BACK AND LIMBS - OUTLINES INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMICAL
... i. Fertilization age – age counting from time of fertilization ii. Gestational age – from first day of last normal menstrual period (doctors use this - 2 weeks longer than fert. age) C. Miscellaneous i. Teratogens – environmental agents that cause congenital abnormalities 1. the embryonic period is ...
... i. Fertilization age – age counting from time of fertilization ii. Gestational age – from first day of last normal menstrual period (doctors use this - 2 weeks longer than fert. age) C. Miscellaneous i. Teratogens – environmental agents that cause congenital abnormalities 1. the embryonic period is ...
Immunohistochemical Identification of Phosphorylated Extracellular
... was constitutional expression of pERK1/2-LI neurons in the solitary nuclei and some reticular nuclei of the brain stem (n=3)(data not shown). As compared with the control, there was significant expression of pERK1/2-LI neurons in the superior, medial, and inferior vestibular nuclei bilaterally, 5 mi ...
... was constitutional expression of pERK1/2-LI neurons in the solitary nuclei and some reticular nuclei of the brain stem (n=3)(data not shown). As compared with the control, there was significant expression of pERK1/2-LI neurons in the superior, medial, and inferior vestibular nuclei bilaterally, 5 mi ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... transversarium. An important anatomic feature of the atlas is the inward projection of a prominent tubercle of bone on each side cranial and medially to the lateral masses. These structures give rise to the transverse ligament that keeps the dens confined to the anterior third of the atlantal ring. ...
... transversarium. An important anatomic feature of the atlas is the inward projection of a prominent tubercle of bone on each side cranial and medially to the lateral masses. These structures give rise to the transverse ligament that keeps the dens confined to the anterior third of the atlantal ring. ...
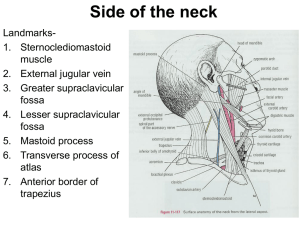
Side of the neck
... Insertion-lateral surface of the mastoid process, from its tip to its superior border & lateral ½ of the superior nuchal line ...
... Insertion-lateral surface of the mastoid process, from its tip to its superior border & lateral ½ of the superior nuchal line ...
VASCULARIZATION OF THE HEAD AND NECK
... --- consists of posterior cerebral connecting to internal carotid via posterior communicating branches AND anterior cerebral arteries connected by an anterior communicating branch -------- variety of clinical concerns with this circle: though the arteries anastomose, these connections are not really ...
... --- consists of posterior cerebral connecting to internal carotid via posterior communicating branches AND anterior cerebral arteries connected by an anterior communicating branch -------- variety of clinical concerns with this circle: though the arteries anastomose, these connections are not really ...
Vertebral column and back Bony framework of the vertebral
... Bony framework of the vertebral column The vertebral column: • Axial skeleton – forms the axis from which our upper and lower limbs hang off • Regionally distinct vertebrae (33) • Intervertebral joints ...
... Bony framework of the vertebral column The vertebral column: • Axial skeleton – forms the axis from which our upper and lower limbs hang off • Regionally distinct vertebrae (33) • Intervertebral joints ...
Anatomy - Beck-Shop
... transversarium. An important anatomic feature of the atlas is the inward projection of a prominent tubercle of bone on each side cranial and medially to the lateral masses. These structures give rise to the transverse ligament that keeps the dens confined to the anterior third of the atlantal ring. ...
... transversarium. An important anatomic feature of the atlas is the inward projection of a prominent tubercle of bone on each side cranial and medially to the lateral masses. These structures give rise to the transverse ligament that keeps the dens confined to the anterior third of the atlantal ring. ...
Vertebral Column, Sinuses that Collect Venous Blood, Dorsal View
... outside the dura matter, extends from the sacral levels to the foramen magnum. Blood goes in different directions because there are no valves which exist in veins of other parts of body, such as those leading to the heart from the legs. That is a problem with the transmission of cancerous cells thro ...
... outside the dura matter, extends from the sacral levels to the foramen magnum. Blood goes in different directions because there are no valves which exist in veins of other parts of body, such as those leading to the heart from the legs. That is a problem with the transmission of cancerous cells thro ...
Gross Written Midterm Review
... where does pterygoid plexus of veins drain – surrounds maxillary a. and its branches; drains into deep facial vein; connected to cavernous sinus via emissary veins that traverse foramina at the base of skull; important because infections in infratemporal region may pass into cavernous sinus and caus ...
... where does pterygoid plexus of veins drain – surrounds maxillary a. and its branches; drains into deep facial vein; connected to cavernous sinus via emissary veins that traverse foramina at the base of skull; important because infections in infratemporal region may pass into cavernous sinus and caus ...
Cerebral Cortex - LSU School of Medicine
... Lesion of left visual cortex causes right homonymous hemianopsia ...
... Lesion of left visual cortex causes right homonymous hemianopsia ...
323Lecture4 - Dr. Stuart Sumida
... transfer of weight through head of the femur to cortical bone of ...
... transfer of weight through head of the femur to cortical bone of ...
ON THE INTERNAL ANATOMY OF THE FAMILIES OF OPISTHOMI.
... their surface. The oesophagus is more or less funnel-shaped and is imperceptibly continuous with the stomach. The inner surface of the oesophagus is raised into numerous longitudinal folds. The stomach is long, straight, tubular and somewhat tapering. It is placed on the left side. The cardiac porti ...
... their surface. The oesophagus is more or less funnel-shaped and is imperceptibly continuous with the stomach. The inner surface of the oesophagus is raised into numerous longitudinal folds. The stomach is long, straight, tubular and somewhat tapering. It is placed on the left side. The cardiac porti ...
The nuclei
... 6- The gracile and cuneate nuclei: They are situated posteriorly in the closed medulla, the gracile being the more medially placed, while the cuneate being the lateral one. Their efferents pass ventrally and cross the midline as the internal arcuate fiber and then they will form the medial lemniscus ...
... 6- The gracile and cuneate nuclei: They are situated posteriorly in the closed medulla, the gracile being the more medially placed, while the cuneate being the lateral one. Their efferents pass ventrally and cross the midline as the internal arcuate fiber and then they will form the medial lemniscus ...
Stephen Gilbert - University of Toronto Libraries
... The embryo and the related part of the chorion. The extra-embryonic mesoderm and the amnion are cut in the sagittal plane. The endoderm is intact, and the embryo is dissected to expose the developing cardiovascular system. ...
... The embryo and the related part of the chorion. The extra-embryonic mesoderm and the amnion are cut in the sagittal plane. The endoderm is intact, and the embryo is dissected to expose the developing cardiovascular system. ...
04Brachial_plexus_&_Radial_nerve2012-09
... .Medial pectoral n. .Medial root to median n. .Medial cutaneous n of arm. .Medial cutaneous n of forearm. ...
... .Medial pectoral n. .Medial root to median n. .Medial cutaneous n of arm. .Medial cutaneous n of forearm. ...
full article (0.56 Mo)
... cap represents the camera spermatis of MICHAEL. In one series of 5-micron crosssections of a gravid female, two fine cellular, but apparently non-tubular strands converge from the intercoxal regions of legs IV to the antero-ventral portion of the central ovarian mass. \Vhile these might conceivably ...
... cap represents the camera spermatis of MICHAEL. In one series of 5-micron crosssections of a gravid female, two fine cellular, but apparently non-tubular strands converge from the intercoxal regions of legs IV to the antero-ventral portion of the central ovarian mass. \Vhile these might conceivably ...
Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
... polyps medial to the middle turbinate, but it is best to preserve this mucosa. A course of preoperative steroids will help reduce the size of the polyps. Only remove polyps that come from the posterior ethmoid cells under the superior turbinate and not polyps that are based on the septum or the midd ...
... polyps medial to the middle turbinate, but it is best to preserve this mucosa. A course of preoperative steroids will help reduce the size of the polyps. Only remove polyps that come from the posterior ethmoid cells under the superior turbinate and not polyps that are based on the septum or the midd ...
1. Stimuli--Orthopedic Anatomical Terminology
... Lateral- on the side; farther from the median or midsaggital plane There is a spiral fx of the lateral malleolus at the level of the mortise with approx 2 mm of displacement of the distal fragment. There is also widening of the medial joint mortise. ...
... Lateral- on the side; farther from the median or midsaggital plane There is a spiral fx of the lateral malleolus at the level of the mortise with approx 2 mm of displacement of the distal fragment. There is also widening of the medial joint mortise. ...
SSN Anatomy #2
... 1. One day, a 48-year-old nurse practitioner comes to your office, complaining of a “colicky” pain in the epigastric region. She notices that eating foods that are high in fat exacerbates the pain. When you examine her, you find that she is jaundiced. Upon taking her history, you also find that she ...
... 1. One day, a 48-year-old nurse practitioner comes to your office, complaining of a “colicky” pain in the epigastric region. She notices that eating foods that are high in fat exacerbates the pain. When you examine her, you find that she is jaundiced. Upon taking her history, you also find that she ...
Drosophila embryogenesis

Drosophila embryogenesis, the process by which Drosophila (fruit fly) embryos form, is a favorite model system for geneticists and developmental biologists studying embryogenesis. The small size, short generation time, and large brood size make it ideal for genetic studies. Transparent embryos facilitate developmental studies. Drosophila melanogaster was introduced into the field of genetic experiments by Thomas Hunt Morgan in 1909.