File
... forehead, nose and cheek IOML parallel to upper edge of bucky Midsagittal plane at 450 to the bucky Central ray, angled 120 cephalad, enters 7-10 cm posterior an 1.5 cm inferior to the EAM remote from film ...
... forehead, nose and cheek IOML parallel to upper edge of bucky Midsagittal plane at 450 to the bucky Central ray, angled 120 cephalad, enters 7-10 cm posterior an 1.5 cm inferior to the EAM remote from film ...
No Slide Title
... OF SPINAL CORD LOSS OF PAIN SENSATION ON LEFT SIDE BELOW LESION LOSS OF TOUCH AND VIBRATION ON RIGHT SIDE BELOW LESION LOSS OF BOTH ON RIGHT SIDE AT SAME ...
... OF SPINAL CORD LOSS OF PAIN SENSATION ON LEFT SIDE BELOW LESION LOSS OF TOUCH AND VIBRATION ON RIGHT SIDE BELOW LESION LOSS OF BOTH ON RIGHT SIDE AT SAME ...
Gastrulation COO
... The two clusters remain connected by a small row of PMC, called dorsal and ventral chain respectively. The PMC form filopodia with which they “probe” the surrounding cells and the ...
... The two clusters remain connected by a small row of PMC, called dorsal and ventral chain respectively. The PMC form filopodia with which they “probe” the surrounding cells and the ...
Topic 7
... In B, we see how the eggs are forced to pass through sperm cells as they mature, which in effect forces fertilization to occur Note that earlier meiotic divisions actually involve sperm production and the spermatheca is only for STORAGE. ...
... In B, we see how the eggs are forced to pass through sperm cells as they mature, which in effect forces fertilization to occur Note that earlier meiotic divisions actually involve sperm production and the spermatheca is only for STORAGE. ...
Illnesses of the Female Reproductive System
... Phase 2 = ________________________ the development of follicles within the ovary, and estrogen is secreted (between day 6 -13) Phase 3 = ___________________________ The egg is released from the ovary Phase 4 = ___________________________ formation of the corpus luteum; hormone secreting struct ...
... Phase 2 = ________________________ the development of follicles within the ovary, and estrogen is secreted (between day 6 -13) Phase 3 = ___________________________ The egg is released from the ovary Phase 4 = ___________________________ formation of the corpus luteum; hormone secreting struct ...
Transgenic Organisms
... 2) They exhibit faster growth and hence achieve the marketable size sooner. ...
... 2) They exhibit faster growth and hence achieve the marketable size sooner. ...
Surface and Regional Anatomy
... Introduction to Surface Anatomy Palpation - examination with the hands, touching feeling, or perceiving by the sense of touch Auscultation - listening to sounds emitted from organs Observation - the art of looking ...
... Introduction to Surface Anatomy Palpation - examination with the hands, touching feeling, or perceiving by the sense of touch Auscultation - listening to sounds emitted from organs Observation - the art of looking ...
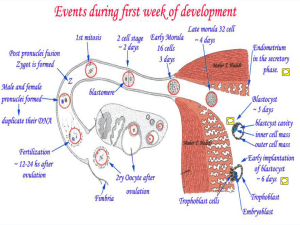
4_Trilaminar_Embyo_(week3)
... NOTE: All the pictures/diagragms for this topic only show the amniotic cavity & the yolk sac (2o), however, these are surrounded by a chorionic cavity (except at the connecting stalk at the caudal end of the developing embryo) & the tri-layer membrane, known as the chorion, (see embryonic wk 2 lectu ...
... NOTE: All the pictures/diagragms for this topic only show the amniotic cavity & the yolk sac (2o), however, these are surrounded by a chorionic cavity (except at the connecting stalk at the caudal end of the developing embryo) & the tri-layer membrane, known as the chorion, (see embryonic wk 2 lectu ...
Embryonic Development Powerpoint
... Gastrulation involves a series of cell migrations to positions where they will form the three primary cell layers. •Ectoderm forms the outer layer. Ectoderm forms skin, hair, sweat glands, epithelium, brain and nervous system. •Endoderm forms the inner layer. The endoderm forms digestive, respirator ...
... Gastrulation involves a series of cell migrations to positions where they will form the three primary cell layers. •Ectoderm forms the outer layer. Ectoderm forms skin, hair, sweat glands, epithelium, brain and nervous system. •Endoderm forms the inner layer. The endoderm forms digestive, respirator ...
Human Embryonic Development
... Gastrulation involves a series of cell migrations to positions where they will form the three primary cell layers. •Ectoderm forms the outer layer. Ectoderm forms skin, hair, sweat glands, epithelium, brain and nervous system. •Endoderm forms the inner layer. The endoderm forms digestive, respirator ...
... Gastrulation involves a series of cell migrations to positions where they will form the three primary cell layers. •Ectoderm forms the outer layer. Ectoderm forms skin, hair, sweat glands, epithelium, brain and nervous system. •Endoderm forms the inner layer. The endoderm forms digestive, respirator ...
Chapter 1 Notes - Social Circle City Schools
... Concept 32.1 - tissues of impulse conduction and movement: nervous and muscle tissue - reproduce sexually; zygote that undergoes cleavage -divides into smaller cells after fertilization creating a multicellular structure called a blastula ...
... Concept 32.1 - tissues of impulse conduction and movement: nervous and muscle tissue - reproduce sexually; zygote that undergoes cleavage -divides into smaller cells after fertilization creating a multicellular structure called a blastula ...
L7: Intro. to Animal Diversity
... • Radial symmetry – Can be divided into equal but opposite halves by any plane through its central axis – Sessile or planktonic ...
... • Radial symmetry – Can be divided into equal but opposite halves by any plane through its central axis – Sessile or planktonic ...
intraembryonic mesoderm胚內中胚層
... -Intraembryonic coelom (cavity)胚內體腔--fusion of isolated coelomic spaces in the lateral mesoderm and cardiogenic mesoderm into a horseshoeshaped cavity. -Lateral mesoderm divided into: -Parietal layer壁層--together with extraembryonic mesoderm covering amnion and ectoderm called somatopleure體壁, embryon ...
... -Intraembryonic coelom (cavity)胚內體腔--fusion of isolated coelomic spaces in the lateral mesoderm and cardiogenic mesoderm into a horseshoeshaped cavity. -Lateral mesoderm divided into: -Parietal layer壁層--together with extraembryonic mesoderm covering amnion and ectoderm called somatopleure體壁, embryon ...
Second Week of Development: Bilaminar Germ Disc
... What makes the conceptus not to be rejected by the mother immune system? placental trophoblast, does not express the polymorphic class I and class II MHC genes and instead expresses HLA-G, a non polymorphic gene. Therefore, antibodies against the fetal proteins not developed The production of immun ...
... What makes the conceptus not to be rejected by the mother immune system? placental trophoblast, does not express the polymorphic class I and class II MHC genes and instead expresses HLA-G, a non polymorphic gene. Therefore, antibodies against the fetal proteins not developed The production of immun ...
Second Week of evelopment: Bilaminar Germ Disc
... What makes the conceptus not to be rejected by the mother immune system? placental trophoblast, does not express the polymorphic class I and class II MHC genes and instead expresses HLA-G, a non polymorphic gene. Therefore, antibodies against the fetal proteins not developed The production of immun ...
... What makes the conceptus not to be rejected by the mother immune system? placental trophoblast, does not express the polymorphic class I and class II MHC genes and instead expresses HLA-G, a non polymorphic gene. Therefore, antibodies against the fetal proteins not developed The production of immun ...
for neural fate
... Determination: A cell is restricted in its developmental potential. Differentiation: Cell elaborates a specific developmental program. ...
... Determination: A cell is restricted in its developmental potential. Differentiation: Cell elaborates a specific developmental program. ...
Homework 1 - cloudfront.net
... 3. Label C points to the ____________________ cavity. 4. Label D points to the ____________________. 5. Label E points to the ____________________ cavity. 6. Label F points to the ____________________ cavity. 7. The central region of the thoracic cavity containing the heart is called the ___________ ...
... 3. Label C points to the ____________________ cavity. 4. Label D points to the ____________________. 5. Label E points to the ____________________ cavity. 6. Label F points to the ____________________ cavity. 7. The central region of the thoracic cavity containing the heart is called the ___________ ...
slides_5
... The hypoblast produces cells that migrate along the inside of the exocoelomic membrane These cells proliferate and gradually form a new cavity within the exocoelomic cavity. This new cavity is known as ...
... The hypoblast produces cells that migrate along the inside of the exocoelomic membrane These cells proliferate and gradually form a new cavity within the exocoelomic cavity. This new cavity is known as ...
Primitive gut
... primitive urogenital sinus and a dorsal primitive anorectal canal. The cloacal membrane breaks down in the 7th week. Distal to the pectinate line (site of the former cloacal membrane), the epithelium of the anal canal is derived from ectoderm of proctodeum (primitive anal pit) ...
... primitive urogenital sinus and a dorsal primitive anorectal canal. The cloacal membrane breaks down in the 7th week. Distal to the pectinate line (site of the former cloacal membrane), the epithelium of the anal canal is derived from ectoderm of proctodeum (primitive anal pit) ...
Week 2 of development
... move cranially forming a median process -the notochordal process. The notochordal process grows cranially between the ectoderm and the endoderm until it reaches the prechordal plate. ...
... move cranially forming a median process -the notochordal process. The notochordal process grows cranially between the ectoderm and the endoderm until it reaches the prechordal plate. ...
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal
... Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like “dorsal,” “ventral,” “anterior” and “posterior” provide a means of locating structures relative to the overall orientation of the nervous system. Complications with those terms mayarise for two ...
... Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like “dorsal,” “ventral,” “anterior” and “posterior” provide a means of locating structures relative to the overall orientation of the nervous system. Complications with those terms mayarise for two ...
Phylum Annelida
... Closed circulation, dorsal (anterior)/ventral (posterior) bv Unidirectional flow by valves Metanephridia, pair/segment ...
... Closed circulation, dorsal (anterior)/ventral (posterior) bv Unidirectional flow by valves Metanephridia, pair/segment ...
Drosophila embryogenesis

Drosophila embryogenesis, the process by which Drosophila (fruit fly) embryos form, is a favorite model system for geneticists and developmental biologists studying embryogenesis. The small size, short generation time, and large brood size make it ideal for genetic studies. Transparent embryos facilitate developmental studies. Drosophila melanogaster was introduced into the field of genetic experiments by Thomas Hunt Morgan in 1909.