Part Ⅰ The Sensory Organs
... A. Organ of hearing and balance B. Three parts 1. External ear: collects sound waves 2. Middle ear: transmits sound waves 3. Internal ear: contains the vestibulocochlear organ concerned with equilibration and hearing Ⅱ. External ear ...
... A. Organ of hearing and balance B. Three parts 1. External ear: collects sound waves 2. Middle ear: transmits sound waves 3. Internal ear: contains the vestibulocochlear organ concerned with equilibration and hearing Ⅱ. External ear ...
152
... • the midline aponeuroses of the external/internal abdominal obliques, and transverse abdominis muscles come together to form the rectus sheath • rectus abdominis is enclosed within the rectus sheath • midline of rectus sheath is the linea alba • 3 fibrous bands called tendinous inscriptions transec ...
... • the midline aponeuroses of the external/internal abdominal obliques, and transverse abdominis muscles come together to form the rectus sheath • rectus abdominis is enclosed within the rectus sheath • midline of rectus sheath is the linea alba • 3 fibrous bands called tendinous inscriptions transec ...
pdf
... reconstruction. The petroclival segment is lined with arachnoid membrane, showing CSF invagination in Dorello's canal. There are three angles in the course of the sixth cranial pair through the petroclival region: 1. at the point of entry into the dura mater, 2. petrous apex, and 3. at the point whe ...
... reconstruction. The petroclival segment is lined with arachnoid membrane, showing CSF invagination in Dorello's canal. There are three angles in the course of the sixth cranial pair through the petroclival region: 1. at the point of entry into the dura mater, 2. petrous apex, and 3. at the point whe ...
15-Minutes-Before-the
... limb pain. Happens to 5-8% of the population after damage of neural arch fusion to body of LV5. Spina Bifida Nonfusion of neural arch at midline – opening of vertebral canal. Slipped Disk Not literally a slipped disk. Pulpus gelatinous center bulges out posteriorly, impinging on spinal nerves. Poste ...
... limb pain. Happens to 5-8% of the population after damage of neural arch fusion to body of LV5. Spina Bifida Nonfusion of neural arch at midline – opening of vertebral canal. Slipped Disk Not literally a slipped disk. Pulpus gelatinous center bulges out posteriorly, impinging on spinal nerves. Poste ...
CERVICO-AURICULAR FISTULAE
... tubercles which develop on the first and second arches on the dorsal end of the first groove which lies between. By growth and fusion, the tubercles and the immediately surrounding area give rise to the primitive pinna. This is situated around the end of the developing external auditory meatus. The ...
... tubercles which develop on the first and second arches on the dorsal end of the first groove which lies between. By growth and fusion, the tubercles and the immediately surrounding area give rise to the primitive pinna. This is situated around the end of the developing external auditory meatus. The ...
Spine - Amazon Web Services
... said to be lumbarisation of S1 and the patient appears to have six lumbar vertebrae. The converse can also occur, known as sacralisation of L5, where the individual appears to have four lumbar vertebrae. The anterior sacral surface, when viewed from the side, is in the form of a concave curvature, e ...
... said to be lumbarisation of S1 and the patient appears to have six lumbar vertebrae. The converse can also occur, known as sacralisation of L5, where the individual appears to have four lumbar vertebrae. The anterior sacral surface, when viewed from the side, is in the form of a concave curvature, e ...
Brachial Plexus Injuries
... the upper limb except an area just above the point of the shoulder (supplied by supraclavicular nerves) and the dorsal scapular area which is supplied by cutaneous branches of dorsal rami. ...
... the upper limb except an area just above the point of the shoulder (supplied by supraclavicular nerves) and the dorsal scapular area which is supplied by cutaneous branches of dorsal rami. ...
Brachial Plexus
... MC secondary mass lesion of benign cause affecting the brachial plexus Entity first described in abdominal wall of ...
... MC secondary mass lesion of benign cause affecting the brachial plexus Entity first described in abdominal wall of ...
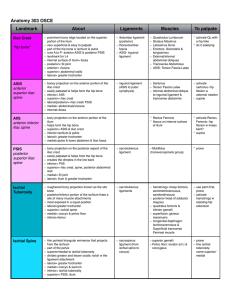
II. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TESTS
... CM Lateral columnof the spinalcord contains thefollowing tracts: a) the corticonuclear tract b) the ventral corticospinal tract c)the dorsalspinocerebellar tract d)the ventralspinocerebellar tract e) the rubrospinal cord ...
... CM Lateral columnof the spinalcord contains thefollowing tracts: a) the corticonuclear tract b) the ventral corticospinal tract c)the dorsalspinocerebellar tract d)the ventralspinocerebellar tract e) the rubrospinal cord ...
Multi-axis passive and active stiffnesses of the glenohumeral joint
... Results. Without muscle loading, glenohumeral stiffness in the superior direction (Ksup ¼ 5:83 N/mm) was higher than that in the inferior (Kinf ¼ 4:32), anterior (Kant ¼ 3:67), and posterior (Kpost ¼ 2:89) directions (P < 0:008), and Kinf was higher than Kpost (P ¼ 0:011). Stiffness in the different di ...
... Results. Without muscle loading, glenohumeral stiffness in the superior direction (Ksup ¼ 5:83 N/mm) was higher than that in the inferior (Kinf ¼ 4:32), anterior (Kant ¼ 3:67), and posterior (Kpost ¼ 2:89) directions (P < 0:008), and Kinf was higher than Kpost (P ¼ 0:011). Stiffness in the different di ...
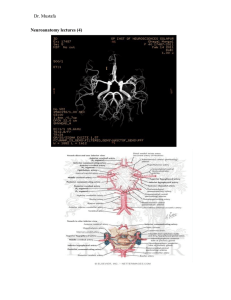
the acoustic complex and its relations in the brain of the
... opossum may first bc pointed out,. The typical situation of the cochlear nuclei in such brains as those of the cat, rabbit aid man, is largely external to the corpus restiforme, the tuberculum being lateral to and somewhat above the ventral nucleus, and largely overlying it. I n the opossum this is ...
... opossum may first bc pointed out,. The typical situation of the cochlear nuclei in such brains as those of the cat, rabbit aid man, is largely external to the corpus restiforme, the tuberculum being lateral to and somewhat above the ventral nucleus, and largely overlying it. I n the opossum this is ...
Welcome to Chiropractic
... Vertebral Subluxations: are misalignments in the vertebrae of the spinal column, that interfere with the transmission of information from the brain, over the spinal cord to the spinal nerves and, ultimately, to all systems of the body. These misalignments disrupt proper nerve function and lead to de ...
... Vertebral Subluxations: are misalignments in the vertebrae of the spinal column, that interfere with the transmission of information from the brain, over the spinal cord to the spinal nerves and, ultimately, to all systems of the body. These misalignments disrupt proper nerve function and lead to de ...
Anatomy Syllabus
... This requires the knowledge of the range of normality and also of normal variants, particularly those that simulate disease or are on the borderlands with disease. 3. Coherent communication with referrers, colleagues, patients and the entire health care team regarding a particular anatomical structu ...
... This requires the knowledge of the range of normality and also of normal variants, particularly those that simulate disease or are on the borderlands with disease. 3. Coherent communication with referrers, colleagues, patients and the entire health care team regarding a particular anatomical structu ...
internal medicine series
... Motion occurs about the superior transverse axis of the sacrum AKA inherent motion During craniosacral flexion the sacral base rotates posteriorly, counernutation During craniosacral extension the sacral base rotates anteriorly, nutation ...
... Motion occurs about the superior transverse axis of the sacrum AKA inherent motion During craniosacral flexion the sacral base rotates posteriorly, counernutation During craniosacral extension the sacral base rotates anteriorly, nutation ...
frontal sphenoids
... Sphenoidectomy The posterior septal brach of the sphenopalatine artery runs on the frontal wall of the sphenoid – risk of troublesome (but not dangerous) bleeding The same branch is used for nasoseptal flap for skull base defects reconstruction! ...
... Sphenoidectomy The posterior septal brach of the sphenopalatine artery runs on the frontal wall of the sphenoid – risk of troublesome (but not dangerous) bleeding The same branch is used for nasoseptal flap for skull base defects reconstruction! ...
The central arteries
... It is the largest and direct branch of the internal carotid artery. It passes within the lateral sulcus and supply the insula. It supplies the lateral surface of the cerebral cortex except the periphery of about one gyrus breadth, so it supplies the contralateral part of the body with the speech and ...
... It is the largest and direct branch of the internal carotid artery. It passes within the lateral sulcus and supply the insula. It supplies the lateral surface of the cerebral cortex except the periphery of about one gyrus breadth, so it supplies the contralateral part of the body with the speech and ...
Anatomy, Joint Orientation and Arthrokinematics
... flavum, supraspinous and interspinous ligaments, posterior fibres of the annulus and the zygapophyseal joint capsules and posterior musculature Extension – ELASTIC – STRETCHING of the anterior zygapophyseal joint capsules, anterior annulus, rectus abdominis, internal and external obliques. HARD – ...
... flavum, supraspinous and interspinous ligaments, posterior fibres of the annulus and the zygapophyseal joint capsules and posterior musculature Extension – ELASTIC – STRETCHING of the anterior zygapophyseal joint capsules, anterior annulus, rectus abdominis, internal and external obliques. HARD – ...
THE PHARYNX Internal Aspect
... posterior wall of the nasal part of the pharynx is an accumulation of lymphoid tissue, the pharyngeal tonsil. This may be prominent in children but becomes indistinct or disappears by adulthood. In children there is a similar accumulations of lymphoid tissue associated with the posterior lip of th ...
... posterior wall of the nasal part of the pharynx is an accumulation of lymphoid tissue, the pharyngeal tonsil. This may be prominent in children but becomes indistinct or disappears by adulthood. In children there is a similar accumulations of lymphoid tissue associated with the posterior lip of th ...
THE HEART AND ARTERIAL CIRCULATORY SYSTEM OF TICKS
... lateral and posterior surfaces of the synganglion, but an more removed dorsally (Figs . 2 , 3) . Here, the aorta enters the sinus just above the point where the esophagus passes ou t of the synganglion . The periganglionic sinus communi;ates anteriorly with the periesophageal arterial sinus (peS) an ...
... lateral and posterior surfaces of the synganglion, but an more removed dorsally (Figs . 2 , 3) . Here, the aorta enters the sinus just above the point where the esophagus passes ou t of the synganglion . The periganglionic sinus communi;ates anteriorly with the periesophageal arterial sinus (peS) an ...
Study of Abnormal Foramen Over the Posterior Arch of
... complete canal for vertebral artery in labourers compared to that of nonlabourers, reveling chances of protective mechanism of the bony canal. He also noted the higher incidence of canal in the 5-44 years of age group. Taitz & Nathan (1986) proposed a hypothesis that carrying heavy objects on head a ...
... complete canal for vertebral artery in labourers compared to that of nonlabourers, reveling chances of protective mechanism of the bony canal. He also noted the higher incidence of canal in the 5-44 years of age group. Taitz & Nathan (1986) proposed a hypothesis that carrying heavy objects on head a ...
Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy/Cat Muscles.2011
... External intercostals: outer layer of muscles lying in the intercostal spaces between adjacent ribs, craniodorsally, similar to the external oblique layer. Internal intercostals: lies directly medial to the external intercostals Transversus thoracis: incomplete third layer beneath the internal inter ...
... External intercostals: outer layer of muscles lying in the intercostal spaces between adjacent ribs, craniodorsally, similar to the external oblique layer. Internal intercostals: lies directly medial to the external intercostals Transversus thoracis: incomplete third layer beneath the internal inter ...
Document
... pass through the pleura or the lung tissue. 2. Stab wounds in the mid-axillary line a. Above the 8th rib, they lead to injury of the lung and pleura. b. Between the 10th and 8th rib, they lead to injury of the pleura. 3. Injury of the pleura leads to the followings: a. Entry of air into the pleural ...
... pass through the pleura or the lung tissue. 2. Stab wounds in the mid-axillary line a. Above the 8th rib, they lead to injury of the lung and pleura. b. Between the 10th and 8th rib, they lead to injury of the pleura. 3. Injury of the pleura leads to the followings: a. Entry of air into the pleural ...
The anterior tibial artery
... areas from a variety of mechanisms, resulting in varying degrees of problems – A torn meniscus is one of the most common knee injuries. Any activity that causes you to forcefully twist or rotate your knee, especially when putting the pressure of your full weight on it, can lead to a torn meniscus. – ...
... areas from a variety of mechanisms, resulting in varying degrees of problems – A torn meniscus is one of the most common knee injuries. Any activity that causes you to forcefully twist or rotate your knee, especially when putting the pressure of your full weight on it, can lead to a torn meniscus. – ...
Drosophila embryogenesis

Drosophila embryogenesis, the process by which Drosophila (fruit fly) embryos form, is a favorite model system for geneticists and developmental biologists studying embryogenesis. The small size, short generation time, and large brood size make it ideal for genetic studies. Transparent embryos facilitate developmental studies. Drosophila melanogaster was introduced into the field of genetic experiments by Thomas Hunt Morgan in 1909.