The nervous system
... ②Relation of between the motor nucleus and sensory nucleus is medial and lateral relationship ③Gray and white matters are not continuous ④Cranial nerve nuclei have seven functional components ⑤The region of reticular formation is widely 2 Cranial nerve nuclei ①General somatic efferent(motor) nuclei: ...
... ②Relation of between the motor nucleus and sensory nucleus is medial and lateral relationship ③Gray and white matters are not continuous ④Cranial nerve nuclei have seven functional components ⑤The region of reticular formation is widely 2 Cranial nerve nuclei ①General somatic efferent(motor) nuclei: ...
Slide 1
... Atresia may effect oocytes at all stages of their "life" - both prenatally and postnatally. By the sixth month of gestation about 7 million oocytes and oogonia are present in the ovaries. By the time of birth this number is reduced to about 2 million. Of these only about 400.000 survive until pubert ...
... Atresia may effect oocytes at all stages of their "life" - both prenatally and postnatally. By the sixth month of gestation about 7 million oocytes and oogonia are present in the ovaries. By the time of birth this number is reduced to about 2 million. Of these only about 400.000 survive until pubert ...
Cranial Nerve Motor Nuclei
... This slide illustrates the trajectories of the facial and abducens nerves in the pons. Compare the three-dimensional course of these nerves shown in this slide with their appearance in the myelin-stained section X030. (Note that the segment of the facial nerve from the nucleus to the genu cannot be ...
... This slide illustrates the trajectories of the facial and abducens nerves in the pons. Compare the three-dimensional course of these nerves shown in this slide with their appearance in the myelin-stained section X030. (Note that the segment of the facial nerve from the nucleus to the genu cannot be ...
THE ANKLE AND FOOT
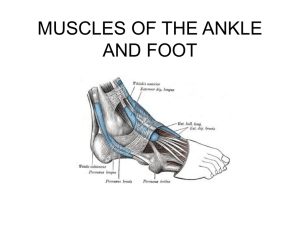
... • Origin: upper 2/3 of the posterior surfaces of the tibia and fibula • Insertion: posterior surface of the calcaneus via Achilles tendon • Action: – plantar flexion • Superficial posterior compartment ...
... • Origin: upper 2/3 of the posterior surfaces of the tibia and fibula • Insertion: posterior surface of the calcaneus via Achilles tendon • Action: – plantar flexion • Superficial posterior compartment ...
DEVELOPMENT of the URINARY SYSTEM
... intermediate mesoderm links up with similar parts in adjacent segments to form a duct. ...
... intermediate mesoderm links up with similar parts in adjacent segments to form a duct. ...
Nervous System Cranial Nerves, Spine and Brain
... gray matter Ventral (anterior) horns-anterior projections of gray matter Lateral horns-lateral gray matter projections in thoracic and lumbuar regions of the spinal cord Central canal-contains cerebrospinal fluid ...
... gray matter Ventral (anterior) horns-anterior projections of gray matter Lateral horns-lateral gray matter projections in thoracic and lumbuar regions of the spinal cord Central canal-contains cerebrospinal fluid ...
Summer 01
... 39) What structure is present on all cervical vertebrae? a) bifid spines process b) transverse foramen c) body d) uncrate process e) vertebral prominent 40) The superior articular facets of the atlas have a ____ surface. a) concave b) convex 41) The groove for the vertebral artery is located on the ...
... 39) What structure is present on all cervical vertebrae? a) bifid spines process b) transverse foramen c) body d) uncrate process e) vertebral prominent 40) The superior articular facets of the atlas have a ____ surface. a) concave b) convex 41) The groove for the vertebral artery is located on the ...
MSK Answers - Mosaiced.org
... Infraspinatus – laterally rotates arm & stabilises shoulder, suprascapular nerve C5-C6 Palmar interossei – ulnar nerve, C8-T1 Pectoralis major – flexes, medially rotates & adducts humerus, lateral & medial pectoral nerves, ...
... Infraspinatus – laterally rotates arm & stabilises shoulder, suprascapular nerve C5-C6 Palmar interossei – ulnar nerve, C8-T1 Pectoralis major – flexes, medially rotates & adducts humerus, lateral & medial pectoral nerves, ...
term 3 answers to questions - Hatzalah of Miami-Dade
... 26. Perineal nerve from pudendal nerve and its posterior scrotal branches. Also anterior branches of the posterior femoral cutaneous nerve. 27. Superior rectal from inferior mesenteric artery, middle rectal from internal iliac and inferior rectal from internal pudendal artery (internal iliac). All a ...
... 26. Perineal nerve from pudendal nerve and its posterior scrotal branches. Also anterior branches of the posterior femoral cutaneous nerve. 27. Superior rectal from inferior mesenteric artery, middle rectal from internal iliac and inferior rectal from internal pudendal artery (internal iliac). All a ...
Paranasal Sinus Anatomy
... Forms by age 12 Anterior and posterior table Nasofrontal duct— misnomer Frontal recess ...
... Forms by age 12 Anterior and posterior table Nasofrontal duct— misnomer Frontal recess ...
Anatomy Ch 2 101-111 [4-20
... Subarachnoid Space – contains cerebrospinal fluid and is continuous at foramen magnum with brain CSF. Terminates at SII. -Arachnoid Trabeculae – tissue strands continuous with arachnoid mater on one side of pia mater and arachnoid mater on the other spans subarachnoid space to interconnect the two m ...
... Subarachnoid Space – contains cerebrospinal fluid and is continuous at foramen magnum with brain CSF. Terminates at SII. -Arachnoid Trabeculae – tissue strands continuous with arachnoid mater on one side of pia mater and arachnoid mater on the other spans subarachnoid space to interconnect the two m ...
Ankle Joint Type
... Anterior talofibular: from anterior margin of lateral malleolus to adjacent lateral aspect of body and neck of talus. Posterior talofibular: horizontally, backwards and medially from lateral margin to posterior process of talus. Calcaneofibular: From malleolar fossa of lateral malleolus posteroinfer ...
... Anterior talofibular: from anterior margin of lateral malleolus to adjacent lateral aspect of body and neck of talus. Posterior talofibular: horizontally, backwards and medially from lateral margin to posterior process of talus. Calcaneofibular: From malleolar fossa of lateral malleolus posteroinfer ...
Decidua capsularis Extraembryonic coelom Placenta
... Completes meiosis II, forming the ovum and second polar ...
... Completes meiosis II, forming the ovum and second polar ...
pectoral region and axilla
... • By the end of the lecture the students should be able to : • Identify and describe the muscles of the pectoral region. Pectoralis major. Pectoralis minor. Subclavius. Serratus anterior. • Describe and demonstrate the boundaries and contents of the axilla. • Describe the formation of the br ...
... • By the end of the lecture the students should be able to : • Identify and describe the muscles of the pectoral region. Pectoralis major. Pectoralis minor. Subclavius. Serratus anterior. • Describe and demonstrate the boundaries and contents of the axilla. • Describe the formation of the br ...
TIBIA BONE Learning objectives
... greater obliquity of the femur. It has a body and two extremities/ ends (upper & lower). ...
... greater obliquity of the femur. It has a body and two extremities/ ends (upper & lower). ...
The_Ruminant_Gastrointestinal_Tract_3
... arise from the mesoderm. The nerves which innervate these tissues have their origin in the neural ectoderm. Liver and pancreas develop as branching, tubular extensions from the duodenum. The form of the digestive tube at an early embryonic age looks like this: ...
... arise from the mesoderm. The nerves which innervate these tissues have their origin in the neural ectoderm. Liver and pancreas develop as branching, tubular extensions from the duodenum. The form of the digestive tube at an early embryonic age looks like this: ...
PG_080_E0 Quick Reference Guide
... Insert a screw guide down to the bone, at least 1cm superior to edge of acetabulum, angled 30 degrees upwards. Insert a self-drilling screw, gently tap it through the cortex and screw it home with the T-wrench, without forcing the screw in any direction. The depth of insertion is 40-50 mm (almost th ...
... Insert a screw guide down to the bone, at least 1cm superior to edge of acetabulum, angled 30 degrees upwards. Insert a self-drilling screw, gently tap it through the cortex and screw it home with the T-wrench, without forcing the screw in any direction. The depth of insertion is 40-50 mm (almost th ...
BASAL FOREBRAIN ORGANIZATION
... between the caudate nucleus and putamen, which are referred to as striatum. Striatum: Although the caudate nucleus and putamen are separated by the projection fibers forming the internal capsule, bridges of cells connect the two nuclei in many places, especially at more rostral levels. The large rou ...
... between the caudate nucleus and putamen, which are referred to as striatum. Striatum: Although the caudate nucleus and putamen are separated by the projection fibers forming the internal capsule, bridges of cells connect the two nuclei in many places, especially at more rostral levels. The large rou ...
Posterior approach to the humerus
... Extending the approach Distal extension Splitting the triceps tendon limits distal exposure, which can be improved by approaching the humerus ...
... Extending the approach Distal extension Splitting the triceps tendon limits distal exposure, which can be improved by approaching the humerus ...
lower_ext_ppt.aug_o7
... 1. To teach clinically relevant gross anatomy 2. To make it easier to understand gross anatomy 3. To introduce a clinical lexicon ...
... 1. To teach clinically relevant gross anatomy 2. To make it easier to understand gross anatomy 3. To introduce a clinical lexicon ...
Mozkový kmen medulla oblongata pons Varoli mesencephalon
... • Compact part - dopaminergic (Tsai group) • Reticular part – GABA • Afferent connection from striatum (basal nuclei) smaller part from pallidum • Efferent connection to striatum, amygdala + ...
... • Compact part - dopaminergic (Tsai group) • Reticular part – GABA • Afferent connection from striatum (basal nuclei) smaller part from pallidum • Efferent connection to striatum, amygdala + ...
Drosophila embryogenesis

Drosophila embryogenesis, the process by which Drosophila (fruit fly) embryos form, is a favorite model system for geneticists and developmental biologists studying embryogenesis. The small size, short generation time, and large brood size make it ideal for genetic studies. Transparent embryos facilitate developmental studies. Drosophila melanogaster was introduced into the field of genetic experiments by Thomas Hunt Morgan in 1909.