What is an autoimmune disease?
... • ALLERGIES- immune response to substances that usually are not recognized as foreign. ...
... • ALLERGIES- immune response to substances that usually are not recognized as foreign. ...
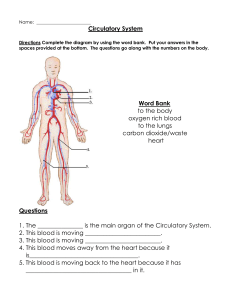
IV Blood – delivers oxygen, hormones and nutrients to cells and
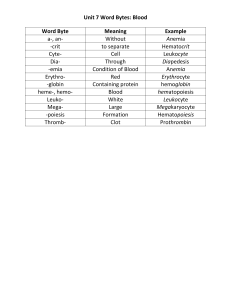
... B. Red Blood Cells (RBC) – carry oxygen from the lungs to the body. a. Hemoglobin – responsible for giving blood it’s red tint. b. RBC – carry CO2 (Carbon Dioxide) the lungs so it can be exhaled from the body. C. White Blood Cells (WBC) – responsible for fighting infections. a. T-cells and B-cells b ...
... B. Red Blood Cells (RBC) – carry oxygen from the lungs to the body. a. Hemoglobin – responsible for giving blood it’s red tint. b. RBC – carry CO2 (Carbon Dioxide) the lungs so it can be exhaled from the body. C. White Blood Cells (WBC) – responsible for fighting infections. a. T-cells and B-cells b ...
Presentación de PowerPoint
... – ventricles – arteries. Atrial systole – Ventricular systole – Diastole . ...
... – ventricles – arteries. Atrial systole – Ventricular systole – Diastole . ...
Study Guide
... The items listed below can be found in the powerpoint and assignment article used in this unit. ...
... The items listed below can be found in the powerpoint and assignment article used in this unit. ...
Quiz 2 - Delmar
... 2. _____ is vital to the function of the red blood cell, helping it transport oxygen to the tissues and some carbon dioxide away from tissues. a. Hemoglobin b. Albumin c. Fibrinogen d. Globulin 3. _____ are formed in the bone marrow and the spleen. a. Neutrophils b. Eosinophils c. Monocytes d. Granu ...
... 2. _____ is vital to the function of the red blood cell, helping it transport oxygen to the tissues and some carbon dioxide away from tissues. a. Hemoglobin b. Albumin c. Fibrinogen d. Globulin 3. _____ are formed in the bone marrow and the spleen. a. Neutrophils b. Eosinophils c. Monocytes d. Granu ...
Video - Blood - Lemon Bay High School
... 5. For blood to clot properly, the dissolved blood protein ___________________________ must be exposed to the “clotting factors” released by the fragments called _____________________. 6. Some white blood cells actually eat invading bacteria and viruses. This process is called ______________________ ...
... 5. For blood to clot properly, the dissolved blood protein ___________________________ must be exposed to the “clotting factors” released by the fragments called _____________________. 6. Some white blood cells actually eat invading bacteria and viruses. This process is called ______________________ ...
4/20 - Katy Independent School District
... 1. Carbon Dioxide is picked up by blood cells and released through inhaling ...
... 1. Carbon Dioxide is picked up by blood cells and released through inhaling ...