lumbo sacral plexus, cutaneus nerves, dermatome, mapping
... L4,5,S1,2- Common peroneal part of sciatic. ...
... L4,5,S1,2- Common peroneal part of sciatic. ...
Embryology GastrointesInal System
... These embryonic structures contribute to formation of the head and neck. ...
... These embryonic structures contribute to formation of the head and neck. ...
Thoracic Sympathetic Trunk
... plexus continues inferiorly on the esophagus toward the diaphragm. Just above the diaphragm, fibers of the plexus converge to form two trunks: •Anterior vagal trunk on the anterior surface of the esophagus, mainly from fibers originally in the left vagus nerve •Posterior vagal trunk on the posterior ...
... plexus continues inferiorly on the esophagus toward the diaphragm. Just above the diaphragm, fibers of the plexus converge to form two trunks: •Anterior vagal trunk on the anterior surface of the esophagus, mainly from fibers originally in the left vagus nerve •Posterior vagal trunk on the posterior ...
Intramuscular Tenderness and Muscle Fiber Orientation
... of the long head BF and ST were tougher than their posterior sides. The first four steaks of the SM were more tender than rest of the muscle. There was a significant tenderness increment from the middle of the AF to its both ends. Based on tenderness values, the first two to four steaks of long head ...
... of the long head BF and ST were tougher than their posterior sides. The first four steaks of the SM were more tender than rest of the muscle. There was a significant tenderness increment from the middle of the AF to its both ends. Based on tenderness values, the first two to four steaks of long head ...
1 The greater omentum is derived from which of the following
... ganglion cells in the wall of the colon. Neural crest cells contribute to the formation of many adult structures. Among these are all of the postganglionic neurons of the autonomic nervous system and the sensory neurons of the peripheral nervous system. Ectoderm (choice A) forms the epidermis of the ...
... ganglion cells in the wall of the colon. Neural crest cells contribute to the formation of many adult structures. Among these are all of the postganglionic neurons of the autonomic nervous system and the sensory neurons of the peripheral nervous system. Ectoderm (choice A) forms the epidermis of the ...
Left ventral conus swelling Truncal swellings
... sac and through the aortic arches to the dorsal aorta. The primitive ventricle is caudal to the bulbus cordis and the primitive atrium is the caudal most structure of the tubular heart. The atrium which is paired connects to the sinus venosus which receives the viteline (from yolk sac), common cardi ...
... sac and through the aortic arches to the dorsal aorta. The primitive ventricle is caudal to the bulbus cordis and the primitive atrium is the caudal most structure of the tubular heart. The atrium which is paired connects to the sinus venosus which receives the viteline (from yolk sac), common cardi ...
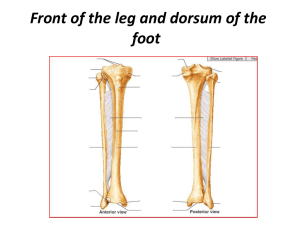
Front of the leg and dorsum of the foot
... from the tendon of the semimembrenosus m. • 5- Arcuate popliteal ligament arise from the back of the head of the fibula and runs medially over the popliteus m. • 6- Collateral ligament they are tibial and fibular collateral ...
... from the tendon of the semimembrenosus m. • 5- Arcuate popliteal ligament arise from the back of the head of the fibula and runs medially over the popliteus m. • 6- Collateral ligament they are tibial and fibular collateral ...
spinal cord
... THE CERVICAL SEGMENTS ARE LARGER WITH MUCH MORE WHITE MATTER IN THEM IN COMPARISON WITH CAUDAL, SACRAL SEGMENTS THE SPINAL CORD SHOWS TWO ENLARGEMENTS THE CERVICAL ENLARGEMENT INCLUDES SEGMENTS C5-T1. THESE SEGMENTS GIVE RISE TO THE BRACHIAL NERVE PLEXUS THAT SUPPLIES THE UPPER EXTREMITIES THE SECON ...
... THE CERVICAL SEGMENTS ARE LARGER WITH MUCH MORE WHITE MATTER IN THEM IN COMPARISON WITH CAUDAL, SACRAL SEGMENTS THE SPINAL CORD SHOWS TWO ENLARGEMENTS THE CERVICAL ENLARGEMENT INCLUDES SEGMENTS C5-T1. THESE SEGMENTS GIVE RISE TO THE BRACHIAL NERVE PLEXUS THAT SUPPLIES THE UPPER EXTREMITIES THE SECON ...
Two cord stage in the infraclavicular part of the brachial plexus
... Department of Anatomy, PSG Institute of Medical Sciences and Research, Peelamedu, Coimbatore, India, a rare unilateral variation of the cords of the infraclavicular part of the brachial plexus was observed. In the left upper limb of the cadaver, the pectoral region, axilla and arm were dissected. Th ...
... Department of Anatomy, PSG Institute of Medical Sciences and Research, Peelamedu, Coimbatore, India, a rare unilateral variation of the cords of the infraclavicular part of the brachial plexus was observed. In the left upper limb of the cadaver, the pectoral region, axilla and arm were dissected. Th ...
neck topography_engl.2011
... - Spatium pretracheale - between the two layers - Extends to mediastinum superius - Spatium retropharyngeum - between fascia endocervicalis & lamina prevertebralis - Extends to mediastinum posterius ...
... - Spatium pretracheale - between the two layers - Extends to mediastinum superius - Spatium retropharyngeum - between fascia endocervicalis & lamina prevertebralis - Extends to mediastinum posterius ...
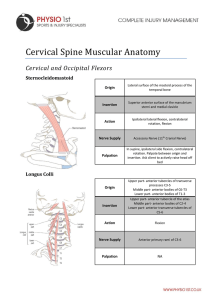
Cervical Spine Muscular Anatomy
... Ipsilateral lateral flexion, flexion. Stabilise first rib during inspiration when upper attachment is fixed. ...
... Ipsilateral lateral flexion, flexion. Stabilise first rib during inspiration when upper attachment is fixed. ...
LAMINA SPREADER SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
... Depending on the surgeon’s preference, rotation may be set with reference to either key anatomical landmarks via a measured resection approach, or by balancing the soft tissues in flexion with the goal of generating a rectangular flexion gap. The following technique describes the use of Lamina Sprea ...
... Depending on the surgeon’s preference, rotation may be set with reference to either key anatomical landmarks via a measured resection approach, or by balancing the soft tissues in flexion with the goal of generating a rectangular flexion gap. The following technique describes the use of Lamina Sprea ...
Vascular Anatomy
... • Rhoton described 4 segments C1-cervical, C2-petrous, C3-cavernous and C4 supraclinoidal which is divided into ophthalmic, posterior communicating and choroidal segments. From its position under the ACP it goes posterolaterally and ends with bifurcating under the anterior perforating substance late ...
... • Rhoton described 4 segments C1-cervical, C2-petrous, C3-cavernous and C4 supraclinoidal which is divided into ophthalmic, posterior communicating and choroidal segments. From its position under the ACP it goes posterolaterally and ends with bifurcating under the anterior perforating substance late ...
The Upper Extremity
... Cross Wrist = flex, extend, abduct, adduct hand Cross Fingers = flex, extend fingers Most muscles fleshy proximally, long tendons distally Flexor + Extensor Retinacula : – The retinaculum is a thick band of deep fascia has bony attachment ; it keeps tendons in position during movements – Under the r ...
... Cross Wrist = flex, extend, abduct, adduct hand Cross Fingers = flex, extend fingers Most muscles fleshy proximally, long tendons distally Flexor + Extensor Retinacula : – The retinaculum is a thick band of deep fascia has bony attachment ; it keeps tendons in position during movements – Under the r ...
ENTRANCE EXAMINATION FOR ADMISSION, MAY 2011. M.Sc. (ANATOMY) COURSE CODE: 501
... The funding agency does not know the treatment ...
... The funding agency does not know the treatment ...
Knee Anatomy
... Originates at the adductor hiatus and passes through the popliteal fossa, then deep to the fibrous arch over the soleus muscle Divides into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries at the distal aspect of the popliteus muscle ...
... Originates at the adductor hiatus and passes through the popliteal fossa, then deep to the fibrous arch over the soleus muscle Divides into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries at the distal aspect of the popliteus muscle ...
Anterior compartment of the leg
... calcaneum above and below the peroneal muscles. 5-Flexor retinacula extends from the medial malleolus downwards and backwards to be attached to the medial tubercle of calcaneum The dorsum of the foot contains the structures which extend from the anterior compartment of the leg. The fascia of the dor ...
... calcaneum above and below the peroneal muscles. 5-Flexor retinacula extends from the medial malleolus downwards and backwards to be attached to the medial tubercle of calcaneum The dorsum of the foot contains the structures which extend from the anterior compartment of the leg. The fascia of the dor ...
The Ankle and Lower Leg notes
... contusions and strains are most common. Although less common, fractures can occur because of direct trauma, such as being struck by a blow or through torsioned forces with the foot fixed to the ground. A number of problems of the leg can also be attributed to repetitive stress and overuse, such as m ...
... contusions and strains are most common. Although less common, fractures can occur because of direct trauma, such as being struck by a blow or through torsioned forces with the foot fixed to the ground. A number of problems of the leg can also be attributed to repetitive stress and overuse, such as m ...
Appendicular &limb by dr.saro0ona
... recognized in the adult In the upper limb, observe that the area supplied by C5 and C6 adjoin the areas supplied by T2, T1 and C8 but the overlap between them is minimal at the ventral axial line. A cutaneous nerve area is the area of skin supplied by a peripheral nerve. ...
... recognized in the adult In the upper limb, observe that the area supplied by C5 and C6 adjoin the areas supplied by T2, T1 and C8 but the overlap between them is minimal at the ventral axial line. A cutaneous nerve area is the area of skin supplied by a peripheral nerve. ...
Neuro Anatomy
... o Move a joint that is at least 2 steps away from the area of symptoms o If this increases/decreases symptoms the neurodynamic system is the structure at fault o Should symptoms remain exactly the same there is a mechanical cause to the clients symptoms ...
... o Move a joint that is at least 2 steps away from the area of symptoms o If this increases/decreases symptoms the neurodynamic system is the structure at fault o Should symptoms remain exactly the same there is a mechanical cause to the clients symptoms ...
Neuro-Anatomy-and-Neurodynamics-Teaching-Pack
... o Reproduction of pain or radiculopathy in an area that they would not be expected confirmed by structural differentiation Therefore when writing patient notes the following can be used o ULTT – Ulnar Nerve – Right- Abnormal- Restricted ROM (unable to reach head with hand)- Familiar pain reported li ...
... o Reproduction of pain or radiculopathy in an area that they would not be expected confirmed by structural differentiation Therefore when writing patient notes the following can be used o ULTT – Ulnar Nerve – Right- Abnormal- Restricted ROM (unable to reach head with hand)- Familiar pain reported li ...
Drosophila embryogenesis

Drosophila embryogenesis, the process by which Drosophila (fruit fly) embryos form, is a favorite model system for geneticists and developmental biologists studying embryogenesis. The small size, short generation time, and large brood size make it ideal for genetic studies. Transparent embryos facilitate developmental studies. Drosophila melanogaster was introduced into the field of genetic experiments by Thomas Hunt Morgan in 1909.