise to chorionic villi that invade the endometrium and promote transfer of nutrients from maternal blood to fetal blood o Yolk sac = functions as circulatory system for first few weeks; observed in prenatal ultrasound; later attaches to the hindgut via vitelline duct External Mo ...
Biology Chapter 9 Starfish development LAB 2009
... Find this stage under low power (40X), then view it under medium power (100X). Using only the fine focus, look at the embryo carefully, and sketch it here: ...
... Find this stage under low power (40X), then view it under medium power (100X). Using only the fine focus, look at the embryo carefully, and sketch it here: ...
The Role of Differential Gene Expression in Cell Differentiation
... The 13 seemingly identical segments of the Drosophila larva correspond to the specialized adult segments. The process of differentiation begins with establishing the polarity of the embryo. • In Drosophila, unequal distribution of morphogens helps establish the basic coordinates. • The morphogen ...
... The 13 seemingly identical segments of the Drosophila larva correspond to the specialized adult segments. The process of differentiation begins with establishing the polarity of the embryo. • In Drosophila, unequal distribution of morphogens helps establish the basic coordinates. • The morphogen ...
Sexual Reproduction - Mr Schmitt
... Embryonic development is the early development of an organism - in humans, it is the first two months after fertilization Stages ...
... Embryonic development is the early development of an organism - in humans, it is the first two months after fertilization Stages ...
File
... corpus luteum would normally degenerate so, estrogen and progesterone continue to “maintain pregnancy” • high hCG production for 2 months, then it drops off but not completely until birth • Placenta eventually takes over to produce estrog. & progest. ...
... corpus luteum would normally degenerate so, estrogen and progesterone continue to “maintain pregnancy” • high hCG production for 2 months, then it drops off but not completely until birth • Placenta eventually takes over to produce estrog. & progest. ...
Germ cells are the only cells which are transmitted from one
... Germ cells are the only cells which are transmitted from one generation to the next and can be considered immortal. Germ cells produce highly specialized cells, called gametes, which carry the genetic and cytoplasmic information defining a given species and which can initiate the formation of an enti ...
... Germ cells are the only cells which are transmitted from one generation to the next and can be considered immortal. Germ cells produce highly specialized cells, called gametes, which carry the genetic and cytoplasmic information defining a given species and which can initiate the formation of an enti ...
Exporter la page en pdf
... Germ cells are the only cells which are transmitted from one generation to the next and can be considered immortal. Germ cells produce highly specialized cells, called gametes, which carry the genetic and cytoplasmic information defining a given species and which can initiate the formation of an enti ...
... Germ cells are the only cells which are transmitted from one generation to the next and can be considered immortal. Germ cells produce highly specialized cells, called gametes, which carry the genetic and cytoplasmic information defining a given species and which can initiate the formation of an enti ...
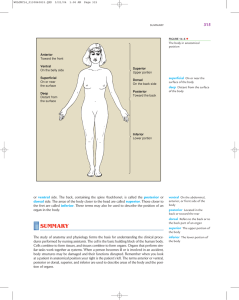
Anterior Toward the front Ventral On the belly side Superficial On or
... The study of anatomy and physiology forms the basis for understanding the clinical procedures performed by nursing assistants. The cell is the basic building block of the human body. Cells combine to form tissues, and tissues combine to form organs. Organs that perform similar tasks work together as ...
... The study of anatomy and physiology forms the basis for understanding the clinical procedures performed by nursing assistants. The cell is the basic building block of the human body. Cells combine to form tissues, and tissues combine to form organs. Organs that perform similar tasks work together as ...
Unit 11 Animal Evolution Chp 32 Intro To Animal
... Which organisms (diagram to the right) illustrate radial symmetry and which illustrated bilateral symmetry? Label the following terms on the crawfish diagram: dorsal, ventral, anterior, posterior Diploblastic vs. Triploblastic “Diplo-“ and “Triploblastic” refer to the number of germ layers the organ ...
... Which organisms (diagram to the right) illustrate radial symmetry and which illustrated bilateral symmetry? Label the following terms on the crawfish diagram: dorsal, ventral, anterior, posterior Diploblastic vs. Triploblastic “Diplo-“ and “Triploblastic” refer to the number of germ layers the organ ...
CHAPTER VII thickness, but is bilateral in form. Each half is somewhat
... the midclle line and to fuse, but the medullary folds llay appear before the fusion has taken place. There is thus pro- ...
... the midclle line and to fuse, but the medullary folds llay appear before the fusion has taken place. There is thus pro- ...
Name: Hour: ______ Date Due: BIOLOGY B Animal Development
... Most animals develop from a single fertilized egg (zygote). How does a zygote develop into the many different kinds of cells that make up the entire animal? This question can be answered by studying the process of embryological development. In this lab, you will observe the various stages of embryol ...
... Most animals develop from a single fertilized egg (zygote). How does a zygote develop into the many different kinds of cells that make up the entire animal? This question can be answered by studying the process of embryological development. In this lab, you will observe the various stages of embryol ...
Name: Hour: ______ Date Due: HONORS BIOLOGY B Animal
... Most animals develop from a single fertilized egg (zygote). How does a zygote develop into the many different kinds of cells that make up the entire animal? This question can be answered by studying the process of embryological development. In this lab, you will observe the various stages of embryol ...
... Most animals develop from a single fertilized egg (zygote). How does a zygote develop into the many different kinds of cells that make up the entire animal? This question can be answered by studying the process of embryological development. In this lab, you will observe the various stages of embryol ...
PPT File
... Through hybridization, sequencing, and comparative genomics, it is known that diverse animals share molecular pathways for gene expression in development. Fruit fly genes have mouse and human orthologs for developmental genes. These genes are arranged on the chromosome in the same order as they are ...
... Through hybridization, sequencing, and comparative genomics, it is known that diverse animals share molecular pathways for gene expression in development. Fruit fly genes have mouse and human orthologs for developmental genes. These genes are arranged on the chromosome in the same order as they are ...
Gene Loss and Organelle Genome Evolution
... large region (cf. LSC) between “red” / “green” lineages: Suggests that transfer between LSC and SSC regions is rare Further evidence for single origin of all plastid genomes ...
... large region (cf. LSC) between “red” / “green” lineages: Suggests that transfer between LSC and SSC regions is rare Further evidence for single origin of all plastid genomes ...
Ch. 32 An Introduction to Animal Diversity
... d. two types of cells only in animals nervous and muscle cells e. most reproduce sexually (diploid stage is dominant) sperm fertilizes egg zygote zygote cleavage blastula (hollow ball of cells) after blastula, get gastrulation (process of making a two cell "cup" shape = ...
... d. two types of cells only in animals nervous and muscle cells e. most reproduce sexually (diploid stage is dominant) sperm fertilizes egg zygote zygote cleavage blastula (hollow ball of cells) after blastula, get gastrulation (process of making a two cell "cup" shape = ...
Ontogeny and Phylogeny - Developmental Biology
... at the embryo as a picture, more or less obscured, of the progenitor, either in its class or larval state, of all the members of the same great class.” ...
... at the embryo as a picture, more or less obscured, of the progenitor, either in its class or larval state, of all the members of the same great class.” ...
Zoology Chapter 8-9: Introduction to Animals Review for Test List the
... 13. Which of the three germ layers in animal embryos gives rise to muscles and much of the circulatory, reproductive, and excretory systems? _____mesoderm___________________________ 14. The lungs develop from which germ layer? ______endoderm_____________________________ 15. A _______blastula________ ...
... 13. Which of the three germ layers in animal embryos gives rise to muscles and much of the circulatory, reproductive, and excretory systems? _____mesoderm___________________________ 14. The lungs develop from which germ layer? ______endoderm_____________________________ 15. A _______blastula________ ...
Zoology Chapter 8-‐9: Introduction to Animals Review for Test
... Which of the three germ layers in animal embryos gives rise to muscles and much of the circulatory, reproductive, and excretory systems? _____mesoderm___________________________ ...
... Which of the three germ layers in animal embryos gives rise to muscles and much of the circulatory, reproductive, and excretory systems? _____mesoderm___________________________ ...
Memories and your Brain
... • There are two basic types of cells in the brain, neurons and glial cells • Neurons do the transmitting • Glia do the support functions • There are many types of neurons and glial cells, but we don’t have to be too concerned about those ...
... • There are two basic types of cells in the brain, neurons and glial cells • Neurons do the transmitting • Glia do the support functions • There are many types of neurons and glial cells, but we don’t have to be too concerned about those ...
Memories and your Brain
... There are two basic types of cells in the brain, neurons and glial cells Neurons do the transmitting Glia do the support functions There are many types of neurons and glial cells, but we don’t have to be too concerned about those ...
... There are two basic types of cells in the brain, neurons and glial cells Neurons do the transmitting Glia do the support functions There are many types of neurons and glial cells, but we don’t have to be too concerned about those ...
Zoo_Unit4_Phylogenetics_Development Tutorial
... blastula into a three-layered (triploblastic) embryo, called a gastrula, that has a ...
... blastula into a three-layered (triploblastic) embryo, called a gastrula, that has a ...
1 * Standard Anatomical Position
... (You will work in groups of 2!) • Stand in Standard Anatomical position • Correct your lab partner’s position • Sketch using stick figures your partner in SAP Label Superior and Inferior • Next sketch a dog in standard anatomical position (also stick figure) Label Dorsal and Ventral • Name two diffe ...
... (You will work in groups of 2!) • Stand in Standard Anatomical position • Correct your lab partner’s position • Sketch using stick figures your partner in SAP Label Superior and Inferior • Next sketch a dog in standard anatomical position (also stick figure) Label Dorsal and Ventral • Name two diffe ...
Chapter 18
... A given gene may have multiple enhancers, each active at a different time or in a different cell type or location in the organism. Each enhancer is associated with only one gene and no other. Activator proteins bind to distal control elements grouped as an enhancer in the DNA. A DNA-bending protein ...
... A given gene may have multiple enhancers, each active at a different time or in a different cell type or location in the organism. Each enhancer is associated with only one gene and no other. Activator proteins bind to distal control elements grouped as an enhancer in the DNA. A DNA-bending protein ...
Drosophila embryogenesis

Drosophila embryogenesis, the process by which Drosophila (fruit fly) embryos form, is a favorite model system for geneticists and developmental biologists studying embryogenesis. The small size, short generation time, and large brood size make it ideal for genetic studies. Transparent embryos facilitate developmental studies. Drosophila melanogaster was introduced into the field of genetic experiments by Thomas Hunt Morgan in 1909.