* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pelvis - ShakEM
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
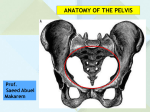
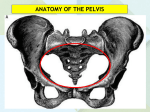
Anatomy - Pelvis Pelvic Girdle Pelvis formed of: 2 hips bones (each made up of ilium, ischium, pubis), Sacrum, Coccyx Joined anteriorly at symphysis pubis Pelvis major (greater or false pelvis) – superior to superior pelvic aperture; Pelvis minor (lessor or true pelvis) Superior pelvic aperture separates major from minor. Edge of this called pelvic rim. Inferior pelvic aperture Pelvic joints Sacroiliac joint Type Synovial joint Articulation articular surfaces ilium/ sacrum Capsule Bound to articular margins Ligaments Anterior sacroiliac ligament Flat band Interosseous sacroiliac ligament Posterior sacroiliac ligament Movement Very little movement Stability Entirely depends on ligaments Sacrotuberous ligament Post ilium/sacrum/coccyx to ischial tuberosity Sacrospinous ligament Lower sacrum and coccyx to ischial spine Iliolumbar ligament Iliac crest/ant SI ligament to transverse process L5 Lumbosacral joints; Sacrococcygeal joint Pubic symphysis Secondary cartilaginous joint, Fibrocartilaginous disc Lumbar and sacral plexuses Lumbar plexus L1-4 Formed in psoas major → lower abdo wall, skin/muscles leg Sacral plexus L4-S4 Formed in front of piriformis → leg, pelvic floor, perineum Bladder flattened 3 side pyramid within pelvis, extending into abdo when full Nerve supply Motor Parasymp via pelvic splanchnic – vasomotor and motor to trigone Symp from L1/2 via superior and inferior hypogastric plexus Sensation Parasympathetic mostly, Symp involved with pain transmission Micturition Bladder filling initially does not increase tension → Tension increase stimulates stretch receptors Pelvic splanchnic nerves transmit to sacral cord then efferents to detrusor to contract and external sphincter/levator ani relax Cortical inhibition from hemispheres 1 Male urethra Prostatic part 3-4cm long Membranous part Spongy/penile part 15cm long Within corpus spongiosum – subdivided into bulbous (enlarged posterior part of the corpus) and pendulous parts Right angled forward turn after passing through perineal membrane within bulbous part Narrowest point is external meatus Rectum Terminal portion of GI tract, 12cm long Anorectal junction slung forwards by loop puborectalis that merges with external anal sphincter Relations Posterior Sacrum and coccyx, ischial spines posterolaterally Anterior Rectovesical pouch - Base of bladder, Prostate, Ureters, Ductus deferens Pouch of Douglas - Upper vagina, Cervix Blood supply Arterial Superior rectal artery (from inferior mesenteric artery), Middle/inferior rectal, Median sacral Venous Free anastomosis occurs with all branches draining the rectum Pelvic floor Levator ani, obturator internus, piriformis Reproductive organs Uterus and fallopian tubes Fundus Body Enclosed by peritoneum that lat becomes broad lig Rests on bladder, vesico-uterine pouch between Cervix Lateral, anterior and posterior fornices Post surface covered with peritoneum, forms ant wall pouch of Douglas Anterior surface is deep to vesicouterine pouch. Fallopian tubes 10cm long, Lies in upper edge of broad ligament Divided into isthmus, ampulla and infundibulum Blood supply Uterine artery from internal iliac Lymph External and internal iliac nodes, sacral nodes, superficial inguinal nodes Ovary 3x2x1cm, ovoid structure in angle between internal and external iliac vessels Obturator nerve is lateral, Ureter is posterior, Tube is medial Blood supply Ovarian artery from abdominal aorta Lymph Para-aortic lymph nodes Vagina 10cm long fibromuscular tube, Directed up and back Anterior to rectum, anal canal and perineal body; Posterior to bladder and urethra Blood supply Vaginal branch of internal iliac artery, Uterine artery, Inferior vesical artery, Middle rectal artery Lymph External and internal iliac nodes, sacral nodes, superficial inguinal nodes Nerve Sensation – pudendal nerve and ilioinguinal nerve Vaginal examination cervix, Bladder, urethra/pubic synthesis anteriorly, Pouch of Douglas and rectum posteriorly Body of uterus, ovaries and tubes felt with abdominal pressure Penis Root Body Two corpus cavernosum bound side by side with corpus spongiosum behind Urethra runs within corpus spongiosum Blood supply Three pairs of arteries from internal pudendal artery Lymph Glans drain to deep inguinal nodes, Skin drains to superficial inguinal nodes Nerve Skin – pudendal nerves (S2), ilioinguinal nerve (L1) 2 Internal Iliac Artery Origin: common iliac, level disc L5/S1 Course: posteriorly into pelvis for 4cm then branches into anterior and posterior divisions Anterior relations: ureter and fallopian tube and ovary Posterior relations: internal iliac vein, lumbosacral trunk, SI joint Lateral relations: external iliac artery and vein, obturator nerve, psoas major Medial relations: parietal peritoneum and small bowel Internal pudendal artery: From anterior division, descends on lateral wall of the pelvis. Leaves pelvis through greater sciatic foramen, inferior to piriformis, then over tip of ischial spine to enter ischo-anal fossa via lesser sciatic foramen. Round ligament supplied by the uterine artery, vas deferens is usually supplied by inferior vesical or superior vesical. Anterior division Superior vesicle Inferior vesicle Obturator - Adductor longus/brevis/magnus, Obturator externus, Gracilis Middle rectal Uterine Internal pudendal Inferior rectal; Deep artery of penis; Dorsal artery of penis; Urethral; Artery to bulb; Perineal Posterior division Iliolumbar Lateral sacral Superior gluteal Superficial branch → glut max; Deep branch → glut med/min, TFL Inferior gluteal Muscular branch → glut max, obturator Anastomotic Coccygeal Arteria comitans nervi ischiadici Lymphatic drainage of pelvis Upper rectum and rectal mucosa to dentate line → inferior mesenteric Gonad plus fallopian tube, superior lateral uterus, ureter → para-aortic Lower rectum and dentate line, bladder, urethra, lower ureter, uterus/cervix/upper vagina/clitoris/labia minora, vas deferens/seminal vesicles/prostate/bulk of penis → lateral pelvic nodes Lumbar plexus – branches T12 – subcostal L1 – iliohypogastric, ilioinguinal L1-2 – genitofemoral L2-3 – lat fem cutaneous L2-3-4 – post division: femoral; anterior division: obturator L4-5 – lumbosacral trunk Sacral plexus From: lumbosacral trunk (L4,5) and anterior primary rami from S1-5 Lies on piriformis on posterior pelvic wall deep to internal iliac vessels, protected by sheet of pelvic fascia Superior gluteal nerve(L4-S1) Sacrum 5 fused bones + coccyx 4 pairs sacral foramina – S1-4 anterior larger than posterior Ala, SI joint, superior articular facets, lumbosacral joint, 5 vertical lines – median, intermediate, lateral 3








![03 Pelvic walls, joints, vessels & nerves[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008603119_1-acbc42b5ee9771f876d810e55400cc51-150x150.png)