Structure Function/Use Brow Spot Nictitating Membrane Cloacal
... Skin attached between the digits of the hind legs that allows the frogs feet to have greater surface area and swim faster (like flipper when snorkeling) ...
... Skin attached between the digits of the hind legs that allows the frogs feet to have greater surface area and swim faster (like flipper when snorkeling) ...
FREE Sample Here - Test bank Store
... http://testbanksstore.eu/Test-Bank-for-Essentials-of-Cardiopulmonary-Physical-Therapy-3rdEdition-by-Hillegass C. The presence of blood in the pleural space D. A bacterial infection with resultant pus in the pleural space ANS: A Infection with a resultant inflammatory response within the pleura is te ...
... http://testbanksstore.eu/Test-Bank-for-Essentials-of-Cardiopulmonary-Physical-Therapy-3rdEdition-by-Hillegass C. The presence of blood in the pleural space D. A bacterial infection with resultant pus in the pleural space ANS: A Infection with a resultant inflammatory response within the pleura is te ...
Proceedings of the United States National Museum
... deep channel on the basioccipital and exoccipital, and terminates on This is interpreted the posterior margin of the last mentioned bone. to represent the posterior lacerated foramen. The basisphenoid is a flat bone and may have been largely concealed by the vomer. No pieces of the vomer were preser ...
... deep channel on the basioccipital and exoccipital, and terminates on This is interpreted the posterior margin of the last mentioned bone. to represent the posterior lacerated foramen. The basisphenoid is a flat bone and may have been largely concealed by the vomer. No pieces of the vomer were preser ...
Development anatomy of the respiratory organ
... embryonic phase the formation of a groove in the ventral lower pharynx, the sulcus laryngotrachealis • Thus the asymmetry of the (stage 10, ca. 28 days, 10 ). main bronchi, as they present in adults, is already • After a couple of days - from established. the lower part - a bud forms, • The subseque ...
... embryonic phase the formation of a groove in the ventral lower pharynx, the sulcus laryngotrachealis • Thus the asymmetry of the (stage 10, ca. 28 days, 10 ). main bronchi, as they present in adults, is already • After a couple of days - from established. the lower part - a bud forms, • The subseque ...
lateral - Personal
... • At 9 months of age, cranium is ½ adult size • Mandible and maxilla are foreshortened but lengthen with age • The arms and legs grow at a faster rate than the head and trunk, leading to adult proportions ...
... • At 9 months of age, cranium is ½ adult size • Mandible and maxilla are foreshortened but lengthen with age • The arms and legs grow at a faster rate than the head and trunk, leading to adult proportions ...
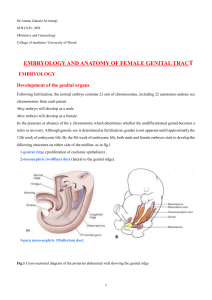
Dr.Amina Zakaria Al-tutunji M.B.Ch.B., MD. Obstetrics and
... The longitudinal axis of the uterus is at right angle to the vagina & normally tilts forwards is called anteversion & its usually flexed forwards on itself at the isthmus is called anteflexion. As in fig.7 .In around 20% of women, this tilt is not forwards but backwards-retroversion & retroflexion. ...
... The longitudinal axis of the uterus is at right angle to the vagina & normally tilts forwards is called anteversion & its usually flexed forwards on itself at the isthmus is called anteflexion. As in fig.7 .In around 20% of women, this tilt is not forwards but backwards-retroversion & retroflexion. ...
Anatomy and physiology of the nose and paranasal sinuses 1
... tissue. The lower lateral cartilages help in shaping the nostrils. The outer surface is covered by skin which is thin and mobile above and thick and adherent to the subcutaneous structures near the tip. Clinical point(2): surgical refashioning of the lower lateral cartilages is an important point in ...
... tissue. The lower lateral cartilages help in shaping the nostrils. The outer surface is covered by skin which is thin and mobile above and thick and adherent to the subcutaneous structures near the tip. Clinical point(2): surgical refashioning of the lower lateral cartilages is an important point in ...
PDF
... The intention in extirpating neuromere d was to remove the notochordal tip. That this was done successfully was seen in the serial sections, which showed that a smaller or larger portion of the tip of the notochord was absent. In other cases the rostral end of the notochord was split into two or was ...
... The intention in extirpating neuromere d was to remove the notochordal tip. That this was done successfully was seen in the serial sections, which showed that a smaller or larger portion of the tip of the notochord was absent. In other cases the rostral end of the notochord was split into two or was ...
The Regional Anatomy of the Upper limb
... lies deep to the pectoralis minor; behind, related to the subscapularis; laterally, posteriorly, medially, related to the lateral cord, posterioe cord and medial cord respectively; The branch--The thoracoacromial a. To pierces clavipectoral fascia and divides into 3 branches to supply the pe ...
... lies deep to the pectoralis minor; behind, related to the subscapularis; laterally, posteriorly, medially, related to the lateral cord, posterioe cord and medial cord respectively; The branch--The thoracoacromial a. To pierces clavipectoral fascia and divides into 3 branches to supply the pe ...
Anatomy – Exam 2 (Part 2)
... Trendelenburg’s Gait – when both sides are paralyzed each leg swings out laterally so it doesn’t drag Trendelenburg’s Test – positive when you have patient stand on leg of affected side (assuming only one superior gluteal nerve is affected) and lift non-affected leg causing the pelvis to tilt do ...
... Trendelenburg’s Gait – when both sides are paralyzed each leg swings out laterally so it doesn’t drag Trendelenburg’s Test – positive when you have patient stand on leg of affected side (assuming only one superior gluteal nerve is affected) and lift non-affected leg causing the pelvis to tilt do ...
Anatomy – Exam 2 (Part 2)
... Trendelenburg’s Gait – when both sides are paralyzed each leg swings out laterally so it doesn’t drag Trendelenburg’s Test – positive when you have patient stand on leg of affected side (assuming only one superior gluteal nerve is affected) and lift non-affected leg causing the pelvis to tilt do ...
... Trendelenburg’s Gait – when both sides are paralyzed each leg swings out laterally so it doesn’t drag Trendelenburg’s Test – positive when you have patient stand on leg of affected side (assuming only one superior gluteal nerve is affected) and lift non-affected leg causing the pelvis to tilt do ...
muscles of the pectoral girdle
... • The only joints between the shoulder girdle and axial skeleton are the sternoclavicular joints on each side. • No joint exists between each scapula and the rib cage; instead the muscular connection between the two permits relatively great mobility of the shoulder girdle in relation to the pelvic g ...
... • The only joints between the shoulder girdle and axial skeleton are the sternoclavicular joints on each side. • No joint exists between each scapula and the rib cage; instead the muscular connection between the two permits relatively great mobility of the shoulder girdle in relation to the pelvic g ...
Thorax – skeleton, joints, muscles, arterial blood supply, venous and
... Thorax – skeleton, joints, muscles, arterial blood supply, venous and lymphatic drainage, innervation, regional anatomy Thorax upper part of the trunk box for vital organs ...
... Thorax – skeleton, joints, muscles, arterial blood supply, venous and lymphatic drainage, innervation, regional anatomy Thorax upper part of the trunk box for vital organs ...
Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 03.January.2014 Friday
... The moon is crescent I am filling my three-cornered hat with beas falling off the sky ...
... The moon is crescent I am filling my three-cornered hat with beas falling off the sky ...
Embryology Review (from Ida) - U
... rule of 4’s, but tongue, lungs, GI and diaphragm also begin formation then Week 4-6 is the critical period for TA, VSD, ASD, etc.) Wk 4-5: limb defect critical period Wk 5-6: cleft lip critical period Wk 5-7: gonad differentiation, kidney, bladder, rectum formation Wk 6-7: teeth/palate c ...
... rule of 4’s, but tongue, lungs, GI and diaphragm also begin formation then Week 4-6 is the critical period for TA, VSD, ASD, etc.) Wk 4-5: limb defect critical period Wk 5-6: cleft lip critical period Wk 5-7: gonad differentiation, kidney, bladder, rectum formation Wk 6-7: teeth/palate c ...
* The function of extensor digitorum :
... •It is originated from medial cord of brachial plexus. •In the upper part of the upper arm it is anterior. •In the midshaft : it pierces the medial intermuscular septum. •In the lower part: it is in the posterior compartment. •It then passes posterior to the medial epicondyle of the humerus. •It doe ...
... •It is originated from medial cord of brachial plexus. •In the upper part of the upper arm it is anterior. •In the midshaft : it pierces the medial intermuscular septum. •In the lower part: it is in the posterior compartment. •It then passes posterior to the medial epicondyle of the humerus. •It doe ...
The distribution of muscle fibre types in chick embryo wings
... 1981). However, it is not known whether motoneurons are intrinsically determined for fast/slow type. If they are, then it would be easy to envisage a simple matching process whereby motoneurons can only make or retain contact with the appropriate fibre type. If they are not, it would be necessary fo ...
... 1981). However, it is not known whether motoneurons are intrinsically determined for fast/slow type. If they are, then it would be easy to envisage a simple matching process whereby motoneurons can only make or retain contact with the appropriate fibre type. If they are not, it would be necessary fo ...
PDF
... 1981). However, it is not known whether motoneurons are intrinsically determined for fast/slow type. If they are, then it would be easy to envisage a simple matching process whereby motoneurons can only make or retain contact with the appropriate fibre type. If they are not, it would be necessary fo ...
... 1981). However, it is not known whether motoneurons are intrinsically determined for fast/slow type. If they are, then it would be easy to envisage a simple matching process whereby motoneurons can only make or retain contact with the appropriate fibre type. If they are not, it would be necessary fo ...
ANATOMY OF THE FOREARM
... INTERMEDIATE COMPARTMENT It can sometimes be classed as a superficial muscle, but in most cadavers it lies between the deep and superficial muscle layers. The muscle is a good anatomical landmark in the forearm – the median nerve and ulnar artery pass between its two heads, and then travel posterior ...
... INTERMEDIATE COMPARTMENT It can sometimes be classed as a superficial muscle, but in most cadavers it lies between the deep and superficial muscle layers. The muscle is a good anatomical landmark in the forearm – the median nerve and ulnar artery pass between its two heads, and then travel posterior ...
Unit 35: Leg and Dorsum of Foot
... foot and toes is supplied by the superficial peroneal nerve. Its branches should have been seen when the dorsal venous arch was cleaned. Follow its branches superiorly to find the common trunk which exits the deep fascia on the lateral side of the leg just below the mid-point of the leg. In the inte ...
... foot and toes is supplied by the superficial peroneal nerve. Its branches should have been seen when the dorsal venous arch was cleaned. Follow its branches superiorly to find the common trunk which exits the deep fascia on the lateral side of the leg just below the mid-point of the leg. In the inte ...
Shoulder
... INDICATION: Shoulder pain and limited range of motion. TECHNIQUE: Axial gradient echo, proton density fat-suppressed, coronal proton density, T2 fatsuppressed, axial T2, and sagittal proton density fat-suppressed images of the right shoulder were performed on the 1.5 Tesla magnet. FINDINGS: Moderate ...
... INDICATION: Shoulder pain and limited range of motion. TECHNIQUE: Axial gradient echo, proton density fat-suppressed, coronal proton density, T2 fatsuppressed, axial T2, and sagittal proton density fat-suppressed images of the right shoulder were performed on the 1.5 Tesla magnet. FINDINGS: Moderate ...
Anatomy and Embryology of the Pharynx
... By end of 4th week, four pairs of arches are visible on the surface (not 5th and 6th ) and a buccopharyngeal membrane ruptures forming communication between primitive oral cavity and foregut ...
... By end of 4th week, four pairs of arches are visible on the surface (not 5th and 6th ) and a buccopharyngeal membrane ruptures forming communication between primitive oral cavity and foregut ...
upper limb joints
... The moon is crescent I am filling my three-cornered hat with beas falling off the sky ...
... The moon is crescent I am filling my three-cornered hat with beas falling off the sky ...
BLOOD SUPPLY OF THE BRAIN
... Hypoplasia or absence of vessels occurs in some brains. Degenerative diseases of the arteries: These can lead to occlusion or to hemorrhage. Inflammatory diseases of the arteries: Inflammatory diseases, ...
... Hypoplasia or absence of vessels occurs in some brains. Degenerative diseases of the arteries: These can lead to occlusion or to hemorrhage. Inflammatory diseases of the arteries: Inflammatory diseases, ...
Drosophila embryogenesis

Drosophila embryogenesis, the process by which Drosophila (fruit fly) embryos form, is a favorite model system for geneticists and developmental biologists studying embryogenesis. The small size, short generation time, and large brood size make it ideal for genetic studies. Transparent embryos facilitate developmental studies. Drosophila melanogaster was introduced into the field of genetic experiments by Thomas Hunt Morgan in 1909.