* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Citizens
Pontic Greeks wikipedia , lookup
Regions of ancient Greece wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek architecture wikipedia , lookup
History of science in classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Greco-Persian Wars wikipedia , lookup
Athenian democracy wikipedia , lookup
Greek mythology wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek literature wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek medicine wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of Greece and the Greek world wikipedia , lookup
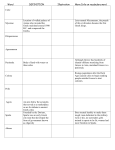
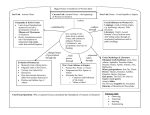
ANCIENT GREECE Ancient Greece History ID’s Polis – a city-state; a central city and the surrounding area it rules Acropolis – a high hill where a fortress was built. Democracy – a type of government in which people rule themselves Citizens – people who had the right to participate in government Mythology – stories about gods and heroes that try to explain how the world works Cavalry – a unit of soldiers who ride horses Alliance – an agreement to work together Strategy – plan for fighting a battle or war Hellenistic – greek-like ideas; combined with other cultures (Persian, Egyptian, Syrian) Philosopher – a person who studies the meaning of life, problems of right and wrong, or how we know things. Mt. Olympus – home of the gods Oracles – priests or priestesses acting as a medium through whom advice or prophecy was sought from the gods. Socrates – taught by asking questions Plato – created the academy aristotle – taught that people should live lives of moderation or balance Geography of Ancient Greece A. Rocky, mountainous land provided for good fresh water running down the mountains in creeks and streams natural defense barriers B. Surrounded by mediterranean sea on three sides (pennisula) many tales and legends grew up about the strange lands and creatures that could be found across the sea Too difficult to go by land so they learned to be great sailors C. More than 1400 Islands D. Very few flat areas for Farmlands E. Climate has mild winters and long, hot and dry summers Politics I. Oligarchy – 1st form of government for the Greeks Benefits: 1. More than one person ruling 2. Free men were citizens Drawbacks: 1. Only a few rich landowners (aristocrats) ran the city’s economy – they became the generals and judges. 2. Common people had little say II. Tyranny – 2nd form of government for the Greeks Benefits: 1. Overthrew the Oligarchy 2. Good leaders with strong armies that supported the people 3. Tyrants seized power to reform laws, aid the poor and cancel debts Drawbacks: 1. Tyrant held power through use of force 2. Common people had little say 3. Some tyrants became harsh and greedy and were overthrown III. Democracy – Final form of government Benefits: 1. All citizens have a say in government 2. All citizens have the right to express opinions 3. Power of nobles is limited Drawbacks: 1. Women, slaves and foreigners have no say because they weren’t citizens 2. Difficult to make decisions with so many people 3. Sometimes citizens were forced to attend assembly Direct Democracy (Athens) – each and every citizen debated each and every issue, created and enforced laws and were judges. Representative Democracy (U.S.) – citizens elect representatives to debate and vote on issues, create and enforce laws and be judges IV. The Persian Wars A. Series of wars between Persia and Greece B. The Persian army was strong and well organized C. Greeks won because they had better weapons and clever leaders V. The Peloponnesian War A. Sparta declared war to stop Athens’ growth B. Greek cities feared Athens would control Greece C.Sparta defeats Athens and becomes the most powerful citystate VI. Alexander the Great A. He was a brilliant commander B. The Egyptians surrendered without a fight and crowned Alexander pharaoh C. He became ruler of what had been the Persian Empire D. After crossing the Indus River, his exhausted troops refused to fight anymore E. Alexander admired and enjoyed Greek culture and ideas so much that he spread them throughout his Empire. Religion in ancient greece I. Centered around the greek gods/goddesses a. 12 major ones B. lived on mount olympus C. human shaped; got married, had children; made friends and enemies; had human failings like jealousy and bad-temper, which made them behave badly sometimes d. center of greek myths e. Each was responsible for some aspect of life and people worshipped the ones they found relevant II. Greek myths a. Illustrated the nature of the gods B. Taught what teased or angered them c. Did not set out rules or ideals like the bible or koran III. Religion and everyday life a. temples built; priests looked after the temples B. People had shrines in their homes c. People believed the gods spoke to ordinary people through oracles Hephaestus – God of blacksmiths