Structure-Function II
... respiratory and vasomotor centers which regulate basic autonomic (involuntary) functions such as heart rate, respiration and blood pressure. In addition, the medulla contains the dorsal column nuclei (cuneatus and gracilis; touch), the solitary nucleus (taste), the cochlear nucleus and the ventral p ...
... respiratory and vasomotor centers which regulate basic autonomic (involuntary) functions such as heart rate, respiration and blood pressure. In addition, the medulla contains the dorsal column nuclei (cuneatus and gracilis; touch), the solitary nucleus (taste), the cochlear nucleus and the ventral p ...
THALAMUS
... Association cortices *Internal Medullary lamina (IML) diffuse projections *Thalamic reticular nucleus (thin sheet of cells on lateral aspect of thal) inhibitory to other thal nuclei FUNCTIONS OF THE THALAMUS 1) Relay all sensory information to cortex (except olfactory – direct to cortex) 2) Selec ...
... Association cortices *Internal Medullary lamina (IML) diffuse projections *Thalamic reticular nucleus (thin sheet of cells on lateral aspect of thal) inhibitory to other thal nuclei FUNCTIONS OF THE THALAMUS 1) Relay all sensory information to cortex (except olfactory – direct to cortex) 2) Selec ...
04 Early Development - Biology Courses Server
... It also implants into the uterine wall and initiates the development of the placenta. The focus of this section will be on the embryo. We will come back to the extraembryonic membranes and implantation in a later lecture. ...
... It also implants into the uterine wall and initiates the development of the placenta. The focus of this section will be on the embryo. We will come back to the extraembryonic membranes and implantation in a later lecture. ...
TOPICAL ANATOMY I Anatomical Terms of
... upper or higher part of body Inferior: lower part of body Medial: structures nearer the midline Lateral: structures farther to the side Proximal: near the point of attachment of a structure (limb) Distal: away from point of attachment of a structure (limb) Cephalic: relates to the head (cranial) Cau ...
... upper or higher part of body Inferior: lower part of body Medial: structures nearer the midline Lateral: structures farther to the side Proximal: near the point of attachment of a structure (limb) Distal: away from point of attachment of a structure (limb) Cephalic: relates to the head (cranial) Cau ...
ANIMALS REVIEW Chapters 33 & 34
... Animals whose embryos display indeterminate radial cleavage and in which the embryonic blastopore becomes the ANUS deuterostomes ...
... Animals whose embryos display indeterminate radial cleavage and in which the embryonic blastopore becomes the ANUS deuterostomes ...
Chapter 16 - Special Senses
... Filaments from OE protrude through the Cribriform Plate of ethmoid bone – CN I runs to the Olfactory Bulb, and to the olfactory cortex of the cerebrum ...
... Filaments from OE protrude through the Cribriform Plate of ethmoid bone – CN I runs to the Olfactory Bulb, and to the olfactory cortex of the cerebrum ...
Body Planes and Directional Terms
... What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy– Physiology– Integration of these two concepts! ...
... What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy– Physiology– Integration of these two concepts! ...
Terminology
... Directional terminology is a standard set of words that are used in anatomy and the medical field. Directional terminology is used to describe the relationship of a structure to the body as a whole or to another body part. Many of the structures that you will learn about in this course have parts of ...
... Directional terminology is a standard set of words that are used in anatomy and the medical field. Directional terminology is used to describe the relationship of a structure to the body as a whole or to another body part. Many of the structures that you will learn about in this course have parts of ...
Comparison of two techniques
... • Axial MRI image at L3–4 demonstrating measurements in relationship to the anterior intervertebral plane: a the anterior edge of the psoas muscle (extending just anterior to the intervertebral plane in this image), b the anterior aspect of the lumbar plexus, c the location of the femoral nerve beg ...
... • Axial MRI image at L3–4 demonstrating measurements in relationship to the anterior intervertebral plane: a the anterior edge of the psoas muscle (extending just anterior to the intervertebral plane in this image), b the anterior aspect of the lumbar plexus, c the location of the femoral nerve beg ...
Anatomical Terms
... • When in the anatomical position, the subject stands erect facing the observer, the upper extremities are placed at the sides, the palms of the hands are turned forward, and the feet are flat on the floor. ...
... • When in the anatomical position, the subject stands erect facing the observer, the upper extremities are placed at the sides, the palms of the hands are turned forward, and the feet are flat on the floor. ...
Directional Terms
... • The chin is superior to the navel. • Inferior • A structure below another • The navel is inferior to the chin. ...
... • The chin is superior to the navel. • Inferior • A structure below another • The navel is inferior to the chin. ...
DEVELOPMENT OF MESODERM,
... GASTRULATION( Week 3-8) • Gastulation is the process which establishes the formation of three germ layered embryo: – Ectoderm – Mesoderm – Endoderm ...
... GASTRULATION( Week 3-8) • Gastulation is the process which establishes the formation of three germ layered embryo: – Ectoderm – Mesoderm – Endoderm ...
Directional Terms Practice Complete the following statements by
... The spinal cord is ...................................................to the vertebral column. ...
... The spinal cord is ...................................................to the vertebral column. ...
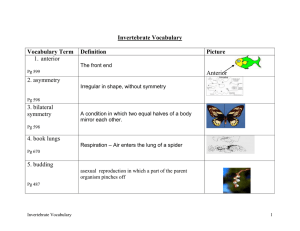
Invertebrate Vocabulary
... A system of canals filled with a watery fluid that circulates through-out the body of an echinoderm. ...
... A system of canals filled with a watery fluid that circulates through-out the body of an echinoderm. ...
Original description (NemasLan)
... farther back, where they are fainter on the lateral fields and where there are also faint wings. The contour of the body is slightly crenate. There are no subcephalic or cervical setae. The neck is cylindroid in the posterior part and somewhat conoid to convexconoid in the anterior part. There are p ...
... farther back, where they are fainter on the lateral fields and where there are also faint wings. The contour of the body is slightly crenate. There are no subcephalic or cervical setae. The neck is cylindroid in the posterior part and somewhat conoid to convexconoid in the anterior part. There are p ...
17. Egg Membranes Placenta `10
... Yolk Sac • 1st extra embryonic membrane to form • mediates nutrition • derived from endodermal cells that grow over yolk to enclose it ...
... Yolk Sac • 1st extra embryonic membrane to form • mediates nutrition • derived from endodermal cells that grow over yolk to enclose it ...
REPORT ON THE SEALS. 147 extends anterior to the spine for 1
... As an instance of the variety in shape, take the sheep as an illustration; in it the plate extends along the entire vertebral border of the scapula, and is of equal depth throughout : it only adds In the Seals it is like a small triangle another inch or so to the transverse length of the bone. with ...
... As an instance of the variety in shape, take the sheep as an illustration; in it the plate extends along the entire vertebral border of the scapula, and is of equal depth throughout : it only adds In the Seals it is like a small triangle another inch or so to the transverse length of the bone. with ...
AP Biology - TeacherWeb
... may be unequal divisions of cytoplasm cleavage pattern determined by amount of yolk in egg leaves different contents in each cell seals development fate of each cell & its descendants vegetal pole = yolk-rich end animal pole = nearest the nucleus ...
... may be unequal divisions of cytoplasm cleavage pattern determined by amount of yolk in egg leaves different contents in each cell seals development fate of each cell & its descendants vegetal pole = yolk-rich end animal pole = nearest the nucleus ...
mesoderm
... 1. formation of epiblast and hypoblast : By the 8th day, the inner cell mass differentiates into two layers of cells epiblast (columnar) bilaminar germ disc ...
... 1. formation of epiblast and hypoblast : By the 8th day, the inner cell mass differentiates into two layers of cells epiblast (columnar) bilaminar germ disc ...
Organogenesis Mesoderm - Relative Positions of Different Types
... Ectoderm - Dorsoventral Patterning of Neural Tube ...
... Ectoderm - Dorsoventral Patterning of Neural Tube ...
Female Anatomy & Physiology
... stimulus, the uterus can not maintain its thick lining, so this falls off and is shed as menstruation. If fertilization and pregnancy occur, the placenta of the embryo secretes a hormone called chorionic gonadotropin, which stimulates the corpus luteum to keep secreting progesterone, which in turn k ...
... stimulus, the uterus can not maintain its thick lining, so this falls off and is shed as menstruation. If fertilization and pregnancy occur, the placenta of the embryo secretes a hormone called chorionic gonadotropin, which stimulates the corpus luteum to keep secreting progesterone, which in turn k ...
Human Torso Model Activity
... Use the torso model to complete the answers below. 1. List 2 organs from the anterior view that are part of the digestive system. 2. Is the nose superior or inferior to the diaphragm muscle which allows breathing to take place? 3. The heart is ___________________ to the lungs. The lungs are ________ ...
... Use the torso model to complete the answers below. 1. List 2 organs from the anterior view that are part of the digestive system. 2. Is the nose superior or inferior to the diaphragm muscle which allows breathing to take place? 3. The heart is ___________________ to the lungs. The lungs are ________ ...
Introduction to Human Anatomy (Chapter 1)
... c. ____Cardiovascular_______________ for transporting oxygen, nutrients, and wastes throughout the body. d. _____Endocrine______ for secreting hormones directly into the blood to regulate internal processes. 4. The upper arm is __________proximal___________ to the lower arm. 5. The head is _________ ...
... c. ____Cardiovascular_______________ for transporting oxygen, nutrients, and wastes throughout the body. d. _____Endocrine______ for secreting hormones directly into the blood to regulate internal processes. 4. The upper arm is __________proximal___________ to the lower arm. 5. The head is _________ ...
Body Cavities
... • As a result of the rapid growth of the lungs, the pericardioperitoneal canals become too small, and the lungs begin to expand into the mesenchyme of the body wall dorsally, laterally, and ventrally. • Ventral and lateral expansion is posterior to the pleuropericardial folds. At first, these folds ...
... • As a result of the rapid growth of the lungs, the pericardioperitoneal canals become too small, and the lungs begin to expand into the mesenchyme of the body wall dorsally, laterally, and ventrally. • Ventral and lateral expansion is posterior to the pleuropericardial folds. At first, these folds ...
Drosophila embryogenesis

Drosophila embryogenesis, the process by which Drosophila (fruit fly) embryos form, is a favorite model system for geneticists and developmental biologists studying embryogenesis. The small size, short generation time, and large brood size make it ideal for genetic studies. Transparent embryos facilitate developmental studies. Drosophila melanogaster was introduced into the field of genetic experiments by Thomas Hunt Morgan in 1909.