Codominance Practice Problems
... 3. Mom has type B blood. Dad has type O blood. They have a child with type O blood. Make a punnett square to show what Mom’s genotype must be to have a child with type O blood. ...
... 3. Mom has type B blood. Dad has type O blood. They have a child with type O blood. Make a punnett square to show what Mom’s genotype must be to have a child with type O blood. ...
A closed, needlefree in-line blood sampling system that reduces
... Hard exterior reservoir protects internal sheath from removal and tearing ...
... Hard exterior reservoir protects internal sheath from removal and tearing ...
Hematology Case Histories
... normal blood test results? The patient has more of everything 12. What are possible causes for an increased hematocrit? dehydration, diarrhea, burns, erythrocytosis (excessive rbc production), or polycythemia ...
... normal blood test results? The patient has more of everything 12. What are possible causes for an increased hematocrit? dehydration, diarrhea, burns, erythrocytosis (excessive rbc production), or polycythemia ...
BLOOD DISORDERS
... types of cells in the bloodstream, like red blood cells (which carry oxygen) and platelets (which help blood to clot). ...
... types of cells in the bloodstream, like red blood cells (which carry oxygen) and platelets (which help blood to clot). ...
red blood cells - Crestwood Local Schools
... types of cells in the bloodstream, like red blood cells (which carry oxygen) and platelets (which help blood to clot). ...
... types of cells in the bloodstream, like red blood cells (which carry oxygen) and platelets (which help blood to clot). ...
Blood disorders - Nutley Public Schools
... types of cells in the bloodstream, like red blood cells (which carry oxygen) and platelets (which help blood to clot). ...
... types of cells in the bloodstream, like red blood cells (which carry oxygen) and platelets (which help blood to clot). ...
Circulation Diagram
... Circulation Diagram Imagine that you are a red blood cell. What would be the path you might follow through Gary’s body as you traveled from his right thumb, through his heart, lungs, and back to his right thumb? a. On the outline of Gary’s body, draw just enough vessels to trace the path of a red bl ...
... Circulation Diagram Imagine that you are a red blood cell. What would be the path you might follow through Gary’s body as you traveled from his right thumb, through his heart, lungs, and back to his right thumb? a. On the outline of Gary’s body, draw just enough vessels to trace the path of a red bl ...
B7 Summary sheet
... Fill in the table below to show the differences between blood groups and the implications for blood transfusions. Then complete the genetic cross diagram and questions below. P227-229 p59-61 Patient’s Blood ...
... Fill in the table below to show the differences between blood groups and the implications for blood transfusions. Then complete the genetic cross diagram and questions below. P227-229 p59-61 Patient’s Blood ...
Lymph II: SPLEEN
... - germinal centers (contains plasmablasts and plasma cells derived from B cells) form after antigenic stimulation can push the central artery into an eccentric position PENICILLI: - straight arteriole branches from the central arteries in the white pulp that lead into red pulp MARGINAL ZONE: - lies ...
... - germinal centers (contains plasmablasts and plasma cells derived from B cells) form after antigenic stimulation can push the central artery into an eccentric position PENICILLI: - straight arteriole branches from the central arteries in the white pulp that lead into red pulp MARGINAL ZONE: - lies ...
RBCs – WBCs - www.jgibbs-vvc
... Antibodies: immune system protein, directed against antigens ABO system Rh system and Rh factor in pregnancy Blood Disorders – Red Blood Cells Anemia: reduction in oxygen-carrying capacity due to inadequate number of red blood cells or inadequate hemoglobin ...
... Antibodies: immune system protein, directed against antigens ABO system Rh system and Rh factor in pregnancy Blood Disorders – Red Blood Cells Anemia: reduction in oxygen-carrying capacity due to inadequate number of red blood cells or inadequate hemoglobin ...
Blood Stain Analysis
... When blood is not immediately obvious at a crime scene (i.e. attempts have been made to wash it away), a chemical called luminol can be sprayed over the area. Luminol reacts with the iron in haemoglobin in a chemiluminescent reaction to emit blue light. ...
... When blood is not immediately obvious at a crime scene (i.e. attempts have been made to wash it away), a chemical called luminol can be sprayed over the area. Luminol reacts with the iron in haemoglobin in a chemiluminescent reaction to emit blue light. ...
Chemical Composition of Blood Plasma
... • High- and low- MW compounds of bl.pl. • Interpretation of investigations in clinical practice: – “Basic set” – Disorders of the kidneys and internal environment – Inflammation – Liver disorders ...
... • High- and low- MW compounds of bl.pl. • Interpretation of investigations in clinical practice: – “Basic set” – Disorders of the kidneys and internal environment – Inflammation – Liver disorders ...
ch13 - WordPress.com
... The suffix -oma means mass or collection. Atheromas are collections of plaque that protrude into the lumen (opening) of an artery, weakening the muscle lining. ...
... The suffix -oma means mass or collection. Atheromas are collections of plaque that protrude into the lumen (opening) of an artery, weakening the muscle lining. ...
Water as an ergogen
... blood in ventricles at the end of diastole – Frank-Starling Law – increase in contractility increases volume pumped per beat – venous return ...
... blood in ventricles at the end of diastole – Frank-Starling Law – increase in contractility increases volume pumped per beat – venous return ...
+ Rh positive
... may have the blood type and Rh factor of either parent, or a combination of both parents. Rh factors follow a common pattern of genetic inheritance. • The Rh positive gene is dominant (stronger) and even when paired with an Rh negative gene, the positive gene takes over. ...
... may have the blood type and Rh factor of either parent, or a combination of both parents. Rh factors follow a common pattern of genetic inheritance. • The Rh positive gene is dominant (stronger) and even when paired with an Rh negative gene, the positive gene takes over. ...
Students of Ashtavakra Donated Blood
... Students of Ashtavakra Donated Blood It’s not how much you accomplish in life That really counts, But much you give to others. Students of Ashtavakra donated blood at Navjeevan Medical Relief & Research Foundation , Pitampura Blood Bank on 8th September 2015 . Some of the patients suffering from den ...
... Students of Ashtavakra Donated Blood It’s not how much you accomplish in life That really counts, But much you give to others. Students of Ashtavakra donated blood at Navjeevan Medical Relief & Research Foundation , Pitampura Blood Bank on 8th September 2015 . Some of the patients suffering from den ...
BLOOD TYPES and CODOMINANT TRAITS
... gene location on your chromosomes. Alleles “IA” and “IB” are CODOMINANT to the” i” allele. IA allele causes enzyme activity to create a variant sugar on the surface of red blood cells. IB causes enzyme activity to create a different variant on the red blood cell surface. “i” lacks the enzyme activit ...
... gene location on your chromosomes. Alleles “IA” and “IB” are CODOMINANT to the” i” allele. IA allele causes enzyme activity to create a variant sugar on the surface of red blood cells. IB causes enzyme activity to create a different variant on the red blood cell surface. “i” lacks the enzyme activit ...
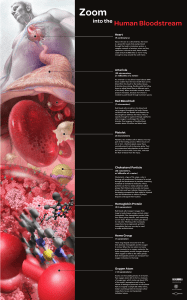
Zoom into the Human Bloodstream Annotated
... An arteriole is a tiny blood vessel (about 2000 times smaller than the heart itself) that carries blood from the heart to the body’s tissues. Arterioles have strong, flexible walls that allow them to adjust blood flow to different parts of the body. When arterioles constrict, blood pressure increase ...
... An arteriole is a tiny blood vessel (about 2000 times smaller than the heart itself) that carries blood from the heart to the body’s tissues. Arterioles have strong, flexible walls that allow them to adjust blood flow to different parts of the body. When arterioles constrict, blood pressure increase ...
BIOT 412: Medical Biotechnology
... Due to blood clot or ruptured artery if blood fails to reach every cell then it lead to failure of oxygen supply and lasting as neurological damage. ...
... Due to blood clot or ruptured artery if blood fails to reach every cell then it lead to failure of oxygen supply and lasting as neurological damage. ...
Normal Sickle Cell
... – Platelets: cell fragments that aid in clotting • Plasma – 90% water (allows materials to dissolve) – Amino acids, glucose, hormones, vitamins, salts, waste – Concentrations allows diffusion in/out of blood stream ...
... – Platelets: cell fragments that aid in clotting • Plasma – 90% water (allows materials to dissolve) – Amino acids, glucose, hormones, vitamins, salts, waste – Concentrations allows diffusion in/out of blood stream ...
HW 1
... Living with sickle cell “I have an illness called sickle cell. This means that my red blood cells are a different shape to everyone else's. Mine are sickle shaped (a sickle is a curved tool), normal blood cells are round. The shape of my cells makes it difficult for the blood to go around my body. T ...
... Living with sickle cell “I have an illness called sickle cell. This means that my red blood cells are a different shape to everyone else's. Mine are sickle shaped (a sickle is a curved tool), normal blood cells are round. The shape of my cells makes it difficult for the blood to go around my body. T ...