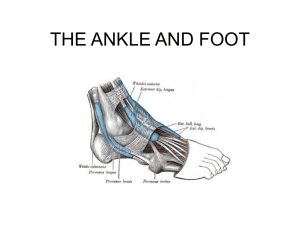
Posterior Leg and Plantar Foot
... 2. Extensor hallucis longus – deep, btw tibialis anterior and EDL Extends the great toe and dorsiflexes the ankle 3. Extensor digitorum longus – most lateral of dorsiflexors (O: fibula) The 4 tendons should be visible during dorsiflexion Each tendon forms an extensor expansion that divides O ...
... 2. Extensor hallucis longus – deep, btw tibialis anterior and EDL Extends the great toe and dorsiflexes the ankle 3. Extensor digitorum longus – most lateral of dorsiflexors (O: fibula) The 4 tendons should be visible during dorsiflexion Each tendon forms an extensor expansion that divides O ...
Bones of upper limb
... Avulsion of the epiphysis of the medial epicondyle is also common in childhood because then the medial ligament is much stronger than the bond of union between the epiphysis and the diaphysis. ...
... Avulsion of the epiphysis of the medial epicondyle is also common in childhood because then the medial ligament is much stronger than the bond of union between the epiphysis and the diaphysis. ...
OTA Tip-of-the-Month: Medial Talar Pin Placement for Universal
... and alignment. All distractor pins are placed from medial to lateral, in the coronal plane. The proximal pin is either in the proximal tibial metaphysis, posteriorly (for IM nailing) or in the meta-diaphysis for ORIF of pilon fractures. The distal Schantz pin may be placed in the posterior tibia, th ...
... and alignment. All distractor pins are placed from medial to lateral, in the coronal plane. The proximal pin is either in the proximal tibial metaphysis, posteriorly (for IM nailing) or in the meta-diaphysis for ORIF of pilon fractures. The distal Schantz pin may be placed in the posterior tibia, th ...
Slide 1 - mcstmf
... trunks. • Nerve supply of the lungs is by a pulmonary plexus which is formed from branches of the sympathetic trunk and ...
... trunks. • Nerve supply of the lungs is by a pulmonary plexus which is formed from branches of the sympathetic trunk and ...
Triangles of the neck
... The hyoid bone, at the level of C3 vertebra, provide an attachment for the two groups. The muscles are called the strap muscles from their flat shape and they are in the same plane as the body wall musculature, rectus abdominis ...
... The hyoid bone, at the level of C3 vertebra, provide an attachment for the two groups. The muscles are called the strap muscles from their flat shape and they are in the same plane as the body wall musculature, rectus abdominis ...
1-The dorsal nasal meatus
... Nasal ethmoid conchae: Are thin osseous scrolls that are covered on each side with m.m. are originated with a basal lamella from the lateral wall of the nasal cavity. This lamella projects medially like a shelf and is continued by one , two , or more spirals lamellae which roll up on themselves and ...
... Nasal ethmoid conchae: Are thin osseous scrolls that are covered on each side with m.m. are originated with a basal lamella from the lateral wall of the nasal cavity. This lamella projects medially like a shelf and is continued by one , two , or more spirals lamellae which roll up on themselves and ...
The Anatomy of Pedal Vasculature and Principals for Pedal
... • Central arterial line of the foot • Major role in limb salvage and ulcers • Conventional angiography can outline the anastomosis • Stem supply for all distal forefoot circulation. ...
... • Central arterial line of the foot • Major role in limb salvage and ulcers • Conventional angiography can outline the anastomosis • Stem supply for all distal forefoot circulation. ...
Pelvis - ShakEM
... Arterial Superior rectal artery (from inferior mesenteric artery), Middle/inferior rectal, Median sacral Venous Free anastomosis occurs with all branches draining the rectum Pelvic floor Levator ani, obturator internus, piriformis Reproductive organs Uterus and fallopian tubes Fundus Body Enclosed b ...
... Arterial Superior rectal artery (from inferior mesenteric artery), Middle/inferior rectal, Median sacral Venous Free anastomosis occurs with all branches draining the rectum Pelvic floor Levator ani, obturator internus, piriformis Reproductive organs Uterus and fallopian tubes Fundus Body Enclosed b ...
01-body cavities2008-02
... During the 5th week , myoblasts from 3,4;5 somites migrate into the developing diaphragm ( S. T. ) bringing their nerve fibers with them ( phrenic n. ) which arise from the venteral primary rami of the 3rd, 4th; 5th cervical spinal nerves. The embryonic phrenic ns. Enter the diaphragm by passing thr ...
... During the 5th week , myoblasts from 3,4;5 somites migrate into the developing diaphragm ( S. T. ) bringing their nerve fibers with them ( phrenic n. ) which arise from the venteral primary rami of the 3rd, 4th; 5th cervical spinal nerves. The embryonic phrenic ns. Enter the diaphragm by passing thr ...
companion animal
... drawn. The first, caudal line, starts on the proximal half of the ilium, and extends distally following the femoral shaft. The second, cranial line is drawn parallel to the caudal. The ventral and dorsal borders are drawn as far as is needed. Reversed saphenous conduit flap(2) The reverse saphenous ...
... drawn. The first, caudal line, starts on the proximal half of the ilium, and extends distally following the femoral shaft. The second, cranial line is drawn parallel to the caudal. The ventral and dorsal borders are drawn as far as is needed. Reversed saphenous conduit flap(2) The reverse saphenous ...
Bones of upper limb
... Avulsion of the epiphysis of the medial epicondyle is also common in childhood because the medial ligament is much stronger than the bond of union between the epiphysis and the diaphysis. ...
... Avulsion of the epiphysis of the medial epicondyle is also common in childhood because the medial ligament is much stronger than the bond of union between the epiphysis and the diaphysis. ...
13 Clam Dissection
... Introduction The phylum Mollusca includes snails, clams, chitons, slugs, limpets, octopi, and squid. As mollusks develop from a fertilized egg to an adult, most pass through a larval stage called the trocophore. The trocophore is a ciliated, free-swimming stage. Mollusks also have a radula or file-l ...
... Introduction The phylum Mollusca includes snails, clams, chitons, slugs, limpets, octopi, and squid. As mollusks develop from a fertilized egg to an adult, most pass through a larval stage called the trocophore. The trocophore is a ciliated, free-swimming stage. Mollusks also have a radula or file-l ...
... Introduction The phylum Mollusca includes snails, clams, chitons, slugs, limpets, octopi, and squid. As mollusks develop from a fertilized egg to an adult, most pass through a larval stage called the trocophore. The trocophore is a ciliated, free-swimming stage. Mollusks also have a radula or file-l ...
41/44 Appendix
... This is a transverse section of the pelvis at the level of the anterior superior iliac spine. The ASIS is a superficial structure in most patients in continuity with the iliac crest superiorly, and inferiorly with the anterior inferior iliac spine which is only palpable in thin patients. Posterior t ...
... This is a transverse section of the pelvis at the level of the anterior superior iliac spine. The ASIS is a superficial structure in most patients in continuity with the iliac crest superiorly, and inferiorly with the anterior inferior iliac spine which is only palpable in thin patients. Posterior t ...
incomplete formation of posterior cord of brachial plexus: a case report
... branching patterns of brachial plexus are quite common and have been reported time and again by several authors. The variations can occur in the formation of trunks, divisions, cords, at the ...
... branching patterns of brachial plexus are quite common and have been reported time and again by several authors. The variations can occur in the formation of trunks, divisions, cords, at the ...
ankle_muscle
... – Plantar flexion • The tendon goes under the foot from the lateral to the medial surface, thus aiding in support for the transverse arch. ...
... – Plantar flexion • The tendon goes under the foot from the lateral to the medial surface, thus aiding in support for the transverse arch. ...
Caroline Hing MB BS BSc MSc MD FRCS FRCS(Tr&Orth) Shamim Umarji
... CT scans evaluate intra-articular fractures MRI if soft tissue injury suspected Bone scans to evaluate RSD / CRPS ...
... CT scans evaluate intra-articular fractures MRI if soft tissue injury suspected Bone scans to evaluate RSD / CRPS ...
Dept of Radiology and Neurology Penn State Milton S
... The posterior fossa is home for the brainstem and cerebellum. The brainstem contains all the cranial nerve nuclei and many efferent and afferent fiber tracts that connect the brain with the rest of the body while the cerebellum is the major organ of coordination for all motor functions, as well as m ...
... The posterior fossa is home for the brainstem and cerebellum. The brainstem contains all the cranial nerve nuclei and many efferent and afferent fiber tracts that connect the brain with the rest of the body while the cerebellum is the major organ of coordination for all motor functions, as well as m ...
document
... • It is composed of two muscles. The psoas major is a long, thick, fusiform one that lies lateral to the lumbar region of the vertebral column. It arises from the transverse process, vertebral bodies and associated intervertebral disc of L1to L5vertebrae. The muscle descends laterally along the brim ...
... • It is composed of two muscles. The psoas major is a long, thick, fusiform one that lies lateral to the lumbar region of the vertebral column. It arises from the transverse process, vertebral bodies and associated intervertebral disc of L1to L5vertebrae. The muscle descends laterally along the brim ...
11-Arm_Elbow_Joint
... o Avulsion of the epiphysis of the medial epicondyle is also common in childhood because then the medial ligament is much stronger than the bond of union between the epiphysis and the diaphysis. ...
... o Avulsion of the epiphysis of the medial epicondyle is also common in childhood because then the medial ligament is much stronger than the bond of union between the epiphysis and the diaphysis. ...
Unit 30: Nose, Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses
... and lateral cartilages (Plates 36; 7.67). On the side with the largest cavity, cut the soft palate, soft parts of the nose and upper lip in line with the cavity. Using your hand saw, cut through the skull in a sagittal plane which passes through the larger of the two cavities. Start the saw cut at t ...
... and lateral cartilages (Plates 36; 7.67). On the side with the largest cavity, cut the soft palate, soft parts of the nose and upper lip in line with the cavity. Using your hand saw, cut through the skull in a sagittal plane which passes through the larger of the two cavities. Start the saw cut at t ...
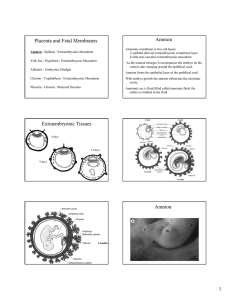
Placenta and Fetal Membranes
... Decidual Reaction – stromal cells – accumulate glycogen and lipid, called Decidual Cells Decidua basalis - forms maternal component of the placenta; associates with the chorion frondosom Decidua capsularis - superfical layer overlying the entire embryoblast - this layer eventually degenerates; assoc ...
... Decidual Reaction – stromal cells – accumulate glycogen and lipid, called Decidual Cells Decidua basalis - forms maternal component of the placenta; associates with the chorion frondosom Decidua capsularis - superfical layer overlying the entire embryoblast - this layer eventually degenerates; assoc ...
08 Placenta and Fetal Membranes total
... Making the Placenta By 8 weeks - chorionic stem villi over the entire surface of the chorionic sac Those villi associated with the decidua basalis increase in size and more villi form. Enlargement includes further branching of the anchoring villus - chorion frondosum. The villi continue to enlarge d ...
... Making the Placenta By 8 weeks - chorionic stem villi over the entire surface of the chorionic sac Those villi associated with the decidua basalis increase in size and more villi form. Enlargement includes further branching of the anchoring villus - chorion frondosum. The villi continue to enlarge d ...
Drosophila embryogenesis

Drosophila embryogenesis, the process by which Drosophila (fruit fly) embryos form, is a favorite model system for geneticists and developmental biologists studying embryogenesis. The small size, short generation time, and large brood size make it ideal for genetic studies. Transparent embryos facilitate developmental studies. Drosophila melanogaster was introduced into the field of genetic experiments by Thomas Hunt Morgan in 1909.