Macromolecule notes
... Carbon can bond with numerous other elements 1. Carbon has 4 free e- in it’s outer energy level 2. It has the ability to form up to 4 covalent bonds ...
... Carbon can bond with numerous other elements 1. Carbon has 4 free e- in it’s outer energy level 2. It has the ability to form up to 4 covalent bonds ...
Flashcards B1.1 How organisms interact with the environment /57
... Stored in uneaten materials (urine, faeces, fur etc) Released during respiration and used for movement and living processes Lost as heat. ...
... Stored in uneaten materials (urine, faeces, fur etc) Released during respiration and used for movement and living processes Lost as heat. ...
Biology Review - Renton School District
... • All matter is made up of atoms • Energy lasts forever ...
... • All matter is made up of atoms • Energy lasts forever ...
Organic Chemistry - Ms. Chambers' Biology
... And carbon can even bond with itself Carbon can form rings, chains, and other shapes of atoms ...
... And carbon can even bond with itself Carbon can form rings, chains, and other shapes of atoms ...
Cycles in Nature - Holy Family Regional School
... The water that falls from the atmosphere to the land and oceans is called precipitation. Rain, snow, sleet, and hail are all forms of precipitation. Most precipitation falls into the ocean. The precipitation that falls on the land and flows into streams, rivers, and lakes is called runoff. Groundwa ...
... The water that falls from the atmosphere to the land and oceans is called precipitation. Rain, snow, sleet, and hail are all forms of precipitation. Most precipitation falls into the ocean. The precipitation that falls on the land and flows into streams, rivers, and lakes is called runoff. Groundwa ...
Living things are energy rich complex chemical structures
... endergonic reactions- bonds are formed and energy absorbed. exergonic reactions – bonds are broken and energy is released. ...
... endergonic reactions- bonds are formed and energy absorbed. exergonic reactions – bonds are broken and energy is released. ...
Chapter 4 Guided Reading
... proteins and enzymes, and now we are going to look at testosterone and estradiol. Notice how similar these two molecules are, and yet you know what a vastly different effect each has. Label each molecule in the sketch below, and circle the differences. ...
... proteins and enzymes, and now we are going to look at testosterone and estradiol. Notice how similar these two molecules are, and yet you know what a vastly different effect each has. Label each molecule in the sketch below, and circle the differences. ...
DC = Dissolved Carbon
... 1. Apply knowledge of the carbon cycle and food web dynamics to explain the conceptual approach that geoengineering strategies (i.e. ocean fertilization) are built on. 2. Analyze the pros and cons of implementing geoengineering solutions to address changes to the global climate system. ...
... 1. Apply knowledge of the carbon cycle and food web dynamics to explain the conceptual approach that geoengineering strategies (i.e. ocean fertilization) are built on. 2. Analyze the pros and cons of implementing geoengineering solutions to address changes to the global climate system. ...
The Four Organic Compounds Notes
... When the amino acids join, they form a polymer called a polypeptide. The monomers are held together by peptide bonds. Proteins can be destroyed by extreme heat (fever) = _____________________________ ...
... When the amino acids join, they form a polymer called a polypeptide. The monomers are held together by peptide bonds. Proteins can be destroyed by extreme heat (fever) = _____________________________ ...
Practice Problems
... Hint: Dichromate = Cr2O72How many grams of ammonium dichromate would be needed to generate 400. grams of water from this decomposition? ...
... Hint: Dichromate = Cr2O72How many grams of ammonium dichromate would be needed to generate 400. grams of water from this decomposition? ...
RuBisCO and C4 plants
... respiration, so the process has been called photorespiration (even though ATP is used up, not made). Photorespiration wastes both carbon and energy, reducing the efficiency of photosynthesis. The C3 pathway of photosynthesis evolved when oxygen concentrations in the atmosphere were very low, much le ...
... respiration, so the process has been called photorespiration (even though ATP is used up, not made). Photorespiration wastes both carbon and energy, reducing the efficiency of photosynthesis. The C3 pathway of photosynthesis evolved when oxygen concentrations in the atmosphere were very low, much le ...
HiQ VERISEQ Carbon dioxide
... With gases used in pharmaceutical production, producers need to fulfil the requirements of US FDA Title 21 Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Parts 210 and 211 in order to assure batch uniformity and integrity of the drug product. API manufacturers should comply with ICH guideline Q7 (harmonised GMP ...
... With gases used in pharmaceutical production, producers need to fulfil the requirements of US FDA Title 21 Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Parts 210 and 211 in order to assure batch uniformity and integrity of the drug product. API manufacturers should comply with ICH guideline Q7 (harmonised GMP ...
AP Biology Topic 1 and 2 Test Preparation Assignment. Research
... AP Biology Topic 1 and 2 Test Preparation Assignment. Research and answer the following questions. You will be required to answer one of these questions (randomly drawn on the test date) on the upcoming test. You will not be allowed to use prewritten answers or any notes you make on the essays on th ...
... AP Biology Topic 1 and 2 Test Preparation Assignment. Research and answer the following questions. You will be required to answer one of these questions (randomly drawn on the test date) on the upcoming test. You will not be allowed to use prewritten answers or any notes you make on the essays on th ...
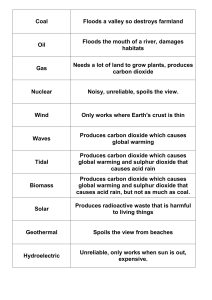
Coal - Rogue Physicist
... Produces carbon dioxide which causes global warming and sulphur dioxide that causes acid rain, but not as much as coal. ...
... Produces carbon dioxide which causes global warming and sulphur dioxide that causes acid rain, but not as much as coal. ...
VERISEQ® pharmaceutical grade gases. Carbon→dioxide.
... to documented manufacturing procedures, with any impurities and contaminants identified by qualified analytical equipment, reported. The specification fulfils the requirements of the European and US pharmacopoeia monographs. The analysis methods are in accordance with the same monographs or equivale ...
... to documented manufacturing procedures, with any impurities and contaminants identified by qualified analytical equipment, reported. The specification fulfils the requirements of the European and US pharmacopoeia monographs. The analysis methods are in accordance with the same monographs or equivale ...
combined with oxygen to form carbon dioxide.The energy that is
... nutrients from the inorganic nutrient pool.These nutrients can usually be found in the soil or water surrounding the plants or algae.These inorganic nutrients are then passed THE CARBON from organism to CYCLE atmospheric carbon dioxide organism as one photosynthesis animal respiration organism is co ...
... nutrients from the inorganic nutrient pool.These nutrients can usually be found in the soil or water surrounding the plants or algae.These inorganic nutrients are then passed THE CARBON from organism to CYCLE atmospheric carbon dioxide organism as one photosynthesis animal respiration organism is co ...
How cars make carbon dioxide
... Cars use the petrol and diesel Cars and lorries have engines that burn petrol or diesel. This gives the energy to move them along the road. ...
... Cars use the petrol and diesel Cars and lorries have engines that burn petrol or diesel. This gives the energy to move them along the road. ...
Name_______________________________
... B. Enzymes are quickly used up during the reactions. C. They can take place at any temperature or pH. D. They occur more quickly than reactions without enzymes. ...
... B. Enzymes are quickly used up during the reactions. C. They can take place at any temperature or pH. D. They occur more quickly than reactions without enzymes. ...
53 word equations
... Plants are able to make glucose from carbon dioxide gas in a reaction called photosynthesis. The other reactant is water, taken in through the roots. Oxygen gas is also formed in the process. Energy from the Sun is required for the reaction. ...
... Plants are able to make glucose from carbon dioxide gas in a reaction called photosynthesis. The other reactant is water, taken in through the roots. Oxygen gas is also formed in the process. Energy from the Sun is required for the reaction. ...
File
... different chemical compounds – it is not much use straight out of the ground (there are too many substances in it, all with different boiling points). As such it needs to be refined… ...
... different chemical compounds – it is not much use straight out of the ground (there are too many substances in it, all with different boiling points). As such it needs to be refined… ...
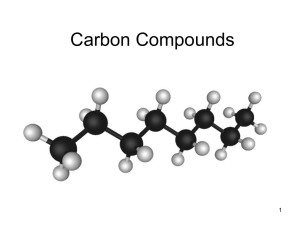
Carbon Compounds
... • Carbon can also bond to other carbon atoms, which gives carbon the ability to form chains that are almost unlimited in length. • These carbon-carbon bonds can be single, double, or triple. • The chains may be straight, branched, or even ring-shaped. • Therefore, carbon is unique in that it can for ...
... • Carbon can also bond to other carbon atoms, which gives carbon the ability to form chains that are almost unlimited in length. • These carbon-carbon bonds can be single, double, or triple. • The chains may be straight, branched, or even ring-shaped. • Therefore, carbon is unique in that it can for ...
Section 4.2 - CPO Science
... 4.2 Carbohydrates, fats and proteins • Carbohydrates are energy-rich compounds made from carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. • Cells use carbohydrates to get and store energy. • Carbohydrates are also called sugars or starches. ...
... 4.2 Carbohydrates, fats and proteins • Carbohydrates are energy-rich compounds made from carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. • Cells use carbohydrates to get and store energy. • Carbohydrates are also called sugars or starches. ...