Development of body cavities
... the Amniotic Sac, as shown here at the end of the third week. Cut edge of amniotic membrane The dashed line shows the approximate plane of section used for the cross sectional drawings on syllabus page 30. ...
... the Amniotic Sac, as shown here at the end of the third week. Cut edge of amniotic membrane The dashed line shows the approximate plane of section used for the cross sectional drawings on syllabus page 30. ...
Cliff - USD Biology
... a. avBNST stimulated by CRF from CeA a. To Glu and CRF cells in avBNST b. Glu projections from the avBNST i. avBNST contains the dmBNST and fuBNST c. CRF projections from the avBNST ...
... a. avBNST stimulated by CRF from CeA a. To Glu and CRF cells in avBNST b. Glu projections from the avBNST i. avBNST contains the dmBNST and fuBNST c. CRF projections from the avBNST ...
Thalamus for the RITE
... and thalami bilaterally. The globus pallidus is also involved but not exclusively as it is in many patients with carbon monoxide poisoning. The heads of the caudate and nuclei appear normal, and there is no significant overall atrophy of the brain. These are findings that tend to exclude Huntington ...
... and thalami bilaterally. The globus pallidus is also involved but not exclusively as it is in many patients with carbon monoxide poisoning. The heads of the caudate and nuclei appear normal, and there is no significant overall atrophy of the brain. These are findings that tend to exclude Huntington ...
Dr.Kaan Yücel yeditepeanatomyfhs122.wordpress.com Cerebellum
... the total number of neurons in the brain. Unlike the cerebral cortex, the cortex of the cerebellum has uniform anatomical structure, suggesting that there may be a similar mode of operation for all its possible functions. The cortex of the cerebellum is deeply folded. If one looks at the human cereb ...
... the total number of neurons in the brain. Unlike the cerebral cortex, the cortex of the cerebellum has uniform anatomical structure, suggesting that there may be a similar mode of operation for all its possible functions. The cortex of the cerebellum is deeply folded. If one looks at the human cereb ...
Head Features
... extends from pharynx (pharyngoesophageal ridge) to stomach entirely striated in dog; only cranial 2/3's striated in cat ...
... extends from pharynx (pharyngoesophageal ridge) to stomach entirely striated in dog; only cranial 2/3's striated in cat ...
Thorax-intercostal spaces
... Lower border and posterior surfaces costal cartilages of 2nd to 6th ribs. Attachments are variable and may even differ on the two sides. Direction of fibres: Lowest fibres are horizontal, become gradually oblique and upper most fibres are directed upwards and laterally. ...
... Lower border and posterior surfaces costal cartilages of 2nd to 6th ribs. Attachments are variable and may even differ on the two sides. Direction of fibres: Lowest fibres are horizontal, become gradually oblique and upper most fibres are directed upwards and laterally. ...
Lower Limb Exercise
... Place each of the following muscles in the appropriate compartment. – Adductor brevis – Vastus medialis – Vastus intermedias – Pectineus – Biceps femoris – Semitendinosus – Gluteus medius – Gluteus maximus – Semimembranosus ...
... Place each of the following muscles in the appropriate compartment. – Adductor brevis – Vastus medialis – Vastus intermedias – Pectineus – Biceps femoris – Semitendinosus – Gluteus medius – Gluteus maximus – Semimembranosus ...
EZMP1640 Arterial and Veneo Arterial and
... to this termination. The internal carotid arteries (ICAs) can be traced from the point where they enter the petrous portion of the temporal bone via the carotid canal and travel medially and anteriorly to emerge on the superior margin of the foramen lacerum. lacerum. It is here that each ICA lies wi ...
... to this termination. The internal carotid arteries (ICAs) can be traced from the point where they enter the petrous portion of the temporal bone via the carotid canal and travel medially and anteriorly to emerge on the superior margin of the foramen lacerum. lacerum. It is here that each ICA lies wi ...
orthopedics appliances used in systemic odontology and pam
... at the anterior part, it is necessary to maintain / keep this appliance at a predetermined period of time because it is possible to have vertical growth on the posterior bone blocks. The posterior PAM, during the orthopedic- orthodontic treatment, oral rehabilitation or others, has the objective of ...
... at the anterior part, it is necessary to maintain / keep this appliance at a predetermined period of time because it is possible to have vertical growth on the posterior bone blocks. The posterior PAM, during the orthopedic- orthodontic treatment, oral rehabilitation or others, has the objective of ...
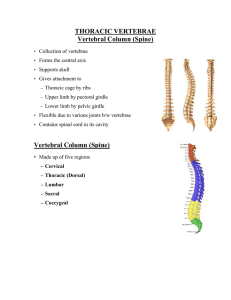
THORACIC VERTEBRAE
... • The spinous process is short, and nearly horizontal in direction. • The transverse processes are very short and have no articular facets for tubercle of ribs ...
... • The spinous process is short, and nearly horizontal in direction. • The transverse processes are very short and have no articular facets for tubercle of ribs ...
PLACE TITLE HERE USING ALL UPPER CASE
... tibial plate was defined as APL (figure 1). And the angle of PTS was defined θ. The change of JL at the posterior border of the plate [A] from 0 degree of PTS is calculated in 1/2APL × sin θ, and the change of JL at plate rear 1/4 [B] is half of [A] (figure 1-a). In addition, when 2 degrees slope os ...
... tibial plate was defined as APL (figure 1). And the angle of PTS was defined θ. The change of JL at the posterior border of the plate [A] from 0 degree of PTS is calculated in 1/2APL × sin θ, and the change of JL at plate rear 1/4 [B] is half of [A] (figure 1-a). In addition, when 2 degrees slope os ...
suboccipital triangle
... odontoid process, turning the face to the same side. The Obliquus capitis superior draws the head backward and to its own side. The Obliquus inferior rotates the atlas, and with it the skull, around the odontoid process, turning the face to the same side. ...
... odontoid process, turning the face to the same side. The Obliquus capitis superior draws the head backward and to its own side. The Obliquus inferior rotates the atlas, and with it the skull, around the odontoid process, turning the face to the same side. ...
(((Hindbrain (stunning) – myelencephalon (conspicuous grouting at
... part of Lateral nucleus (the basement of Debenhams; working there), OPTIC CHIASm! (lunatic tendencies in evidence in the pub) – Subfornical organ (stout), periventricular nucleus (rotund, singularly attrac- tive), infundibulum (dreaming of X), tuber cinereum (that rhythm!), tuberal nucleus (an erect ...
... part of Lateral nucleus (the basement of Debenhams; working there), OPTIC CHIASm! (lunatic tendencies in evidence in the pub) – Subfornical organ (stout), periventricular nucleus (rotund, singularly attrac- tive), infundibulum (dreaming of X), tuber cinereum (that rhythm!), tuberal nucleus (an erect ...
Scapula and Shoulder
... medial to its insertion to leave some tendon for reattachment during closure. The interval between the subscap and capsule is developed and the 2 layers are taken down individually. The subscap and capsule are divergent medially and are more easily separated here. The long head of the biceps can be ...
... medial to its insertion to leave some tendon for reattachment during closure. The interval between the subscap and capsule is developed and the 2 layers are taken down individually. The subscap and capsule are divergent medially and are more easily separated here. The long head of the biceps can be ...
Surgical Technique
... The Minimal Incision Total Hip (MITH ) surgical technique reduces the usual standard posterior lateral incision and expands the viewing area by using retractors and retraction maneuvers that take advantage of skin, fat, fascia and muscle compliances that are encountered at each layer of exposure. It ...
... The Minimal Incision Total Hip (MITH ) surgical technique reduces the usual standard posterior lateral incision and expands the viewing area by using retractors and retraction maneuvers that take advantage of skin, fat, fascia and muscle compliances that are encountered at each layer of exposure. It ...
Posterior Arch as Landmark for Atlas Horizontal Position
... one lateral mass may be large and the opposite small, or one can' have a different size and shape from the other. When the lateral masses are different sizes, the posterior arch may be in the correct center of each one, but the atlas plane line may not be a true landmark in relationship to the infer ...
... one lateral mass may be large and the opposite small, or one can' have a different size and shape from the other. When the lateral masses are different sizes, the posterior arch may be in the correct center of each one, but the atlas plane line may not be a true landmark in relationship to the infer ...
Nervous Structure of the Spinal Cord of the Young
... the neural canal: the peripheral motor fibre is derived from a collateral of a longitudinal fibre. The chief form of intercalary cell is very large: its dendrites extend into the contralateral dorsal funiculus, while its axon runs longitudinally and then crosses into the contralateral ventral funicu ...
... the neural canal: the peripheral motor fibre is derived from a collateral of a longitudinal fibre. The chief form of intercalary cell is very large: its dendrites extend into the contralateral dorsal funiculus, while its axon runs longitudinally and then crosses into the contralateral ventral funicu ...
PowerPoint Sunusu
... The moon is crescent I am filling my three-cornered hat with beas falling off the sky ...
... The moon is crescent I am filling my three-cornered hat with beas falling off the sky ...
Abdomen Part 2
... from the celiac, entering the liver ANTERIOR to the portal vein. The common hepatic artery arises from the celiac and branches into the Rt gastric and gastroduodenal arteries and ...
... from the celiac, entering the liver ANTERIOR to the portal vein. The common hepatic artery arises from the celiac and branches into the Rt gastric and gastroduodenal arteries and ...
Document
... upper limb. It begins in the lateral cervical region (posterior triangle) and extends into the axilla. • The brachial plexus is formed by the union of the anterior rami of the (C5-8) and T1 nerves, which constitute the roots of brachial plexus • The roots usually pass through the gap between the ant ...
... upper limb. It begins in the lateral cervical region (posterior triangle) and extends into the axilla. • The brachial plexus is formed by the union of the anterior rami of the (C5-8) and T1 nerves, which constitute the roots of brachial plexus • The roots usually pass through the gap between the ant ...
Elbow arthroscopy (R)
... • An 18G needle is inserted into the midlateral (soft spot) portal and the joint distended with 15-30mL of saline. The average volume capacity is 23mL but this is reduced in elbow contractures by up to half. • The anteromedial portal is developed first. A small incision is made anterior to the inter ...
... • An 18G needle is inserted into the midlateral (soft spot) portal and the joint distended with 15-30mL of saline. The average volume capacity is 23mL but this is reduced in elbow contractures by up to half. • The anteromedial portal is developed first. A small incision is made anterior to the inter ...
Drosophila embryogenesis

Drosophila embryogenesis, the process by which Drosophila (fruit fly) embryos form, is a favorite model system for geneticists and developmental biologists studying embryogenesis. The small size, short generation time, and large brood size make it ideal for genetic studies. Transparent embryos facilitate developmental studies. Drosophila melanogaster was introduced into the field of genetic experiments by Thomas Hunt Morgan in 1909.