The Early Greeks (p. 117-123) The Geography of Greece What
... How did new colonies affect industry? (2 ways) Which islands were home to Greek colonies? On which continents could Greek colonies be found? Describe the steps the Greeks followed when they started a new colony. First they consulted an oracle to see if their efforts would be successful. Next the ...
... How did new colonies affect industry? (2 ways) Which islands were home to Greek colonies? On which continents could Greek colonies be found? Describe the steps the Greeks followed when they started a new colony. First they consulted an oracle to see if their efforts would be successful. Next the ...
Chapter 4 Identifications By Alex Diaz
... Persian Wars- were a series of conflicts between several Greek city-states and the Persian Empire that started in 499 BC and lasted until 448 BC. ...
... Persian Wars- were a series of conflicts between several Greek city-states and the Persian Empire that started in 499 BC and lasted until 448 BC. ...
History of the Greeks
... A middle class results Democracy begins to evolve as leaders and middle class demand a voice Women and slaves are not considered “citizens” Olympics begin (776 B.C.) ...
... A middle class results Democracy begins to evolve as leaders and middle class demand a voice Women and slaves are not considered “citizens” Olympics begin (776 B.C.) ...
Greece Study Guide KEY - Warren County Schools
... 6. How was ancient Greek democracy different from democracy in the United States today? citizens voted directly on all issues 7. The word “philosophy” comes from the Greek word for: “love of wisdom” 8. How was ancient Greek democracy different from American democracy? all citizens voted on every iss ...
... 6. How was ancient Greek democracy different from democracy in the United States today? citizens voted directly on all issues 7. The word “philosophy” comes from the Greek word for: “love of wisdom” 8. How was ancient Greek democracy different from American democracy? all citizens voted on every iss ...
File
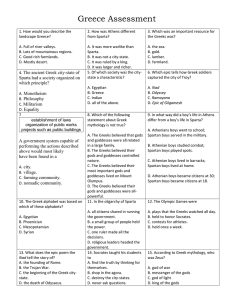
... 23. Which of the following epics is the world’s oldest story? A. Iliad B. Odyssey C. Epic of Gilgamesh D. Mahabharata 26. What unites of government existed in ancient Greece? A. Assemblies B. Monarchies C. Empires D. City-states ...
... 23. Which of the following epics is the world’s oldest story? A. Iliad B. Odyssey C. Epic of Gilgamesh D. Mahabharata 26. What unites of government existed in ancient Greece? A. Assemblies B. Monarchies C. Empires D. City-states ...
Roles of Governments in History
... communities in eastern Europe were ruled by monarchs. These rulers had total power over in their communities. ...
... communities in eastern Europe were ruled by monarchs. These rulers had total power over in their communities. ...
Twenty Questions - Norwell Public Schools
... Follow Up Question: How is the U.S. government similar or different to Athens? ...
... Follow Up Question: How is the U.S. government similar or different to Athens? ...
Greece Wars and Culture - 6th Grade Social Studies
... 480BC King Xerxes invaded Greece with 200,000 foot soldiers. 479BC- Greeks defeated Persia 449BC- Peace between Greece and Persia 300’s BC- Persia so weakened by outside attacks Alexander is able to over throw. ...
... 480BC King Xerxes invaded Greece with 200,000 foot soldiers. 479BC- Greeks defeated Persia 449BC- Peace between Greece and Persia 300’s BC- Persia so weakened by outside attacks Alexander is able to over throw. ...
5. Roman Medicine - Garforth Academy
... Roman doctors Anyone could practise as a doctor without training or any regulation. Like the Greeks, however, many doctors were keen to find out more and trained by working for experienced doctors and/or by reading the Hippocratic Collection of books. Others travelled to Alexandria, the capital of ...
... Roman doctors Anyone could practise as a doctor without training or any regulation. Like the Greeks, however, many doctors were keen to find out more and trained by working for experienced doctors and/or by reading the Hippocratic Collection of books. Others travelled to Alexandria, the capital of ...
DISCOVERING ANCIENT GREECE (1500
... 3. ____ Theaters in ancient Greece were temples to this god. ...
... 3. ____ Theaters in ancient Greece were temples to this god. ...
The Glory That Was Greece PowerPoint Presentation in PPT Format
... Culture: Leaders in Greek Science ...
... Culture: Leaders in Greek Science ...
Chapter 8: Ancient Greece Study Guide 1. The mountain ranges
... the poet Homer told the story of a long war the early Greeks waged against Troy. 16. The type of government in which the “best” people inherited the right to rule a Greek citystate was call an aristocracy. 17. Government in Sparta differed from government in Athens in that Sparta’s citizens ha ...
... the poet Homer told the story of a long war the early Greeks waged against Troy. 16. The type of government in which the “best” people inherited the right to rule a Greek citystate was call an aristocracy. 17. Government in Sparta differed from government in Athens in that Sparta’s citizens ha ...
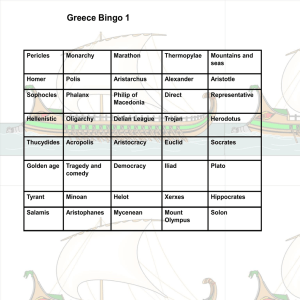
Greece Bingo (Review) - Mr. George Academics
... the Persians and sent Pheidippides the messenger running back with the good news ...
... the Persians and sent Pheidippides the messenger running back with the good news ...
Roman Medicine - kings-grove.cheshire.sch.uk
... Roman doctors Anyone could practise as a doctor without training or any regulation. Like the Greeks, however, many doctors were keen to find out more and trained by working for experienced doctors and/or by reading the Hippocratic Collection of books. Others travelled to Alexandria, the capital of ...
... Roman doctors Anyone could practise as a doctor without training or any regulation. Like the Greeks, however, many doctors were keen to find out more and trained by working for experienced doctors and/or by reading the Hippocratic Collection of books. Others travelled to Alexandria, the capital of ...
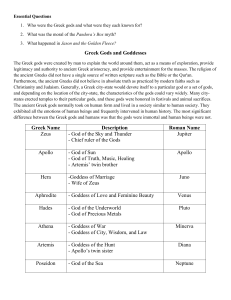
Greek Gods and Goddesses
... The Greek gods were created by man to explain the world around them, act as a means of exploration, provide legitimacy and authority to ancient Greek aristocracy, and provide entertainment for the masses. The religion of the ancient Greeks did not have a single source of written scripture such as th ...
... The Greek gods were created by man to explain the world around them, act as a means of exploration, provide legitimacy and authority to ancient Greek aristocracy, and provide entertainment for the masses. The religion of the ancient Greeks did not have a single source of written scripture such as th ...
THE ANCIENT GREEKS NAME: To complete this worksheet use the
... To complete this worksheet use the information found on the following website: http://www.mythologyteacher.com/GreekIntro.html ...
... To complete this worksheet use the information found on the following website: http://www.mythologyteacher.com/GreekIntro.html ...
Citizens
... E. Alexander admired and enjoyed Greek culture and ideas so much that he spread them throughout his Empire. ...
... E. Alexander admired and enjoyed Greek culture and ideas so much that he spread them throughout his Empire. ...
File
... 15. Pericles— Pericles, an Athenian politician/leader, introduced reforms that strengthened the democracy. He encouraged the spread of democracy and led Athens when the city was at its height. 16. Philosophy-System of beliefs and values. Aristotle, Plato and Socrates were all notable Greek philosoph ...
... 15. Pericles— Pericles, an Athenian politician/leader, introduced reforms that strengthened the democracy. He encouraged the spread of democracy and led Athens when the city was at its height. 16. Philosophy-System of beliefs and values. Aristotle, Plato and Socrates were all notable Greek philosoph ...
6TH GRADE SOCIAL STUDIES FIRST SEMESTER FINAL
... 22. a way of teaching still used today SOCRATIC METHOD 23. a time when Greek ideas spread to non-Greek people HELLENISTIC ERA 24. belief that happiness comes from doing your duty and following reason, not emotion STOICISM 25. a traditional story about gods and goddesses MYTHS 26. The Paleolithic peo ...
... 22. a way of teaching still used today SOCRATIC METHOD 23. a time when Greek ideas spread to non-Greek people HELLENISTIC ERA 24. belief that happiness comes from doing your duty and following reason, not emotion STOICISM 25. a traditional story about gods and goddesses MYTHS 26. The Paleolithic peo ...
Adobe Acrobat - Ancient Greece
... “….Our modern notion of history as a critical, disinterested enquiry into the significant facts of the past and a rational, objective exploration of them, is thus a legacy of Herodotus and Thucydides” ...
... “….Our modern notion of history as a critical, disinterested enquiry into the significant facts of the past and a rational, objective exploration of them, is thus a legacy of Herodotus and Thucydides” ...
People of Greece
... opposed some of Plato's teachings, and when Plato died, Aristotle was not appointed head of the Academy.Whereas Aristotle's teacher Plato had located ultimate reality in Ideas or eternal forms, knowable only through reflection and reason, Aristotle saw ultimate reality in physical objects, knowable ...
... opposed some of Plato's teachings, and when Plato died, Aristotle was not appointed head of the Academy.Whereas Aristotle's teacher Plato had located ultimate reality in Ideas or eternal forms, knowable only through reflection and reason, Aristotle saw ultimate reality in physical objects, knowable ...
Saraswati River - Ancient Greece
... “….Our modern notion of history as a critical, disinterested enquiry into the significant facts of the past and a rational, objective exploration of them, is thus a legacy of Herodotus and Thucydides” ...
... “….Our modern notion of history as a critical, disinterested enquiry into the significant facts of the past and a rational, objective exploration of them, is thus a legacy of Herodotus and Thucydides” ...
Chapter 4: The Rise of Ancient Greece
... science 2. Thales 3. Pythagoras a. Pythagorean theorem, taught that the world was round and that it revolved around a fixed point B. Greek Medicine 1. Hippocrates a. Hippocratic Oath b. Believed that diseases had natural causes and that the body could heal itself c. Advocated proper hygiene, a sound ...
... science 2. Thales 3. Pythagoras a. Pythagorean theorem, taught that the world was round and that it revolved around a fixed point B. Greek Medicine 1. Hippocrates a. Hippocratic Oath b. Believed that diseases had natural causes and that the body could heal itself c. Advocated proper hygiene, a sound ...
Ancient Greek medicine

Ancient Greek medicine was a compilation of theories that were constantly expanding through new ideologies and trials. Many components were considered in Ancient Greek Medicine, intertwining the spiritual with the physical. Specifically, the theories and ideologies from which Ancient Greek Medicine derived included the humors, gender, geographic location, social class, diet, trauma, beliefs, and mind set.Early on, Ancient Greeks believed that illnesses were “divine punishments” and that healing was a “gift from the Gods.” (Cartwright, Mark in “Greek Medicine.”) As trials continued wherein theories were tested against symptoms and results, Ancient Greek medicine also grew such that the pure spiritual beliefs as to “punishments” and “gifts” were converted to a foundation based in the physical, i.e., cause and effect.Humorism refers to blood, yellow bile, black bile and phlegm. It was also theorized that gender played a role in medicine because some diseases and treatments were different for women than for men. Moreover, geographic location and social class affected the living conditions of the people and might subject them to different environmental issues such as mosquitoes, rats, and availability of clean drinking water. Diet was thought to be an issue as well and might be affected by a lack of access to adequate nourishment. Trauma, such as suffered by gladiators, or from dog bites or other injury played a role in theories relating to understanding anatomy, and infections. Additionally there was significant focus on the beliefs and mind set of the patient in the diagnosis and treatment theories. It was recognized that the mind played a role in healing, or that it might also be the sole basis for the illness.Ancient Greek medicine began to revolve around the theory of humors. Humoral theory states that good health comes from perfect balance of the four humors blood, phlegm, yellow bile, and black bile. Consequently, poor health resulted from improper balance of the four humors. Hippocrates, known as the ""Father of Modern Medicine"", established a medical school at Kos and is the most important figure in ancient Greek medicine. Hippocrates and his students documented numerous illnesses in the Hippocratic Corpus, and developed the Hippocratic Oath for physicians, which is still in use today. The contributions to ancient Greek medicine of Hippocrates, Socrates and others had a lasting influence on Islamic medicine and Medieval European medicine until many of their findings eventually became obsolete in the 14th century.The earliest known Greek medical school opened in Cnidus in 700 BC. Alcmaeon, author of the first anatomical compilation, worked at this school, and it was here that the practice of observing patients was established. Despite their known respect for Egyptian medicine, attempts to discern any particular influence on Greek practice at this early time have not been dramatically successful because of the lack of sources and the challenge of understanding ancient medical terminology. It is clear, however, that the Greeks imported Egyptian substances into their pharmacopoeia, and the influence became more pronounced after the establishment of a school of Greek medicine in Alexandria.