BDS Ist YEAR EXAMINATION 2008-09
... The mucosa of pecten part of anal canal is smooth and characterized by: a) Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium b) Presence of sweat and sebaceous glands c) Presence of hair follicles d) Presence of numerous somatic nerve endings Many types of neuroendocrine cell are scattered among the wall o ...
... The mucosa of pecten part of anal canal is smooth and characterized by: a) Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium b) Presence of sweat and sebaceous glands c) Presence of hair follicles d) Presence of numerous somatic nerve endings Many types of neuroendocrine cell are scattered among the wall o ...
DEVELOPMENT OF HUMAN BRAIN AND SPINAL CORD
... The neural canal narrows and becomes cerebral aqueduct. Neuroblasts from alar plates of midbrain into tectum (roof) and aggregate to form four large group of neurons, the paired superior and inferior colliculi. Neuroblasts from basal plates give rise to group of neurons in tegmentum (red nuclei, nuc ...
... The neural canal narrows and becomes cerebral aqueduct. Neuroblasts from alar plates of midbrain into tectum (roof) and aggregate to form four large group of neurons, the paired superior and inferior colliculi. Neuroblasts from basal plates give rise to group of neurons in tegmentum (red nuclei, nuc ...
video slide - Course
... (fertilized egg) Mitotic cell division Two-celled embryo (a) Cytoplasmic determinants in the egg. The unfertilized egg cell has molecules in its cytoplasm, encoded by the mother’s genes, that influence development. Many of these cytoplasmic determinants, like the two shown here, are unevenly distrib ...
... (fertilized egg) Mitotic cell division Two-celled embryo (a) Cytoplasmic determinants in the egg. The unfertilized egg cell has molecules in its cytoplasm, encoded by the mother’s genes, that influence development. Many of these cytoplasmic determinants, like the two shown here, are unevenly distrib ...
video slide - Biology Junction
... (fertilized egg) Mitotic cell division Two-celled embryo (a) Cytoplasmic determinants in the egg. The unfertilized egg cell has molecules in its cytoplasm, encoded by the mother’s genes, that influence development. Many of these cytoplasmic determinants, like the two shown here, are unevenly distrib ...
... (fertilized egg) Mitotic cell division Two-celled embryo (a) Cytoplasmic determinants in the egg. The unfertilized egg cell has molecules in its cytoplasm, encoded by the mother’s genes, that influence development. Many of these cytoplasmic determinants, like the two shown here, are unevenly distrib ...
Perch Dissection Introduction
... Important External Body Parts to Know • lateral line - a series of sensory pores (small openings) that are located along the sides of fish -they sense vibrations in the water • mouth - the part of the body which the fish uses to catch food - it is located at the front of the body • eye - sight orga ...
... Important External Body Parts to Know • lateral line - a series of sensory pores (small openings) that are located along the sides of fish -they sense vibrations in the water • mouth - the part of the body which the fish uses to catch food - it is located at the front of the body • eye - sight orga ...
Development of Body Cavities
... It does not completely separate the thoracic and abdominal cavities, since there are two large posterior openings, known as the pericardioperitoneal canals, on either side of the foregut. ...
... It does not completely separate the thoracic and abdominal cavities, since there are two large posterior openings, known as the pericardioperitoneal canals, on either side of the foregut. ...
Cycles Ch 3 BI
... The fertilised egg (zygote) passes slowly along the oviduct towards the uterus, where its lining continues to thicken. During this journey, the zygote divides repeatedly and forms a ball of cells called an embryo. Upon reaching the uterus, the embryo attaches or implants itself to the uterine lining ...
... The fertilised egg (zygote) passes slowly along the oviduct towards the uterus, where its lining continues to thicken. During this journey, the zygote divides repeatedly and forms a ball of cells called an embryo. Upon reaching the uterus, the embryo attaches or implants itself to the uterine lining ...
Introduction to Animal Diversity
... Animals can be categorized according to the symmetry of their bodies or lack of it. Symmetry Reflects Lifestyle Radial animals are sessile or planktonic Bilaterial animals more actively from one place to another The nervous system enables these organisms to move. ...
... Animals can be categorized according to the symmetry of their bodies or lack of it. Symmetry Reflects Lifestyle Radial animals are sessile or planktonic Bilaterial animals more actively from one place to another The nervous system enables these organisms to move. ...
Document
... • This is important for the cerebellum to integrate neuronal inputs from the cerebral cortex with activities in the peripheral and for body balance • Proprioceptive information is obtained by Golgi tendon organs and muscle spindles. • Golgi tendon organs consist of a fibrous capsule enclosing tendon ...
... • This is important for the cerebellum to integrate neuronal inputs from the cerebral cortex with activities in the peripheral and for body balance • Proprioceptive information is obtained by Golgi tendon organs and muscle spindles. • Golgi tendon organs consist of a fibrous capsule enclosing tendon ...
american museum novitates - AMNH Library Digital Repository
... attachment of the soft palate; the basioccipital is practically excluded from the condyle, but, antero-ventrally, it has two fairly strong tubera to which the basisphenoid is applied; the basisphenoid has no tubera; anteriorly, it is clasped by the pterygoids; although here described as the Ven. ...
... attachment of the soft palate; the basioccipital is practically excluded from the condyle, but, antero-ventrally, it has two fairly strong tubera to which the basisphenoid is applied; the basisphenoid has no tubera; anteriorly, it is clasped by the pterygoids; although here described as the Ven. ...
orientation
... …because personal discovery is an important aspect of learning Why cats? …because homology allows us to use cats as model organisms (and we can’t dissect human cadavers) “homology” defined: inheritance from common ancestor regardless of similarity in form or function Advantage of using non-human org ...
... …because personal discovery is an important aspect of learning Why cats? …because homology allows us to use cats as model organisms (and we can’t dissect human cadavers) “homology” defined: inheritance from common ancestor regardless of similarity in form or function Advantage of using non-human org ...
2.germ disc differentiation(20160108).
... In general terms it may be stated that the ectoderm gives rise to those organs and structures that maintain contact with the outside world. ...
... In general terms it may be stated that the ectoderm gives rise to those organs and structures that maintain contact with the outside world. ...
video slide
... Blastomeres that receive half or all of the gray crescent develop into normal embryos, but a blastomere that receives none of the gray crescent gives rise to an abnormal embryo without dorsal structures. Spemann called it a “belly piece.” CONCLUSION ...
... Blastomeres that receive half or all of the gray crescent develop into normal embryos, but a blastomere that receives none of the gray crescent gives rise to an abnormal embryo without dorsal structures. Spemann called it a “belly piece.” CONCLUSION ...
document
... • Organogenesis is the process of tissue and organ formation that begins once gastrulation is complete and the embryonic germ layers are in place. • During organogenesis, cells proliferate and become differentiated, meaning that they become a specialized cell type. – Differentiated cells have a dist ...
... • Organogenesis is the process of tissue and organ formation that begins once gastrulation is complete and the embryonic germ layers are in place. • During organogenesis, cells proliferate and become differentiated, meaning that they become a specialized cell type. – Differentiated cells have a dist ...
because personal discovery is an important aspect
... dorsal / ventral – back (i.e., spinal) side, belly side superior / inferior – above, below (separated by transverse plane) medial / lateral – towards midline, towards side (sep’d by sagittal plane) cranial or cephalad / caudal – towards head, towards tail proximal / distal – towards beginning, towar ...
... dorsal / ventral – back (i.e., spinal) side, belly side superior / inferior – above, below (separated by transverse plane) medial / lateral – towards midline, towards side (sep’d by sagittal plane) cranial or cephalad / caudal – towards head, towards tail proximal / distal – towards beginning, towar ...
Crayfish dissection guide
... the microscope. Note the many facets. What is their shape? Each facet is the external surface of an ommatidium, the visual unit of which arthropod compound eyes are composed. By pressing on the coverglass, the ommatidia can be separated and individual ones observed. What is their shape and how do th ...
... the microscope. Note the many facets. What is their shape? Each facet is the external surface of an ommatidium, the visual unit of which arthropod compound eyes are composed. By pressing on the coverglass, the ommatidia can be separated and individual ones observed. What is their shape and how do th ...
Organs from the mesoderm
... forms the dorsal mesentery of the heitrt. The mesoderm around the tube continues to thicken, and forms later the musculature of the heart. At first the heart has also a ventral mesentery formed by the union of the walls of the cælomic cavities below it (Fig. 45, B), but later the mesentery is in par ...
... forms the dorsal mesentery of the heitrt. The mesoderm around the tube continues to thicken, and forms later the musculature of the heart. At first the heart has also a ventral mesentery formed by the union of the walls of the cælomic cavities below it (Fig. 45, B), but later the mesentery is in par ...
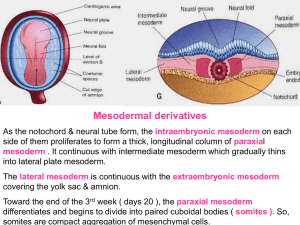
07 - mesodermal
... As the notochord & neural tube form, the intraembryonic mesoderm on each side of them proliferates to form a thick, longitudinal column of paraxial mesoderm . It continuous with intermediate mesoderm which gradually thins into lateral plate mesoderm. The lateral mesoderm is continuous with the extra ...
... As the notochord & neural tube form, the intraembryonic mesoderm on each side of them proliferates to form a thick, longitudinal column of paraxial mesoderm . It continuous with intermediate mesoderm which gradually thins into lateral plate mesoderm. The lateral mesoderm is continuous with the extra ...
PDF
... New cues for neurite growth and patterning The molecules and mechanisms that govern the growth and patterning of neurites (neural processes such as axons or dendrites) are poorly understood. However, two papers in this issue provide important new insights into the control of these essential aspects ...
... New cues for neurite growth and patterning The molecules and mechanisms that govern the growth and patterning of neurites (neural processes such as axons or dendrites) are poorly understood. However, two papers in this issue provide important new insights into the control of these essential aspects ...
Zebrafish Angiotensin II Receptor-like 1a - MPI
... vasculature. The primordial midbrain channel (pmbc), middle cerebral vein (mcev) and developing eye (ey) are indicated. (F) Lateral view of the yolk extension and cloaca region of an embryo at 24 hpf showing expression in the primary caudal vein (pcv) and intermediate cell mass (icm). (G) Transverse ...
... vasculature. The primordial midbrain channel (pmbc), middle cerebral vein (mcev) and developing eye (ey) are indicated. (F) Lateral view of the yolk extension and cloaca region of an embryo at 24 hpf showing expression in the primary caudal vein (pcv) and intermediate cell mass (icm). (G) Transverse ...
ch 29 Development Inheritance
... 2) The process leading to fertilization begins as peristaltic contractions and the actions of cilia transport the oocyte through the uterine tube. 3) Sperm swim up the uterus and into the uterine tube by the whip like movements of their tails and muscular contractions of the uterus. b. The function ...
... 2) The process leading to fertilization begins as peristaltic contractions and the actions of cilia transport the oocyte through the uterine tube. 3) Sperm swim up the uterus and into the uterine tube by the whip like movements of their tails and muscular contractions of the uterus. b. The function ...
Anatomical Position, etc. Notes Handout
... Posterior knee area ________________________ Area between hips ________________________ Shoulder blade region ________________________ Posterior surface of leg (calf) ________________________ Area of spinal column ...
... Posterior knee area ________________________ Area between hips ________________________ Shoulder blade region ________________________ Posterior surface of leg (calf) ________________________ Area of spinal column ...
Second Week of Development
... Chorion develops from the trophoblast and the extraembryonic mesoderm Surrounds the embryo and, later, the fetus Eventually becomes the major embryonic component of the placenta Protects the embryo and fetus from maternal immune responses and produces human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) Inn ...
... Chorion develops from the trophoblast and the extraembryonic mesoderm Surrounds the embryo and, later, the fetus Eventually becomes the major embryonic component of the placenta Protects the embryo and fetus from maternal immune responses and produces human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) Inn ...
Germ disc differentiation
... In general terms it may be stated that the ectoderm gives rise to those organs and structures that maintain contact with the outside world. ...
... In general terms it may be stated that the ectoderm gives rise to those organs and structures that maintain contact with the outside world. ...
19) Differential Gene expression in Development
... 10.2 Development and Evolutionary change Modularity also allows the timing of developmental processes to be independent—heterochrony. The neck vertebrae of giraffes are much longer than those of other mammals. Bone growth is stopped by a signal that results in death of chondrocytes (cartilage-produ ...
... 10.2 Development and Evolutionary change Modularity also allows the timing of developmental processes to be independent—heterochrony. The neck vertebrae of giraffes are much longer than those of other mammals. Bone growth is stopped by a signal that results in death of chondrocytes (cartilage-produ ...
Drosophila embryogenesis

Drosophila embryogenesis, the process by which Drosophila (fruit fly) embryos form, is a favorite model system for geneticists and developmental biologists studying embryogenesis. The small size, short generation time, and large brood size make it ideal for genetic studies. Transparent embryos facilitate developmental studies. Drosophila melanogaster was introduced into the field of genetic experiments by Thomas Hunt Morgan in 1909.