* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ancient Greece Study Guide Vocab: Peninsula: land surrounded by
Regions of ancient Greece wikipedia , lookup
History of science in classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Pontic Greeks wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek literature wikipedia , lookup
First Persian invasion of Greece wikipedia , lookup
Direct democracy wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek cuisine wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of Greece and the Greek world wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek religion wikipedia , lookup
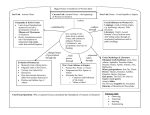
Ancient Greece Study Guide Vocab: Peninsula: land surrounded by water on 3 sides Monarch: rule by 1 (king or queen), first form of government in Greece Oligarchy: rule by few, rich families called aristocrats Tyranny: rule by a military leader, came to power by initially making laws to improve people’s lives Democracy: power of the people, citizens shared the ruling power Representative Democracy: citizens vote for people to represent them in government Direct Democracy: citizens vote directly on issues and laws Imports: Items brought in from other regions Exports: Items sent to other regions for trade Mt. Olympus: A place where the Greeks believed the gods/goddesses lived 1. Describe the geography of Greece. What feature of Greece’s geography had the greatest impact on their economy? Peninsulas and islands, mountains. The soil was rocky which prevented them from growing a lot of crops. The people were isolated from each other because of the mountains. They were close to the sea which was good for trading. 2. How was it possible that Greece was not unified under one form of government? The steep mountains isolated the city states from each other and made communication difficult 3. Why did the Greeks establish colonies? How did these colonies affect Greek culture? Colonies were established because there was a shortage of good farmland and Greece lacked a major river. The colonies spread all over the Mediterranean and it helped spread Greek culture 4. What are some similarities between ancient Athenian democracy and democracy in the U.S. today? Citizens shared the ruling power. Rule of the people, people debated and voted on issues, trials with judges and lawyers, citizens can hold government positions 5. What are some differences between ancient Athenian democracy and democracy in the U.S. today? In Athens, citizens voted directly on all issues, only free men voted, 100 jurors. US has representative democracy, women can vote, 12 jurors, 3 branches of government. 6. How did the assembly of Athens differ from the Council of 500? Assembly-all citizens voted on every issue Council of 500-citizens chosen at random (drawing) to serve a 1 year term. 7. What was most important to the way of life of Spartans? Military training, strict discipline, very physical, ruled by an oligarchy (had 2 kings), discouraged trade 8. What was the focus of daily life in Athens? Education, the arts, philosophy, learning was important so educated citizens could participate in democracy, trade encouraged 9. How were education and the role of women different between Athens and Sparta? Athens – women where in charge of the raising and educating children, household chores Sparta – very physical, military training, could own property 10. What was an important outcome of the Persian Wars? Why do we remember the Battle of Salamis? How did the Greeks win? Greek city states bonded together to fight off a common enemy. The Greeks saved the rest of Europe from Persian rule and also saved “Western Culture”. The Battle of Salamis was won based on the Greeks knowledge of local waterways. The Greeks won because of their knowledge of the geography and better military strategy 11. What was the outcome of the Peloponnesian War? Why could it be considered a defeat for both sides? Sparta defeated Athens. The war weakened both sides and made them a target for Phillip of Macedonia and later Alexander the Great. 12. Why was Alexander “Great”? He conquered a huge area in the Mediterranean World He admired and spread Greek culture all over the world because he was educated by Aristotle 13. What are some similarities between the ancient Olympics and the Olympics of today? An athlete lights the flame, occur every 4 years. 14. How did the Greeks make so many scientific discoveries? By observing and answering questions 15. Is Greek architecture common in the U.S. today? Explain. The use of columns on important government buildings. 16. How did oligarchs rule? Why did they get overthrown? They passed laws that favored the rich. The poor people with the help of a military leader overthrew the oligarchs. 17. How do ancient Greeks Pythagoras and Euclid still impact life today? These mathematicians added to modern day Geometry. Geometry is a Greek word “to measure land”. Geometry measures shapes and spaces used to plant a field or lay out a city. The PyTHAGORIUM Ancient Greece Study Guide Vocab: Peninsula: Monarch: Oligarchy: Tyranny: Democracy: Representative Democracy: Direct Democracy: Imports: Exports Mt. Olympus: 1. Describe the geography of Greece. What feature of Greece’s geography had the greatest impact on their economy? 2. How was it possible that Greece was not unified under one form of government? 3. Why did the Greeks establish colonies? How did these colonies affect Greek culture? 4. What are some similarities between ancient Athenian democracy and democracy in the U.S. today? 5. What are some differences between ancient Athenian democracy and democracy in the U.S. today? 6. How did the assembly of Athens differ from the Council of 500? 7. What was most important to the way of life of Spartans? 8. What was the focus of daily life in Athens? 9. How were education and the role of women different between Athens and Sparta? 10. What was an important outcome of the Persian Wars? Why do we remember the Battle of Salamis? How did the Greeks win? 11. What was the outcome of the Peloponnesian War? Why could it be considered a defeat for both sides? 12. Why was Alexander “Great”? 13. What are some similarities between the ancient Olympics and the Olympics of today? 14. How did the Greeks make so many scientific discoveries? 15. Is Greek architecture common in the U.S. today? Explain. 16. How did oligarchs rule? Why did they get overthrown? 17. How do ancient Greeks Pythagoras and Euclid still impact life today?