* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Paranasal Sinus Anatomy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
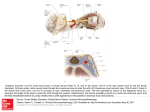
Paranasal Sinus Anatomy Marilene B. Wang, MD, FACS Professor UCLA Division of Head and Neck Surgery Chief of Otolaryngology VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System Paranasal Sinus Function Lining – pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium Mucous and serosanguinous glands Parasympathetic and sympathetic innervation Paranasal Sinus Function Mucous blanket renewed every 10-15 minutes Warm and humidify air Secrete immunoglobulins, interferons, inflammatory cells Paranasal Sinus Function Cilia beat 10-15 times/second Cilia function varies with environment, allergies, smoking, etc. Mucociliary system—cleanse sinus, immunoprotective Move mucous to natural ostia of sinuses Four Paired Sinuses Ethmoid Maxillary Frontal Sphenoid Ethmoid Sinus Greatest anatomic variation Pyramidal shape with base posteriorly 4-5 cm length A-P 2.5 cm height 0.5 cm wide anteriorly 1.5 cm wide posteriorly Ethmoid Sinus Numerous small air cells Filled with fluid at birth Visualized at 1 year of age Ethmoid Sinus Roof---fovea ethmoidalis Lateral wall—lamina papyracea Average 9 air cells Anterior group Posterior group Anterior Ethmoid Cells Frontal recess Infundibular Bullar Conchal Agger nasi Posterior Ethmoid Cells Onodi cells—surrounding optic nerve within sphenoid bone Posterior ethmoid artery—junction of fovea ethmoidalis and frontal bone, anterior to optic nerve Anterior ethmoid artery—dome of ethmoid posterior to frontal recess Middle Turbinate Conchal cell (concha bullosa) Attached superiorly to the cribriform plate Middle Turbinate Attached to ethmoid capsule and lamina papyracea by basal lamellae Posterior end at sphenopalatine foramen Maxillary Sinus Present at birth Rapid growth age 0-3, then 7-12 Triangular shape Natural ostium superior medial wall Frontal Sinus Not present at birth Forms by age 12 Anterior and posterior table Nasofrontal duct— misnomer Frontal recess Frontal Recess Connection of the frontal sinus to the anterior ethmoid Term first used by Killian in 1898 Frontal Sinus Van Alyea—performed 247 cadaver dissections in 1930s Used the term “frontal recess” Warned of various cells obstructing it Van Alyea DE. Archives of Otolaryngol 29:881901, 1939 Frontal Sinus Embryology 4 frontal pits—form frontal and ethmoid sinuses 1st pit—Agger Nasi cell 2nd pit—Frontal Sinus 3rd pit—other ethmoid cells 4th pit—other ethmoid cells Schaeffer JP, Amer J Anatomy 1916 Kasper, Archives of Otolaryngol, 1936 Sphenoid Sinus Evagination of sphenoethmoid recess at birth Pneumatization begins age 3 Reaches sella by age 7 Development continues through adulthood Sphenoid Sinus 20 mm high, 23 mm deep, 17 mm wide Vessels and nerves on lateral aspect (internal carotid artery, optic nerve, vidian nerve) Sphenoid Sinus Dehiscent or minimal bony covering over vessels and superior wall (dura) Intersinus septum rarely midline Caution—intersinus septum often inserts onto carotid canal Sphenoid sinus—3 types Conchal Presellar Sellar Sphenoid Sinus Distances From Anterior Nasal Spine To Sphenoid Ostium 7 cm To Pituitary Fossa 8.5 cm Key Anatomic Landmarks in the Nose and Paranasal Sinuses Middle turbinate Lamina papyracea Ethmoid fovea Cribriform plate Sphenoid Endoscopic Dissection Nasal endoscopy Identify turbinates, uncinate, bulla Uncinectomy, middle meatal antrostomy Anterior ethmoidectomy, identify lamina papyracea, skull base, anterior ethmoid artery Endoscopic Dissection Posterior ethmoidectomy, identify skull base, posterior ethmoid artery, anterior sphenoid, superior turbinate Sphenoid sinusotomy, identify optic nerve, carotid, sella, V2 Frontal recess dissection, identify agger nasi Draf Procedures (I-III) Type I—removal of disease inferior to frontal sinus ostium Type IIA—Removal of ethmoid cells projecting into the frontal sinus; IIB—Removal of frontal sinus floor from the lamina papyracea to the nasal septum Type III—removal of bilateral floor with superior nasal septum and intersinus septum (EMLP) Endoscopic Modified Lothrop Procedure Lothrop—1914 described external ethmoidectomy approach through which he removed the intersinus septum and floor of the frontal sinus EMLP Close (1994) and Gross (1995) described a modification through a transnasal endoscopic approach Not a functional procedure since it disrupts the normal mucociliary clearance from the frontal sinus EMLP--Indications Medically refractory chronic frontal sinusitis Failure of intranasal frontal sinusotomy or more conservative techniques No identifiable bony remnants in the frontal recess EMLP--Results Variable results Ostial patency rates 82-95% Complications Bleeding Scarring/Stenosis Orbital Intracranial Advanced Dissection Endoscopic DCR Modified Lothrop Orbital decompression Optic nerve decompression Sphenopalatine artery ligation April 29, 2009 Dissection Course Endoscopic Sinus Dissection 1-4 PM Facial Plastic Dissection 4-7 PM Dinner at Napa Valley Grille 7:00 PM