* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The central arteries
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
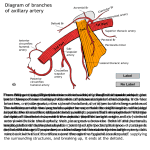
Dr. Mustafa Neuroanatomy lectures (4) Dr. Mustafa Blood supply of the C.N.S. I- Arterial blood supply of the C.N.S.: The brain is supplied by two systems: 1- Internal carotid system (right and left). 2- Vertebrobasilar system (right and left). These two systems are joined together by the circle of Willis. Dr. Mustafa Vertebrobasilar system: It is formed of two vertebral arteries (right and left). Each artery arises from the first part of the subclavain artery and passes through the foramen transversorum of the sixth cervical vertebra till the foramen transversorum of the first cervical vertebra (atlas), while the vertebral vein passes through the foramen transversorum of the seventh cervical vertebra. Then the Dr. Mustafa vertebral arteries pass through the foramen magnum to enter the skull. These two vertebral arteries unit together at lower pons to form the basilar artery. Branches of the vertebral arteries: 1- spinal arteries: Dr. Mustafa a- Single anterior spinal artery: this artery is formed by a branch from each vertebral artery. The ventral 2/3 are supplied by the anterior spinal artery. b- Pair of posterior spinal arteries: each vertebral artery gives a single posterior spinal artery. So the spinal cord is supplied by three arteries which are two posterior spinal arteries and one anterior spinal artery. 2- Posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA): It is large and tortuous artery to supply the posterior and inferior parts of the cerebellum. Branches of the basilar artery: 1- Anterior inferior cerebellar arteries (AICA). 2- Pontine branches. 3- Labyrinthine arteries. 4- Superior cerebellar artery. So the cerebellum is supplied by three main arteries → PICA + AICA + Superior cerebellar arteries. 5- Posterior cerebral arteries. The Vertebrobasilar system end into two posterior cerebral arteries. Internal carotid system: Internal carotid artery passes through the carotid canal and it has a bending course inside the carotid canal which is called the carotid siphon. Dr. Mustafa Branches: 1- Ophthalmic artery. 2- Hypophyseal artery (to pituitary gland). 3- Anterior choriodal artery to choroid plexus. 4- Anterior cerebral artery. 5- Middle cerebral artery. So the cerebrum has three main arteries → anterior cerebral artery + middle cerebral artery + posterior cerebral artery. Circle of Willis: Dr. Mustafa It is composed of: 1- Anterior communicating artery, between two anterior cerebral arteries. 2- Anterior cerebral artery. 3- Internal carotid artery and middle cerebral artery. Dr. Mustafa 4- Posterior communicating artery, between the posterior cerebral artery and the internal carotid artery. 5- Posterior cerebral artery. This circle will help in controlling the balance of the blood flow in between the two systems, but it is insufficient balance. The circle is situated at the basilar part of the brain. The circle of Willis gives cortical and central branches: 1- The cortical domain of the middle cerebral artery: It is the largest and direct branch of the internal carotid artery. It passes within the lateral sulcus and supply the insula. It supplies the lateral surface of the cerebral cortex except the periphery of about one gyrus breadth, so it supplies the contralateral part of the body with the speech and auditory areas, motor and somatosensory areas, except the leg, foot and perineum that is functionally responsible for defecation and micturition, which are supplied by the anterior cerebral artery. 2- The cortical domain of the anterior cerebral artery: Dr. Mustafa It supplies the whole medial surface of the cerebral hemisphere above the corpus callosum as far back as the parieto-occipital sulcus. It extends over the superior border to meet the area which is supplied by the middle cerebral artery. 3- The cortical domain of the posterior cerebral artery: It supplies the inferomedial surface of the temporal and occipital lobes. It extends to supply the inferior temporal gyrus and the periphery of the lateral surface of the occipital lobe. It meets the area supplied by the anterior cerebral artery at the parieto-occipital sulcus. Dr. Mustafa The central arteries: The inside parts of the cerebrum are supplied by the central arteries which are arising from the component of the circle of Willis. The insult to these central arteries can lead to intracerebral hemorrhage. They are mainly of two groups: 1- The anterior group of the central arteries is coming from the anterior cerebral artery, anterior communicating artery, and the middle cerebral artery which gives the major central arteries of the anterior group. Dr. Mustafa This anterior group of the central arteries will enter to inside of the cerebrum through the anterior perforated substances which are present on each side of the optic chiasm. 3- The posterior group of the central arteries is coming from the posterior communicating artery and the posterior cerebral arteries. They enter to inside of the cerebrum through the posterior perforated substance which is present in the interpeduncular fossa. II- The venous drainage of the brain: All veins of the brain will drain into the intracranial venous sinuses. ■ The insult to the blood vessels of the C.N.S. will lead to cerebro-vascular accident (C.V.A.). ■ The brain needs continuous arterial blood supply and if the blood supply interrupt (10) seconds will lead to loss of consciousness, and if continue till (3) minutes will lead to irreversible damage to C.N.S. Dr. Mustafa