Open approaches for rectal prolapse
... Open operations for rectal prolapse • Perineal operations inferior to abdominal procedures, but definite role • Delorme’s procedure – simple but high recurrence rate, can be repeated • Perineal rectosigmoidectomy – more complex but lower recurrence rate • “If the patient is fit enough and life expe ...
... Open operations for rectal prolapse • Perineal operations inferior to abdominal procedures, but definite role • Delorme’s procedure – simple but high recurrence rate, can be repeated • Perineal rectosigmoidectomy – more complex but lower recurrence rate • “If the patient is fit enough and life expe ...
Muscles, osteofascial compartments, vessels, and nerves of the
... migrates into the limb bud forming posterior and anterior condensations – condensation – mesoderm condenses and differentiates into myoblasts; condensations split into recognizable muscles ...
... migrates into the limb bud forming posterior and anterior condensations – condensation – mesoderm condenses and differentiates into myoblasts; condensations split into recognizable muscles ...
Enumerate the organs of female reproductive system. Discuss the
... • Two layers • Medulla • Cortex • Medulla – framework of connective tissue or stroma • Covered by germinal epithelium • Contains ovarian follicles ...
... • Two layers • Medulla • Cortex • Medulla – framework of connective tissue or stroma • Covered by germinal epithelium • Contains ovarian follicles ...
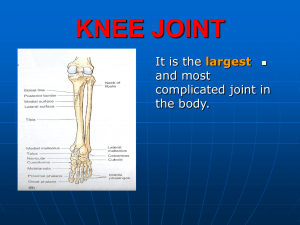
Knee Joint
... • Prevents posterior displacement of femur on tibia. • It becomes tense during extension of the knee joint. • Prevents hyperextension. • More liable to injury ...
... • Prevents posterior displacement of femur on tibia. • It becomes tense during extension of the knee joint. • Prevents hyperextension. • More liable to injury ...
Elbow Trauma
... Galeazzi fracture-dislocations consist of fracture of the distal part of the radius with dislocation of distal radioulnar joint and an intact ulna. Galeazzi fractures are primarily encountered in children, with a peak incidence of 9-12 years of age 3. ...
... Galeazzi fracture-dislocations consist of fracture of the distal part of the radius with dislocation of distal radioulnar joint and an intact ulna. Galeazzi fractures are primarily encountered in children, with a peak incidence of 9-12 years of age 3. ...
SURFACE ANATOMY OF THE KIDNEY I
... The convex anterior surface of the kidney faces antero- laterally. Its relations differ on both sides of the body (Fig. 2). On the right side, a small area at the superior pole contacts the right suprarenal gland. A large area below this (about three quarters) of the surface adjoins the renal impres ...
... The convex anterior surface of the kidney faces antero- laterally. Its relations differ on both sides of the body (Fig. 2). On the right side, a small area at the superior pole contacts the right suprarenal gland. A large area below this (about three quarters) of the surface adjoins the renal impres ...
BRAIN STEM: MEDULLA OBLONGATA AND ITS LESIONS
... o By anatomical terms of location it is rostral to the spinal cord o The medulla oblongata extends from the lower margin of the pons to a plane passing transversely below the pyramidal decussation and above the first pair of cervical nerves o This plane corresponds with the upper border of the atlas ...
... o By anatomical terms of location it is rostral to the spinal cord o The medulla oblongata extends from the lower margin of the pons to a plane passing transversely below the pyramidal decussation and above the first pair of cervical nerves o This plane corresponds with the upper border of the atlas ...
Surgical dislocation
... For a complete inspection of the acetabulum three retractors are used (Fig. 5). The knee is elevated with an assistant applying axial pressure to bring the femoral head posterior to the acetabulum. No retractors are needed for visualisation of the femoral head, the knee being merely lowered to allow ...
... For a complete inspection of the acetabulum three retractors are used (Fig. 5). The knee is elevated with an assistant applying axial pressure to bring the femoral head posterior to the acetabulum. No retractors are needed for visualisation of the femoral head, the knee being merely lowered to allow ...
Intercostal Muscles
... 2) where the SVC, inferior vena cava (IVC), and pulmonary veins enter the ...
... 2) where the SVC, inferior vena cava (IVC), and pulmonary veins enter the ...
The Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Cranial
... • Radial nerve damage causes the fingers, wrist, or hand to be in the chronically flexed position – Radial nerve is constantly pushed against the humerus, and cannot innervate extensor muscles – Improves quickly with therapy ...
... • Radial nerve damage causes the fingers, wrist, or hand to be in the chronically flexed position – Radial nerve is constantly pushed against the humerus, and cannot innervate extensor muscles – Improves quickly with therapy ...
Surgical and angiographic anatomy of the posterior
... The AChA has 2 segments throughout its course as originally proposed by Goldberg and Rhoton et al [16]: the first, cisternal segment begins from origin and ends at the point where the artery reaches to the choroidal fissure (choroidal or plexal point). The second segment, plexal segment, consists of ...
... The AChA has 2 segments throughout its course as originally proposed by Goldberg and Rhoton et al [16]: the first, cisternal segment begins from origin and ends at the point where the artery reaches to the choroidal fissure (choroidal or plexal point). The second segment, plexal segment, consists of ...
Practical 1 Worksheet-‐KEY
... 44. Can you see the posterior cruciate ligament from both the anterior and posterior side of the knee? No (at least not without trying really, really hard) 45. On the posterior side, doe ...
... 44. Can you see the posterior cruciate ligament from both the anterior and posterior side of the knee? No (at least not without trying really, really hard) 45. On the posterior side, doe ...
The hand
... abdominal wall, these muscles come from lumbar fascia but superiorly they take origin from the ribs which are floating and 8th, 9th and 10th ribs and if you go anterior these muscles, they fuse together with aponeuroses and these aponeuroses are thin. The crest is thicker anteriorly compared with po ...
... abdominal wall, these muscles come from lumbar fascia but superiorly they take origin from the ribs which are floating and 8th, 9th and 10th ribs and if you go anterior these muscles, they fuse together with aponeuroses and these aponeuroses are thin. The crest is thicker anteriorly compared with po ...
Chapter 12 PowerPoint - Hillsborough Community College
... that connect different parts of same hemisphere – Commissural fibers: horizontal fibers that connect gray matter of two hemispheres – Projection fibers: vertical fibers that connect hemispheres with lower brain or spinal cord • Internal capsule: projection fibers on each side of brain stem form comp ...
... that connect different parts of same hemisphere – Commissural fibers: horizontal fibers that connect gray matter of two hemispheres – Projection fibers: vertical fibers that connect hemispheres with lower brain or spinal cord • Internal capsule: projection fibers on each side of brain stem form comp ...
PRACTICAL-Upper limb
... Deltoid tuberosity: anterior view where the deltoid muscle attach Spiral (Radial) groove: posterior view Distal end : The Medial Epicondyles bigger than lateral epicondyles The lateral epicondyles. Trochlea: articulates with ulna Capitulum : articulates with radius Coronoid fossa: above the trochlea ...
... Deltoid tuberosity: anterior view where the deltoid muscle attach Spiral (Radial) groove: posterior view Distal end : The Medial Epicondyles bigger than lateral epicondyles The lateral epicondyles. Trochlea: articulates with ulna Capitulum : articulates with radius Coronoid fossa: above the trochlea ...
Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma
... Type 2 and extends to the body of C2 in Type 3. Anterior or posterior displacement of the dens and C1 may occur. In severe injury distraction may be present. A "step-off" configuration of the spinolaminar line at C1 and C2 indicates that C1 has subluxed either anteriorly or posteriorly on C2. If you ...
... Type 2 and extends to the body of C2 in Type 3. Anterior or posterior displacement of the dens and C1 may occur. In severe injury distraction may be present. A "step-off" configuration of the spinolaminar line at C1 and C2 indicates that C1 has subluxed either anteriorly or posteriorly on C2. If you ...
Anatomy of Nose & P.N.S. - The Medical Post | Trusting
... 1. External nose & anterior nasal cavity submandibular lymph nodes 2. Remaining nasal cavity upper deep cervical lymph nodes 3. Nasal roof (dangerous area of nose) subarachnoid space along olfactory nv 4. P.N.S. retropharyngeal & J.D. node ...
... 1. External nose & anterior nasal cavity submandibular lymph nodes 2. Remaining nasal cavity upper deep cervical lymph nodes 3. Nasal roof (dangerous area of nose) subarachnoid space along olfactory nv 4. P.N.S. retropharyngeal & J.D. node ...
Surgical anatomy and landmarks for the basal vein of Rosenthal
... between the dorsal diencephalic vein and the internal cerebral vein or a tributary of the vein of Galen. The deep middle cerebral vein and the anterior cerebral veins develop from the deep telencephalic vein, and the ventral diencephalic vein drains from the primitive tentorial sinus into the transv ...
... between the dorsal diencephalic vein and the internal cerebral vein or a tributary of the vein of Galen. The deep middle cerebral vein and the anterior cerebral veins develop from the deep telencephalic vein, and the ventral diencephalic vein drains from the primitive tentorial sinus into the transv ...
View as PDF - VH Dissector
... A. Fibrous capsule of knee attachments - from the margins of the femoral condyles to the margins of the tibial condyles B. Tibial (medial) collateral attachments - from the medial epicondyle of the femur to the medial condyle & shaft of the tibia function - stabilizes the medial aspect of the joint ...
... A. Fibrous capsule of knee attachments - from the margins of the femoral condyles to the margins of the tibial condyles B. Tibial (medial) collateral attachments - from the medial epicondyle of the femur to the medial condyle & shaft of the tibia function - stabilizes the medial aspect of the joint ...
Nasal Cavity - Dr. Meredith
... 1. Posterior ethmoid artery (from Ophthalmic a.) 2. Anterior ethmoid artery (from Opthalmic a.) 3. Superior lateral posterior nasal (from sphenopalatine-from Maxillary a.) 4. Inferior lateral posterior nasal (from decending palatine-from Maxillary a.) ...
... 1. Posterior ethmoid artery (from Ophthalmic a.) 2. Anterior ethmoid artery (from Opthalmic a.) 3. Superior lateral posterior nasal (from sphenopalatine-from Maxillary a.) 4. Inferior lateral posterior nasal (from decending palatine-from Maxillary a.) ...
Neuraxial Blockade Anatomy and Landmarks
... Posterior spinal arteries are formed by posterior cerebellar arteries and travel down the dorsal surface of the spinal cord just medial to the dorsal nerve roots. They supply 1/3rd of the posterior cord. Additional blood flow is contributed by the anterior and posterior spinal arteries from the inte ...
... Posterior spinal arteries are formed by posterior cerebellar arteries and travel down the dorsal surface of the spinal cord just medial to the dorsal nerve roots. They supply 1/3rd of the posterior cord. Additional blood flow is contributed by the anterior and posterior spinal arteries from the inte ...
NECK AND MEDIASTINUM
... Because the C-spine is built for mobility, we require extensive musculature that both facilitates motion and increases stability. Cervical region also features extensive ligamentous support. Some of these features have been covered previously (scalenes, longus colli, longus capitis, ligaments), not ...
... Because the C-spine is built for mobility, we require extensive musculature that both facilitates motion and increases stability. Cervical region also features extensive ligamentous support. Some of these features have been covered previously (scalenes, longus colli, longus capitis, ligaments), not ...
Fetal Pig Dissection Instructions External Anatomy
... Day 1 - External Anatomy 1 Obtain a fetal pig and rinse off the excess preservative by holding it under running water. Lay the pig on its side in the dissecting pan and locate dorsal, ventral,& lateral surfaces. Also locate the anterior and posterior ends. 2 A fetal pig has not been born yet, but it ...
... Day 1 - External Anatomy 1 Obtain a fetal pig and rinse off the excess preservative by holding it under running water. Lay the pig on its side in the dissecting pan and locate dorsal, ventral,& lateral surfaces. Also locate the anterior and posterior ends. 2 A fetal pig has not been born yet, but it ...
INCISION PLANNING AND PLACEMENT IN THE LOWER
... Angiosomes provide a description of blood flow patterns and distribution to tissues. The understanding of angiosomes and the relationship among them can be emphasized by the choke vessel phenomenon. Choke vessels link neighboring angiosomes together via tributaries. These vessels are only dilated in ...
... Angiosomes provide a description of blood flow patterns and distribution to tissues. The understanding of angiosomes and the relationship among them can be emphasized by the choke vessel phenomenon. Choke vessels link neighboring angiosomes together via tributaries. These vessels are only dilated in ...
Drosophila embryogenesis

Drosophila embryogenesis, the process by which Drosophila (fruit fly) embryos form, is a favorite model system for geneticists and developmental biologists studying embryogenesis. The small size, short generation time, and large brood size make it ideal for genetic studies. Transparent embryos facilitate developmental studies. Drosophila melanogaster was introduced into the field of genetic experiments by Thomas Hunt Morgan in 1909.