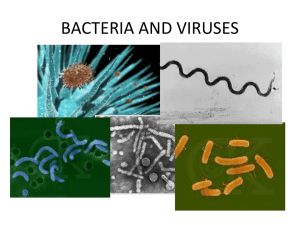
Biology 11 Notes: Kingdom Monera
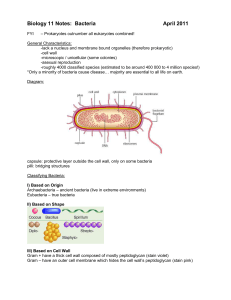
... Archaebacteria – ancient bacteria (live in extreme environments) Eubacteria – true bacteria II) Based on Shape ...
... Archaebacteria – ancient bacteria (live in extreme environments) Eubacteria – true bacteria II) Based on Shape ...
4 The dominant form of life on Earth
... The total volume of the Earth’s oceans is 1.4 × 1018 m3 . The total number of bacteria is therefore 1012 bacteria m−3 × 1.4 × 1018 m3 = 1.4 × 1030 bacteria. What is the mass of a single bacterium? A typical bacterium is 1µm (10−6 m) in size or 1µm3 (10−18 m3 ) in volume. Being made mostly of water, ...
... The total volume of the Earth’s oceans is 1.4 × 1018 m3 . The total number of bacteria is therefore 1012 bacteria m−3 × 1.4 × 1018 m3 = 1.4 × 1030 bacteria. What is the mass of a single bacterium? A typical bacterium is 1µm (10−6 m) in size or 1µm3 (10−18 m3 ) in volume. Being made mostly of water, ...
Bacteria
... Bacterial Adaptations for Survival. ENDOSPORES: • Hard, outer covering produced during harsh environments • Resistant to: ...
... Bacterial Adaptations for Survival. ENDOSPORES: • Hard, outer covering produced during harsh environments • Resistant to: ...
Food and Agriculture
... organic matter - typically about 1% in nature litter - partially decayed organic matter on the soil surface. humus - highly decomposed, fine, amorphous organic matter in the soil. ...
... organic matter - typically about 1% in nature litter - partially decayed organic matter on the soil surface. humus - highly decomposed, fine, amorphous organic matter in the soil. ...
Food and Agriculture
... organic matter - typically about 1% in nature litter - partially decayed organic matter on the soil surface. humus - highly decomposed, fine, amorphous organic matter in the soil. ...
... organic matter - typically about 1% in nature litter - partially decayed organic matter on the soil surface. humus - highly decomposed, fine, amorphous organic matter in the soil. ...
المحاضرة الثالثة عشر Thirteenth lecture
... Different types of diseases are caused by bacteria include: cholera, many sexually diseases األمراض الجنسية, and certain types of food poisoning التسمم الغذائي However, more bacteria are beneficial مفيدة. o Bacteria in our intestines أمعائنا produce important vitamins. o Bacteria recycle ...
... Different types of diseases are caused by bacteria include: cholera, many sexually diseases األمراض الجنسية, and certain types of food poisoning التسمم الغذائي However, more bacteria are beneficial مفيدة. o Bacteria in our intestines أمعائنا produce important vitamins. o Bacteria recycle ...
Biogeochemical cycling
... gases that are transparent to sunlight but trap heat radiating from the Earth’s surface. Gases: Methane, CO2, water vapor, N2O and O3 when it is in the troposhere. ...
... gases that are transparent to sunlight but trap heat radiating from the Earth’s surface. Gases: Methane, CO2, water vapor, N2O and O3 when it is in the troposhere. ...
Glycerol + Fatty acids
... their fatty acid tails, thus all the carbons are also bonded to the maximum number of hydrogens possible. ● saturated fats ● The hydrocarbon chains in these fatty acids are, thus, fairly straight and can pack closely together, making these fats solid at room temperature. ...
... their fatty acid tails, thus all the carbons are also bonded to the maximum number of hydrogens possible. ● saturated fats ● The hydrocarbon chains in these fatty acids are, thus, fairly straight and can pack closely together, making these fats solid at room temperature. ...
Bacteria and Viruses (SE).
... every 5 minutes. If one bacterium invades the human body, how many bacteria will be present in the body after 3 hours? ...
... every 5 minutes. If one bacterium invades the human body, how many bacteria will be present in the body after 3 hours? ...
Helpful and Harmful Bacteria Graphic Organizer PP
... • Some bacteria cause foods to go bad and become unsafe to eat • Bacteria cause foods like milk to sour • Vegetables get soft and spoil because of bacteria • Pathogens: bacteria that produce diseases • Lyme Disease, strep throat, pneumonia, anthrax, tetanus, and whooping cough are caused by bacteria ...
... • Some bacteria cause foods to go bad and become unsafe to eat • Bacteria cause foods like milk to sour • Vegetables get soft and spoil because of bacteria • Pathogens: bacteria that produce diseases • Lyme Disease, strep throat, pneumonia, anthrax, tetanus, and whooping cough are caused by bacteria ...
10 YEARS OF MICROBIAL COMMUNITIES IN ACTION
... the Southern Ocean: Can we establish links between biodiversity and carbon fluxes? Maggiopoulos, I.: A multi-parametric assessment of decontamination protocols for the subglacial Lake Ellsworth probe Meziti, A.: Seasonal changes of bacterial communities along the Kalamas River at the individual popu ...
... the Southern Ocean: Can we establish links between biodiversity and carbon fluxes? Maggiopoulos, I.: A multi-parametric assessment of decontamination protocols for the subglacial Lake Ellsworth probe Meziti, A.: Seasonal changes of bacterial communities along the Kalamas River at the individual popu ...
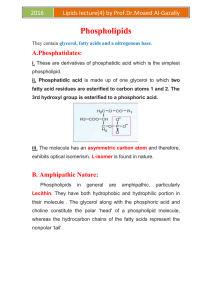
Lipids lecture(4) by Prof.Dr.Moaed Al
... form monolayers. This explains their role as components of biomembranes The self-assembly of phospholipids into bilayers is driven by hydrophobic interaction. They also act as detergents and emulsifying agents. In vivo, they act as pulmonary surfactants. ...
... form monolayers. This explains their role as components of biomembranes The self-assembly of phospholipids into bilayers is driven by hydrophobic interaction. They also act as detergents and emulsifying agents. In vivo, they act as pulmonary surfactants. ...
DiscBio_C2 Voc Part 1
... 15. one or more long, whiplike structures for locomotion in bacteria 16. a group of closely related species 17] archaeans living in environments of high salinity (10x the ocean) 18. lines of descent from a common ancestor 19. system of biological classification devised by Carolus Linnaeus 20. Archae ...
... 15. one or more long, whiplike structures for locomotion in bacteria 16. a group of closely related species 17] archaeans living in environments of high salinity (10x the ocean) 18. lines of descent from a common ancestor 19. system of biological classification devised by Carolus Linnaeus 20. Archae ...
Diversity of Prokaryotic Organisms
... swamps, marine sediments and digestive tract of mammals Highly sensitive to oxygen Produce energy (ATP) the reaction: ...
... swamps, marine sediments and digestive tract of mammals Highly sensitive to oxygen Produce energy (ATP) the reaction: ...
Lipids-I
... make it insoluble in water, where solve these ions replace the sodium or potassium ions are present in soap. -Due to the hard water to contain significant quantities of Ca2+ , Mg2+ and some Fe3+ that react with the charged ends of the soaps to form insoluble salts of fatty acid. The insoluble salts ...
... make it insoluble in water, where solve these ions replace the sodium or potassium ions are present in soap. -Due to the hard water to contain significant quantities of Ca2+ , Mg2+ and some Fe3+ that react with the charged ends of the soaps to form insoluble salts of fatty acid. The insoluble salts ...
Fatty acids
... Presence of one or more double bonds in hydrocarbon chain of unsaturated fatty acids results “ BENDS” in the molecules. These molecules do not stack well. As a result of that inter-molecular interactions become much weaker than saturated fatty acids leading to lower melting points. ...
... Presence of one or more double bonds in hydrocarbon chain of unsaturated fatty acids results “ BENDS” in the molecules. These molecules do not stack well. As a result of that inter-molecular interactions become much weaker than saturated fatty acids leading to lower melting points. ...
StudyBlue Guide - Microbiology Study Guides
... The sour Kraus and tomato juice have a pH in what range? acidic The process by which DNA is copied is replication Which microbe would be better suited to grow in/on orange juice fungus This binds (attaches) to the active site Competitive inhibitor Enzymes can A, B, C, and D Which of these allows for ...
... The sour Kraus and tomato juice have a pH in what range? acidic The process by which DNA is copied is replication Which microbe would be better suited to grow in/on orange juice fungus This binds (attaches) to the active site Competitive inhibitor Enzymes can A, B, C, and D Which of these allows for ...
The Nitrogen Cycle
... N/ha/yr). Some Cyanobacteria (blue-‐green algae) also fix nitrogen. Because they are photosynthetic, they can fix up to 50-‐100 kg N/ha/yr. ...
... N/ha/yr). Some Cyanobacteria (blue-‐green algae) also fix nitrogen. Because they are photosynthetic, they can fix up to 50-‐100 kg N/ha/yr. ...
Chapter 01 doc
... plants, giving rise to use of the term flora for microbes This term has been replaced by microbiota Microbes normally present in and on the human body are called normal microbiota ...
... plants, giving rise to use of the term flora for microbes This term has been replaced by microbiota Microbes normally present in and on the human body are called normal microbiota ...
Prokaryotes
... B. live in unusual habitats or generate unusual metabolic byproducts. C. have the same cell wall composition as other prokaryotes. D. are classified in one phylum. ...
... B. live in unusual habitats or generate unusual metabolic byproducts. C. have the same cell wall composition as other prokaryotes. D. are classified in one phylum. ...
Microorganisms Review Sheet
... 23. What are the characteristics of fungi? (nutrition, movement, how many cells, etc.) 24. How do they reproduce? 25. When do fungi undergo sexual reproduction? Why? 26. How is mitosis in a fungus different from that of an animal or plant? 27. What are hyphae? 28. Where is the reproductive body of a ...
... 23. What are the characteristics of fungi? (nutrition, movement, how many cells, etc.) 24. How do they reproduce? 25. When do fungi undergo sexual reproduction? Why? 26. How is mitosis in a fungus different from that of an animal or plant? 27. What are hyphae? 28. Where is the reproductive body of a ...
Chapter 1: The Microbial World and You
... Microbe Involved: _______________ These bacteria eat methane gas and are used to clean up hazardous waste dumps and landfills. They make an enzyme that breaks down more than 250 pollutants into harmless molecules. By piping methane into the soil, we can increase the number of methanotrophs that norm ...
... Microbe Involved: _______________ These bacteria eat methane gas and are used to clean up hazardous waste dumps and landfills. They make an enzyme that breaks down more than 250 pollutants into harmless molecules. By piping methane into the soil, we can increase the number of methanotrophs that norm ...
Lipids • Triglycerides –Fats and oils • Phospholipids
... • “0 Trans Fat” – can still contain up to 0.5 grams • Look for “partially hydrogenated vegetable oil” or “vegetable shortening” • IOM recommends trans fat intake be “as low as possible” ...
... • “0 Trans Fat” – can still contain up to 0.5 grams • Look for “partially hydrogenated vegetable oil” or “vegetable shortening” • IOM recommends trans fat intake be “as low as possible” ...
Phospholipid-derived fatty acids
Phospholipid-derived fatty acids (PLFA) are widely used in microbial ecology as chemotaxonomic markers of bacteria and other organisms. Phospholipids are the primary lipids composing cellular membranes. Phospholipids can be saponified, which releases the fatty acids contained in their diglyceride tail. Once the phospholipids of an unknown sample are saponified, the composition of the resulting PLFA can be compared to the PLFA of known organisms to determine the identity of the sample organism. PLFA analysis may be combined with other techniques, such as stable isotope probing to determine which microbes are metabolically active in a sample. PLFA analysis was pioneered by D.C. White, MD, PhD, at the University of Tennessee, in the early to mid 1980s.