Cytoplasmic determinants in the egg.
... (a) Cytoplasmic determinants in the egg. The unfertilized egg cell has molecules in its cytoplasm, encoded by the mother’s genes, that influence development. Many of these cytoplasmic determinants, like the two shown here, are unevenly distributed in the egg. After fertilization and mitotic division ...
... (a) Cytoplasmic determinants in the egg. The unfertilized egg cell has molecules in its cytoplasm, encoded by the mother’s genes, that influence development. Many of these cytoplasmic determinants, like the two shown here, are unevenly distributed in the egg. After fertilization and mitotic division ...
Ch_47
... (a) Cytoplasmic determinants in the egg. The unfertilized egg cell has molecules in its cytoplasm, encoded by the mother’s genes, that influence development. Many of these cytoplasmic determinants, like the two shown here, are unevenly distributed in the egg. After fertilization and mitotic division ...
... (a) Cytoplasmic determinants in the egg. The unfertilized egg cell has molecules in its cytoplasm, encoded by the mother’s genes, that influence development. Many of these cytoplasmic determinants, like the two shown here, are unevenly distributed in the egg. After fertilization and mitotic division ...
3_Bilaminar Embryo_(week2)
... With the exception of a “connecting stalk” (described below), Extraembryonic mesoderm “splits” leaving a space between the two mesoderm layers The space b/w the 2 margins becomes the extraembryonic coelom or chorionic cavity Cytotrophoblast still surround the outer most layer of mesoderm Cho ...
... With the exception of a “connecting stalk” (described below), Extraembryonic mesoderm “splits” leaving a space between the two mesoderm layers The space b/w the 2 margins becomes the extraembryonic coelom or chorionic cavity Cytotrophoblast still surround the outer most layer of mesoderm Cho ...
Vertebrate Zoology
... • Centrolecithal eggs – Nuclei copied without cytokinesis (cytoplasm division). Yolk in center of egg. Nuclei move to surface before forming cell membranes- most insects . • Holoblastic : complete cleavage. • Meroblastic : incomplete cleavage. ...
... • Centrolecithal eggs – Nuclei copied without cytokinesis (cytoplasm division). Yolk in center of egg. Nuclei move to surface before forming cell membranes- most insects . • Holoblastic : complete cleavage. • Meroblastic : incomplete cleavage. ...
embryology PAP 2 Fertilization and implantation
... cleavage spindle in preparation for cleavage. ...
... cleavage spindle in preparation for cleavage. ...
Human Anatomy and Physiology
... 2) Identify the major body cavities and subdivisions 3) Be able to label, define, or determine through a scenario (ex: The sternum is ___________to the heart) Assignment 1) Take photos in the anterior/posterior anatomical position and a side view. 2) Create a file and save it to your b: drive. Call ...
... 2) Identify the major body cavities and subdivisions 3) Be able to label, define, or determine through a scenario (ex: The sternum is ___________to the heart) Assignment 1) Take photos in the anterior/posterior anatomical position and a side view. 2) Create a file and save it to your b: drive. Call ...
ANPR_AYS_Anatom_Translate_V01
... Translate the sentences below. The words in italics do not need to be translated. 1. A transverse of the superior thoracic cavity. 2. A frontal of the dorsal cavity. 3. The right radius is distal to the humerus. 4. Proximal phalange. 5. Anterior fontanel. 6. Medial longitudinal arch. 7. Superior art ...
... Translate the sentences below. The words in italics do not need to be translated. 1. A transverse of the superior thoracic cavity. 2. A frontal of the dorsal cavity. 3. The right radius is distal to the humerus. 4. Proximal phalange. 5. Anterior fontanel. 6. Medial longitudinal arch. 7. Superior art ...
File
... Superior (cranial) Inferior (caudal) Ventral (anterior) Dorsal (posterior) Medial Lateral Intermediate Proximal Distal Superficial (external) Deep (internal) ...
... Superior (cranial) Inferior (caudal) Ventral (anterior) Dorsal (posterior) Medial Lateral Intermediate Proximal Distal Superficial (external) Deep (internal) ...
Playdough Surgery Group quiz
... Playdough Surgery Group Quiz Be prepared to explain and demonstrate what each of these words mean. Superior / Inferior ...
... Playdough Surgery Group Quiz Be prepared to explain and demonstrate what each of these words mean. Superior / Inferior ...
Slide ()
... The directions used in the nervous system. The rostral direction is toward the nose and caudal is toward the tail. In the head of a person standing, rostral and anterior are roughly the same direction, and caudal and posterior are the same for the cerebral cortex. However, as the brainstem forms and ...
... The directions used in the nervous system. The rostral direction is toward the nose and caudal is toward the tail. In the head of a person standing, rostral and anterior are roughly the same direction, and caudal and posterior are the same for the cerebral cortex. However, as the brainstem forms and ...
10. Human Reproduction Outline
... A fertilized egg is known as a _____________. Fertilization generally occurs when the egg is in the upper portion of the _________. If the egg is not fertilized within about ___________ after ___________, it breaks down and disappears. _____________ of the fertilized egg begins while the egg ...
... A fertilized egg is known as a _____________. Fertilization generally occurs when the egg is in the upper portion of the _________. If the egg is not fertilized within about ___________ after ___________, it breaks down and disappears. _____________ of the fertilized egg begins while the egg ...
filled-in vers.
... is delayed. Consequently, slightly different process accomplishes same ends. Lateral mesoderm moves in from sides and ventral area of blastopore heading for the head. ...
... is delayed. Consequently, slightly different process accomplishes same ends. Lateral mesoderm moves in from sides and ventral area of blastopore heading for the head. ...
Procedure For Laryngeal Tie Forward Surgery
... wire passer and retrieved. The procedure is repeated on the other side such that the dorsal (leader) and ventral (trailer) sutures of each side can be tied over the ventral aspect of the basihyoid. A bilateral partial sternothyroidectomy is performed at this time. The sutures on each side are then t ...
... wire passer and retrieved. The procedure is repeated on the other side such that the dorsal (leader) and ventral (trailer) sutures of each side can be tied over the ventral aspect of the basihyoid. A bilateral partial sternothyroidectomy is performed at this time. The sutures on each side are then t ...
test1fall15.ede
... Compared to their better off peers, children living in poverty are more likely to experience greater rates of illness and disabilities, have lower IQ scores, and underperform in school. Researchers have concluded that a. constant poverty has a greater negative impact than occasional poverty b. rural ...
... Compared to their better off peers, children living in poverty are more likely to experience greater rates of illness and disabilities, have lower IQ scores, and underperform in school. Researchers have concluded that a. constant poverty has a greater negative impact than occasional poverty b. rural ...
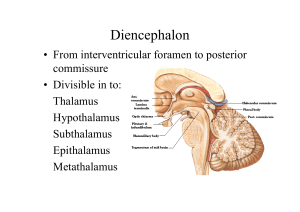
13 -DiencephalonI2009-04-11 09:211.1 MB
... 1. Pineal gland: secretes melatonin that regulates onset of puberty 2. Habenular nuclei: a part of limbic system ...
... 1. Pineal gland: secretes melatonin that regulates onset of puberty 2. Habenular nuclei: a part of limbic system ...
12 DiencephalonI
... 1. Pineal gland: secretes melatonin that regulates onset of puberty 2. Habenular nuclei: a part of limbic system ...
... 1. Pineal gland: secretes melatonin that regulates onset of puberty 2. Habenular nuclei: a part of limbic system ...
Conceptus – anything developed from fertilized egg
... proliferation of cells on the median plane at the dorsal/epiblastic aspect. The streak elongates by proliferation of cells at the caudal end, pushing it towards the cranial end forming a primitive node at the cranial most end. As this occurs, the primitive groove forms as an indentation along the ce ...
... proliferation of cells on the median plane at the dorsal/epiblastic aspect. The streak elongates by proliferation of cells at the caudal end, pushing it towards the cranial end forming a primitive node at the cranial most end. As this occurs, the primitive groove forms as an indentation along the ce ...
Reproductive System, Day 4 (Professor Powerpoint)
... ♦ The haploid nuclei of the ovum & sperm fuse to form a common diploid segmentation nucleus (the ZYGOTE) ♦ Occasionally a single fertilized egg splits into two shortly after fertilization = monozygotic/identical twins • Sometimes (very rare) the “split” is not complete, so they remain joined = siame ...
... ♦ The haploid nuclei of the ovum & sperm fuse to form a common diploid segmentation nucleus (the ZYGOTE) ♦ Occasionally a single fertilized egg splits into two shortly after fertilization = monozygotic/identical twins • Sometimes (very rare) the “split” is not complete, so they remain joined = siame ...
- Free Documents
... develops into the anus. Review As a group, the coelomates have a body cavity lined on both sides with tissue derived from the mesoderm. The phylogenetic tree on the left depicts the fact that the coelomates are taxonomically grouped into protostomes and deuterostomes. The groupings are based on fund ...
... develops into the anus. Review As a group, the coelomates have a body cavity lined on both sides with tissue derived from the mesoderm. The phylogenetic tree on the left depicts the fact that the coelomates are taxonomically grouped into protostomes and deuterostomes. The groupings are based on fund ...
Document
... Pseudocoelom – coelom is not completely lined by tissue derived from mesoderm (pseudocoelomates) Acoelomates – lack a body cavity entirely Fluid-filled body cavity can protect internal organs or be used as hydrostatic skeleton ...
... Pseudocoelom – coelom is not completely lined by tissue derived from mesoderm (pseudocoelomates) Acoelomates – lack a body cavity entirely Fluid-filled body cavity can protect internal organs or be used as hydrostatic skeleton ...
Diencephalon
... • Receives fibres from stria medullares, habenular nuclei & post. Com. • Inhibits gonadal function. • After 16 yrs., calcerous bodies present which are visible in skull x-rays. • Identification & position of pineal gland in skull films. ...
... • Receives fibres from stria medullares, habenular nuclei & post. Com. • Inhibits gonadal function. • After 16 yrs., calcerous bodies present which are visible in skull x-rays. • Identification & position of pineal gland in skull films. ...
Drosophila embryogenesis

Drosophila embryogenesis, the process by which Drosophila (fruit fly) embryos form, is a favorite model system for geneticists and developmental biologists studying embryogenesis. The small size, short generation time, and large brood size make it ideal for genetic studies. Transparent embryos facilitate developmental studies. Drosophila melanogaster was introduced into the field of genetic experiments by Thomas Hunt Morgan in 1909.