* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download RBCs – WBCs - www.jgibbs-vvc
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Schmerber v. California wikipedia , lookup
Blood transfusion wikipedia , lookup
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Autotransfusion wikipedia , lookup
Blood donation wikipedia , lookup
Jehovah's Witnesses and blood transfusions wikipedia , lookup
Men who have sex with men blood donor controversy wikipedia , lookup
Plateletpheresis wikipedia , lookup
Hemorheology wikipedia , lookup
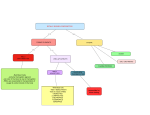
Chapter 7 Blood • • Three Primary Functions of the Blood Transportation – Nutrients, waste, hormones • Regulation • Defense • The Components of Blood • • • – Temperature, water volume, pH – Against infections and bleeding Plasma (55%) – – – – – – Water Electrolytes Proteins (albumins, globulins, clotting proteins) Hormones Gases Nutrients and wastes Formed elements (45%) – – – RBCs WBCs Platelets Red Blood Cells • • • • • • • • • • • Functions: transport oxygen and carbon dioxide Measurement: hematocrit, hemoglobin Origin: stem cells in the bone marrow Life span: 120 days in humans Control of production: erythropoietin White Blood Cells Functions – Protection from infection – Regulation of the inflammatory reaction Two Types – Granular: neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils – Agranular: lymphocytes and monocytes Granular Leukocytes Neutrophils – 60% of circulating wbcs – First on the scene to fight infection by engulfing microorganisms Eosinophils – 2 – 4% of circulating wbcs – Defend against large parasites (worms) – Moderate severity of allergic reactions • • • • • • • • • Basophils – 0.5% of circulating wbcs – Histamine in granules – role in inflammation Agranular Leukocytes Monocytes – 5% of circulating wbcs – Leave the blood and transform into macrophages Lymphocytes – 30% of circulating wbcs – Play a large role in the immune response – Two types • • B lymphocytes T lymphocytes Platelets Small cell fragments derived from megakaryocytes Important role in hemostasis Hemostasis Three stages – Vascular spasm: constriction of blood vessels to reduce blood flow – Platelet plug formation: sealing of the ruptured blood vessel – Coagulation: formation of a blood clot • • • • • • • • • • • Complicated series of reactions Fibrinogen → Fibrin Bleeding disorder – Hemophilia Blood Typing Concepts Antigen vs. antibody A and B antigens: surface markers on red blood cells Antibodies: immune system protein, directed against antigens ABO system Rh system and Rh factor in pregnancy Blood Disorders – Red Blood Cells Anemia: reduction in oxygen-carrying capacity due to inadequate number of red blood cells or inadequate hemoglobin – Iron-deficiency anemia: caused by inadequate intake or malabsorption of dietary iron • • • – Hemorrhagic anemia: caused by blood loss – Pernicious anemia: caused by Vitamin B12 deficiency – Hemolytic anemia: caused by destruction of red blood cells Blood Disorders – White Blood Cells Leukemia – Forms of cancer due to proliferation of white blood cells Mononucleosis • – Contagious Epstein-Barr virus infection of lymphocytes Septicemia (blood poisoning) – Bacteria proliferating in blood, overwhelming body’s defenses