Unit 14. Who were the ancient Greeks?
... When and where was ancient Greece? Greece is a country in Europe. Click on the map to have a closer look. ...
... When and where was ancient Greece? Greece is a country in Europe. Click on the map to have a closer look. ...
Chapter 6: Ancient Greece (Notes and Study Guide)
... 1. The country of Greece is a _____________ and many smaller _____________. It’s mainland is a peninsula because it is almost completely surrounded by __________ and connected to the mainland by only a narrow _________________________. 2. The country of Greece is very __________________ and as a res ...
... 1. The country of Greece is a _____________ and many smaller _____________. It’s mainland is a peninsula because it is almost completely surrounded by __________ and connected to the mainland by only a narrow _________________________. 2. The country of Greece is very __________________ and as a res ...
WHI.05: Ancient Greece: Geography to Persian Wars
... Aristocracy – a government that is ruled by a small group of noble, land-owning families Oligarchy – a government ruled a few powerful people, usually by military leaders Democracy – a government in which all citizens have power ...
... Aristocracy – a government that is ruled by a small group of noble, land-owning families Oligarchy – a government ruled a few powerful people, usually by military leaders Democracy – a government in which all citizens have power ...
Chapter 4, Section 1 Study Guide – Early Civilizations in Greece
... 3. What things did the Minoans trade? ...
... 3. What things did the Minoans trade? ...
My World History Chapter 10 – Ancient Greece: Secti
... 50 members from each clan. (Aim to think of clans like a city’s various districts such as East Boston, the North End, Charlestown, etc.) This system ensured that the council had a balance of both wealthy and poor members. This was a pretty revolutionary practice for these ancient times. The boule vo ...
... 50 members from each clan. (Aim to think of clans like a city’s various districts such as East Boston, the North End, Charlestown, etc.) This system ensured that the council had a balance of both wealthy and poor members. This was a pretty revolutionary practice for these ancient times. The boule vo ...
Chapter 10 section 3 Athens and Democracy
... tyranny – The main difference between an oligarchy and a tyranny is that a tyranny is a form of government that is run entirely by one key political figure head. The tyrant leader often gains support by offering to improve the lives of the poorer members of the citizenship. Sometimes these tyrants k ...
... tyranny – The main difference between an oligarchy and a tyranny is that a tyranny is a form of government that is run entirely by one key political figure head. The tyrant leader often gains support by offering to improve the lives of the poorer members of the citizenship. Sometimes these tyrants k ...
Ancient Greece Study Guide Vocab: Peninsula: land surrounded by
... from each other because of the mountains. They were close to the sea which was good for trading. 2. How was it possible that Greece was not unified under one form of government? The steep mountains isolated the city states from each other and made communication difficult ...
... from each other because of the mountains. They were close to the sea which was good for trading. 2. How was it possible that Greece was not unified under one form of government? The steep mountains isolated the city states from each other and made communication difficult ...
NEW UNIT – Create a divider for your binder!
... Do your notes look like this? Add any relevant details you may have missed. • I. Geography of Greece • A. Rocky and mountainous peninsula– barriers, moving over land difficult, independent city-states • B. Few natural resources – land was not fertile, farming difficult, grapes and olives grown i ...
... Do your notes look like this? Add any relevant details you may have missed. • I. Geography of Greece • A. Rocky and mountainous peninsula– barriers, moving over land difficult, independent city-states • B. Few natural resources – land was not fertile, farming difficult, grapes and olives grown i ...
The Great Persian Wars If you were there
... them. The Ionians were no exception to this rule, but they were the only ones who dared rebel against the rulers of Asia. In 499BC, the Ionians began their rebellion which had Darius, ruler of Persia, fuming. Athens sent their countrymen 20 triremes to aid them against the Persians, but this generos ...
... them. The Ionians were no exception to this rule, but they were the only ones who dared rebel against the rulers of Asia. In 499BC, the Ionians began their rebellion which had Darius, ruler of Persia, fuming. Athens sent their countrymen 20 triremes to aid them against the Persians, but this generos ...
Challenges in Physical Education and sports
... the love and care of one s body, the responsibility to society, bravery, wisdom-were all accomplished through physical education and athletics. ...
... the love and care of one s body, the responsibility to society, bravery, wisdom-were all accomplished through physical education and athletics. ...
A Techno-Buffet of Hands-On Learning Activities (Tiered Learning
... the Olympians. Cronus had been warned that he would be overthrown by one of his own children. To prevent this, he swallowed his first five children as soon as they were born. Rhea did not like this. She substituted a stone wrapped in swaddling clothes for their sixth child, Zeus. He was hidden in Cr ...
... the Olympians. Cronus had been warned that he would be overthrown by one of his own children. To prevent this, he swallowed his first five children as soon as they were born. Rhea did not like this. She substituted a stone wrapped in swaddling clothes for their sixth child, Zeus. He was hidden in Cr ...
A Techno-Buffet of Hands-On Learning Activities (Tiered Learning
... the Olympians. Cronus had been warned that he would be overthrown by one of his own children. To prevent this, he swallowed his first five children as soon as they were born. Rhea did not like this. She substituted a stone wrapped in swaddling clothes for their sixth child, Zeus. He was hidden in Cr ...
... the Olympians. Cronus had been warned that he would be overthrown by one of his own children. To prevent this, he swallowed his first five children as soon as they were born. Rhea did not like this. She substituted a stone wrapped in swaddling clothes for their sixth child, Zeus. He was hidden in Cr ...
Four Forms of Government in Ancient Greece
... A monarchy is a form of government in which the ruling power is in the hands of a single person. Most monarchies have been ruled by kings, usually with the help of a council of advisors. The word monarchy comes from the Greek term, monos (meaning “single”) and arkhein (meaning “rule”). The Mycenaean ...
... A monarchy is a form of government in which the ruling power is in the hands of a single person. Most monarchies have been ruled by kings, usually with the help of a council of advisors. The word monarchy comes from the Greek term, monos (meaning “single”) and arkhein (meaning “rule”). The Mycenaean ...
Rowan Gate Primary School Creative Curriculum
... Locate Athens and Sparta on a map. Children to describe physical features of location - near to ...
... Locate Athens and Sparta on a map. Children to describe physical features of location - near to ...
Ancient Greece Powerpoint - Bullis Haiku
... • Dating back to 1400 BC, the Oracle of Delphi was the most important shrine in all Greece as the sanctuary of Apollo • Built around a sacred spring, Delphi was considered to be the center (literally navel) of the world • Questions about the future were answered by the Pythia, the priestess of Apoll ...
... • Dating back to 1400 BC, the Oracle of Delphi was the most important shrine in all Greece as the sanctuary of Apollo • Built around a sacred spring, Delphi was considered to be the center (literally navel) of the world • Questions about the future were answered by the Pythia, the priestess of Apoll ...
worksheet - Mrs. Hatlen`s History Classes
... that was also mentioned in the Bible? A) The Victory Stele of Naram-Sin. B) The Law Code of Hammurabi. C) The Palette of King Narmer. D) The Moabite Stone. 4. In 586 B.C., the armies of Nebuchadnezzar sacked Jerusalem and took the Israelite captives to __________. 5. All of the following could be se ...
... that was also mentioned in the Bible? A) The Victory Stele of Naram-Sin. B) The Law Code of Hammurabi. C) The Palette of King Narmer. D) The Moabite Stone. 4. In 586 B.C., the armies of Nebuchadnezzar sacked Jerusalem and took the Israelite captives to __________. 5. All of the following could be se ...
Ancient Greece
... kings (aristocracy) and 28 nobles (over age of 60) who made most political decisions and foreign policy and was supreme criminal court • Assembly of the Spartiate (democracy)- Spartan males over the age of 30 who could veto and approve decisions made by Kings and Council • 5 Ephors (oligarchy)- led ...
... kings (aristocracy) and 28 nobles (over age of 60) who made most political decisions and foreign policy and was supreme criminal court • Assembly of the Spartiate (democracy)- Spartan males over the age of 30 who could veto and approve decisions made by Kings and Council • 5 Ephors (oligarchy)- led ...
Ancient Greek Civilization - TReavis
... constitutional reforms that destroyed the remaining power of the nobility. • Created TEN NEW TRIBES, embracing citizens of all classes and districts. • Gave the popular ASSEMBLY the RIGHT TO INITIATE LEGISLATION. • Gave the new and democratic COUNCIL OF FIVE HUNDRED, SELECTED BY LOT from the ten tri ...
... constitutional reforms that destroyed the remaining power of the nobility. • Created TEN NEW TRIBES, embracing citizens of all classes and districts. • Gave the popular ASSEMBLY the RIGHT TO INITIATE LEGISLATION. • Gave the new and democratic COUNCIL OF FIVE HUNDRED, SELECTED BY LOT from the ten tri ...
CHAPTER 2 - THE RISE OF GREEK CIVILIZATION
... For Greek civilization, the Bronze Age (2900–1150 B.C.E.) was centered in two regions: on the island of Crete, the smaller islands of the Aegean Sea, and on the mainland of Greece itself. Our knowledge of civilization on Crete (Minoan) depends primarily on archaeological evidence obtained at Cnossus ...
... For Greek civilization, the Bronze Age (2900–1150 B.C.E.) was centered in two regions: on the island of Crete, the smaller islands of the Aegean Sea, and on the mainland of Greece itself. Our knowledge of civilization on Crete (Minoan) depends primarily on archaeological evidence obtained at Cnossus ...
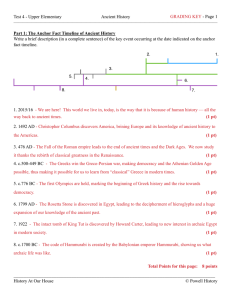
Test 4 - Upper Elementary
... 9. Complete this sentence: “If the Greeks had lost the Greco-Persian War…” Briefly explain your statement. If the Greeks had lost the Greco-Persian War…history would be radically different! There could not have been a Renaissance. The Renaissance is the rebirth of Greek ideas. If Greece was conquere ...
... 9. Complete this sentence: “If the Greeks had lost the Greco-Persian War…” Briefly explain your statement. If the Greeks had lost the Greco-Persian War…history would be radically different! There could not have been a Renaissance. The Renaissance is the rebirth of Greek ideas. If Greece was conquere ...
Ancient Greece - Effingham County Schools
... A. Sparta became jealous of Athenian culture, prosperity, and trade leadership after the Persian War. B. Sparta and Athens go to war to resolve the leadership of Greece. 1. Athens had the strongest navy, but a weak army. 2. Sparta had a weak navy, but a powerful army. C. After fifty years of fightin ...
... A. Sparta became jealous of Athenian culture, prosperity, and trade leadership after the Persian War. B. Sparta and Athens go to war to resolve the leadership of Greece. 1. Athens had the strongest navy, but a weak army. 2. Sparta had a weak navy, but a powerful army. C. After fifty years of fightin ...
File - History with Mr. Bayne
... Textbook worksheet “Ancient Greece” Finish Packet and STUDY for test tomorrow ...
... Textbook worksheet “Ancient Greece” Finish Packet and STUDY for test tomorrow ...
Regions of ancient Greece

The regions of ancient Greece were areas identified by the ancient Greeks as geographical sub-divisions of the Hellenic world. These regions are described in the works of ancient historians and geographers, and in the legends and myths of the ancient Greeks.Conceptually, there is no clear theme to the structure of these regions. Some, particularly in the Peloponnese, can be seen primarily as distinct geo-physical units, defined by physical boundaries such as mountain ranges and rivers. These regions retained their identity, even when the identity of the people living there changed during the Greek Dark Ages (or at least, was conceived by the Greeks to have changed). Conversely, the division of central Greece between Boeotia, Phocis, Doris and the three parts of Locris, cannot be understood as a logical division by physical boundaries, and instead seems to follow ancient tribal divisions. Nevertheless, these regions also survived the upheaval of the Greek Dark Ages, showing that they had acquired less political connotations. Outside the Peloponnese and central Greece, geographical divisions and identities did change over time suggesting a closer connection with tribal identity. Over time however, all the regions also acquired geo-political meanings, and political bodies uniting the cities of a region (such as the Arcadian League) became common in the Classical period.These traditional sub-divisions of Greece form the basis for the modern system of regional units of Greece. However, there are important differences, with many of the smaller ancient regions not represented in the current system. To fully understand the ancient history of Greece therefore requires more detailed description of the ancient regions.