Radiology of Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses
... Helpful for evaluation of regional and intracranial complications Detection and staging of neoplastic processes Improved display between intraorbital and extraorbital compartments Helpful for diagnosing fungal concretions which show low or no signal on T2 • Helps for evaluation of mucoceles and ceph ...
... Helpful for evaluation of regional and intracranial complications Detection and staging of neoplastic processes Improved display between intraorbital and extraorbital compartments Helpful for diagnosing fungal concretions which show low or no signal on T2 • Helps for evaluation of mucoceles and ceph ...
Radiology of Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses
... Helpful for evaluation of regional and intracranial complications Detection and staging of neoplastic processes Improved display between intraorbital and extraorbital compartments Helpful for diagnosing fungal concretions which show low or no signal on T2 • Helps for evaluation of mucoceles and ceph ...
... Helpful for evaluation of regional and intracranial complications Detection and staging of neoplastic processes Improved display between intraorbital and extraorbital compartments Helpful for diagnosing fungal concretions which show low or no signal on T2 • Helps for evaluation of mucoceles and ceph ...
Human development notes
... Epiblast migrates inward through the primitive streak to form both mesodern and endoderm. Gastrulation Begins with 2-layered embryo. Hypoblast (lower layer) grows down around "yolk" to form yolk sac. Epiblast (upper layer) -- grows up to form amnionic sac. --invaginates through primitive streak to f ...
... Epiblast migrates inward through the primitive streak to form both mesodern and endoderm. Gastrulation Begins with 2-layered embryo. Hypoblast (lower layer) grows down around "yolk" to form yolk sac. Epiblast (upper layer) -- grows up to form amnionic sac. --invaginates through primitive streak to f ...
投影片 1
... undergoes rapid cell division called cleavage • Cleavage leads to formation of a blastula • The blastula undergoes gastrulation, forming a gastrula with different layers of embryonic tissues ...
... undergoes rapid cell division called cleavage • Cleavage leads to formation of a blastula • The blastula undergoes gastrulation, forming a gastrula with different layers of embryonic tissues ...
chapter twenty-one
... A second vertebrate model, the zebra fish Danio rerio, has some unique advantages. These small fish (2–4 cm long) are easy to breed in the laboratory in large numbers. The transparent embryos develop outside the mother’s body. Although generation time is two to four months, the early stages of ...
... A second vertebrate model, the zebra fish Danio rerio, has some unique advantages. These small fish (2–4 cm long) are easy to breed in the laboratory in large numbers. The transparent embryos develop outside the mother’s body. Although generation time is two to four months, the early stages of ...
embryology of the chick
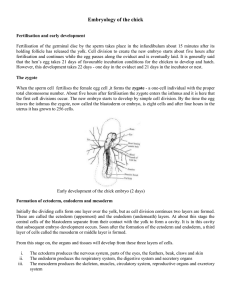
... 1. Yolk sac: This sac envelops the yolk and produces an enzyme that changes the yolk material to a form that can be used as a food source by the developing embryo. Any remaining, unused yolk material in the yolk sac when the chicken hatches from the egg is drawn into the abdomen for use by the chick ...
... 1. Yolk sac: This sac envelops the yolk and produces an enzyme that changes the yolk material to a form that can be used as a food source by the developing embryo. Any remaining, unused yolk material in the yolk sac when the chicken hatches from the egg is drawn into the abdomen for use by the chick ...
Your Inner Fish - 06_Chapter Six
... another at the tail. If we were to cut ourselves in half right about now, we would find a tube within a tube. The outer tube would be our body wall, the inner tube our eventual digestive tract. A space, the future body cavity, separates the two tubes. This tube-within-a-tube structure stays with us ...
... another at the tail. If we were to cut ourselves in half right about now, we would find a tube within a tube. The outer tube would be our body wall, the inner tube our eventual digestive tract. A space, the future body cavity, separates the two tubes. This tube-within-a-tube structure stays with us ...
Pregnancy & Development
... Hundreds of sperm cells must release their acrosomal enzymes before fertilization can occur Acrosomal enzymes cut through the zona pelucida ...
... Hundreds of sperm cells must release their acrosomal enzymes before fertilization can occur Acrosomal enzymes cut through the zona pelucida ...
Biology Chapter 43-2 Human Development
... Biology Chapter 43-2 Human Development VOCAB Cleavages- mitotic cell divisions of the zygote Morula- four days after fertilization the embryo is a solid ball of about 50 cells Blastocyst – a fluid filled cavity forms in the center of the embryo transforming it into a hollow structure Implantation- w ...
... Biology Chapter 43-2 Human Development VOCAB Cleavages- mitotic cell divisions of the zygote Morula- four days after fertilization the embryo is a solid ball of about 50 cells Blastocyst – a fluid filled cavity forms in the center of the embryo transforming it into a hollow structure Implantation- w ...
The physical appearance of an individual is referred to as its
... 28) Every three base code on DNA (a triplet) codes for a single a. Carbohydrate monomer b. Lipid c. Amino acid d. Nucleic acid e. Carboxylic acid 29) The process whereby small molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration is a. Diffusion b. Active transport c. En ...
... 28) Every three base code on DNA (a triplet) codes for a single a. Carbohydrate monomer b. Lipid c. Amino acid d. Nucleic acid e. Carboxylic acid 29) The process whereby small molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration is a. Diffusion b. Active transport c. En ...
Introduction to Animal Diversity
... Ingest organic molecules and digest them via enzymes Cell structure and specialization Multicellular with structural proteins (collagen) for support Muscle and nervous tissue to send signals and allow mobility Reproduction and development Reproduce sexually with diploid (2n) stage as dom ...
... Ingest organic molecules and digest them via enzymes Cell structure and specialization Multicellular with structural proteins (collagen) for support Muscle and nervous tissue to send signals and allow mobility Reproduction and development Reproduce sexually with diploid (2n) stage as dom ...
Embryonic and Fetal Development
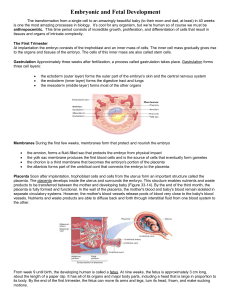
... During weeks 12 through 23, the period of the second trimester, the fetus increases in length to about 25 cm. By the end of this period, the fetus weighs about 0.5 kg and has the face of an infant, complete with eyebrows and eyelashes. At this point, the fetal heartbeat is easily detected and the fe ...
... During weeks 12 through 23, the period of the second trimester, the fetus increases in length to about 25 cm. By the end of this period, the fetus weighs about 0.5 kg and has the face of an infant, complete with eyebrows and eyelashes. At this point, the fetal heartbeat is easily detected and the fe ...
Human Embryology Development
... • The sperm cells travel through the cervix into the uterus, although they do not all reach fallopian tubes. It takes approximately 3-5 days for the fertilized ovum to travel from the fallopian tube to uterus. • Cell division, or cleavage, occurs and the zygote gets smaller. The zygote develops into ...
... • The sperm cells travel through the cervix into the uterus, although they do not all reach fallopian tubes. It takes approximately 3-5 days for the fertilized ovum to travel from the fallopian tube to uterus. • Cell division, or cleavage, occurs and the zygote gets smaller. The zygote develops into ...
Animals – Invertebrates Part 1
... o Cleavage pattern: In most protostomes early cell division leads to an eight-celled embryo twisted in arrangement called In deuterostomes, cells divide into eight-celled embryos with cells that are lined up atop the other in an arrangement called ...
... o Cleavage pattern: In most protostomes early cell division leads to an eight-celled embryo twisted in arrangement called In deuterostomes, cells divide into eight-celled embryos with cells that are lined up atop the other in an arrangement called ...
Gastrulation
... specific target location. These filopodia then organize into syncytial cables that deposit the calcium carbonate that makes up the spicules (the skeleton of the pluteus larva). During the second phase of gastrulation, the vegetal plate invaginates into the interior, replacing the blastocoelic cavit ...
... specific target location. These filopodia then organize into syncytial cables that deposit the calcium carbonate that makes up the spicules (the skeleton of the pluteus larva). During the second phase of gastrulation, the vegetal plate invaginates into the interior, replacing the blastocoelic cavit ...
Chapter 25 The History of Life on Earth
... Miller and Urey tested the hypothesis which yielded amino acids ...
... Miller and Urey tested the hypothesis which yielded amino acids ...
21.1
... 4. There are vast amounts of information on its genes and other aspects of its biology. 5. However, because first rounds of mitosis occur without cytokinesis, parts of its development are superficially quite different from that of other organisms. 6. Sequencing of the Drosophila genome was complete ...
... 4. There are vast amounts of information on its genes and other aspects of its biology. 5. However, because first rounds of mitosis occur without cytokinesis, parts of its development are superficially quite different from that of other organisms. 6. Sequencing of the Drosophila genome was complete ...
Ch. 42 - Development and Aging
... Pattern formation • Embryonic cells express genes differently in graded, periodic, and striped arrangements • Anteroposterior polarity is established in the egg before fertilization • Gap genes divide the anteroposterior axis into broad regions ...
... Pattern formation • Embryonic cells express genes differently in graded, periodic, and striped arrangements • Anteroposterior polarity is established in the egg before fertilization • Gap genes divide the anteroposterior axis into broad regions ...
Kingdom Animalia - Clayton High School
... Symmetry is when two or more halves are a mirror image of each other. Animals display asymmetry, radial symmetry or bilateral symmetry ...
... Symmetry is when two or more halves are a mirror image of each other. Animals display asymmetry, radial symmetry or bilateral symmetry ...
The Living World
... Certain groups of cells move inwards from the inner cell mass at about 10-11 days after fertilization This process of gastrulation results in the three primary germ layers Endoderm Ectoderm Mesoderm ...
... Certain groups of cells move inwards from the inner cell mass at about 10-11 days after fertilization This process of gastrulation results in the three primary germ layers Endoderm Ectoderm Mesoderm ...
L2 Cleavage to gastrulation
... --growth by deposition of extracellular matrix,intracellular organelles and matrix. --spread of epithelial sheets e.g. extraembryonic membranes. 2.Restriction and determinationtotipotent blastomeresrestricted potency 3.Gene activation and differential expression of functional genes. 4.Differentiat ...
... --growth by deposition of extracellular matrix,intracellular organelles and matrix. --spread of epithelial sheets e.g. extraembryonic membranes. 2.Restriction and determinationtotipotent blastomeresrestricted potency 3.Gene activation and differential expression of functional genes. 4.Differentiat ...
Animal Development Lab
... Starfish larval forms are called bipinnaria. They are significantly more developed than the previous stages. They move using cilia, and you can see a mouth, a digestive system, and an anus. This larva will metamorphose into an adult starfish. ...
... Starfish larval forms are called bipinnaria. They are significantly more developed than the previous stages. They move using cilia, and you can see a mouth, a digestive system, and an anus. This larva will metamorphose into an adult starfish. ...
Drosophila embryogenesis

Drosophila embryogenesis, the process by which Drosophila (fruit fly) embryos form, is a favorite model system for geneticists and developmental biologists studying embryogenesis. The small size, short generation time, and large brood size make it ideal for genetic studies. Transparent embryos facilitate developmental studies. Drosophila melanogaster was introduced into the field of genetic experiments by Thomas Hunt Morgan in 1909.