Lipids
... • Important cell component – animal cell membranes – precursor of all other steroids • including vertebrate sex hormones ...
... • Important cell component – animal cell membranes – precursor of all other steroids • including vertebrate sex hormones ...
Classes of Biomolecules Lipids Biological Functions of Lipids
... constructing the honeycomb, • any of numerous substances of plant or animal origin that differ from fats in being less greasy, harder, and more brittle and in containing principally compounds of high molecular weight (as fatty acids, alcohols, and saturated hydrocarbons) • Long chain fatty acid wi ...
... constructing the honeycomb, • any of numerous substances of plant or animal origin that differ from fats in being less greasy, harder, and more brittle and in containing principally compounds of high molecular weight (as fatty acids, alcohols, and saturated hydrocarbons) • Long chain fatty acid wi ...
PPT
... Protective wax coatings found on some plants Energy-rich compounds with low densities Storage form of energy for plants and animals Structural components, especially in cellular membrane formation ...
... Protective wax coatings found on some plants Energy-rich compounds with low densities Storage form of energy for plants and animals Structural components, especially in cellular membrane formation ...
FATS - Catherine Huff`s Site
... 3) waxes Compound lipids: 1) phospholipids (a major component of biological membranes) 2) glycolipids 3) lipoproteins Derived lipids: 1) fatty acids : * saturated (milk fat) no double bonds in the fatty acid chain * unsaturated (corn oil) one or more double bonds in the fatty acid chain 2) prostagla ...
... 3) waxes Compound lipids: 1) phospholipids (a major component of biological membranes) 2) glycolipids 3) lipoproteins Derived lipids: 1) fatty acids : * saturated (milk fat) no double bonds in the fatty acid chain * unsaturated (corn oil) one or more double bonds in the fatty acid chain 2) prostagla ...
Soil Bacteria: useful in studying processes of organic matter
... lacking, the nitrate and organic compounds interact in such a way as to convert nitrate-a common constituent of soils and fertilizers-to nitrogen gas which cannot be used by most plants. Even a relatively small concentration of oxygen, not more than one tenth that of normal air, largely prevents thi ...
... lacking, the nitrate and organic compounds interact in such a way as to convert nitrate-a common constituent of soils and fertilizers-to nitrogen gas which cannot be used by most plants. Even a relatively small concentration of oxygen, not more than one tenth that of normal air, largely prevents thi ...
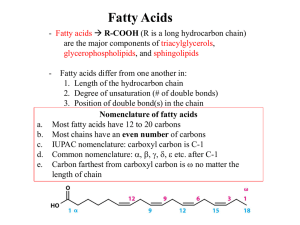
Fatty acids and their derivatives
... ◦ structural components in cell membranes (e.g phospolipids) ◦ means to store energy (e.g triacylglycerols) ◦ chemical signals, vitamins, or pigments, ◦ protective molecules (outer coatings for cells). ...
... ◦ structural components in cell membranes (e.g phospolipids) ◦ means to store energy (e.g triacylglycerols) ◦ chemical signals, vitamins, or pigments, ◦ protective molecules (outer coatings for cells). ...
Organisms
... Nutrient elements like N, S and P are released in simple inorganic (mineral) forms that are available to plants and other soil organisms, including other ...
... Nutrient elements like N, S and P are released in simple inorganic (mineral) forms that are available to plants and other soil organisms, including other ...
Munks - No-Till
... What do the microbes really do? • Simple answer • Microbes are involved in every aspect of soil quality • Organic matter production and processing • Decomposition of plant and animal residue and toxins ...
... What do the microbes really do? • Simple answer • Microbes are involved in every aspect of soil quality • Organic matter production and processing • Decomposition of plant and animal residue and toxins ...
Most membrane phospholipids contain glycerol
... • sphingomyelin *** Most membrane phospholipids contain glycerol (lecithin, phosphatidylcholine phosphatidylserine and cardiolipin). Sphingomyelin contains a sphingosine backbone instead of glycerol. Phospholipids are lipids. Each molecule is made up of one glycerol molecule attached to two fatty ac ...
... • sphingomyelin *** Most membrane phospholipids contain glycerol (lecithin, phosphatidylcholine phosphatidylserine and cardiolipin). Sphingomyelin contains a sphingosine backbone instead of glycerol. Phospholipids are lipids. Each molecule is made up of one glycerol molecule attached to two fatty ac ...
- Grasses and Greens
... A robust root system stimulated by Biohumate, reinforced by fungal VA mycorrhzae (VAM) and sustained by selected micro organisms (Bactolife) leads to a more effective use of available nutrients, a stronger more disease resistant plant and an improvement in crop yield and quality. The beneficial soil ...
... A robust root system stimulated by Biohumate, reinforced by fungal VA mycorrhzae (VAM) and sustained by selected micro organisms (Bactolife) leads to a more effective use of available nutrients, a stronger more disease resistant plant and an improvement in crop yield and quality. The beneficial soil ...
Saturated fatty acid
... • Saturated fatty acid: A long-chain carboxylic acid containing only carbon–carbon single bonds. • Unsaturated fatty acid: A long-chain carboxylic acid containing one or more carbon–carbon double bonds. • If double bonds are present in naturally occurring fats and oils, the double bonds are usually ...
... • Saturated fatty acid: A long-chain carboxylic acid containing only carbon–carbon single bonds. • Unsaturated fatty acid: A long-chain carboxylic acid containing one or more carbon–carbon double bonds. • If double bonds are present in naturally occurring fats and oils, the double bonds are usually ...
Principles of Biochemistry 4/e
... - TGs that have 3 saturated fatty acid groups are solid at room temp. - TGs with unsaturated groups tend to be liquids at room temp. Olive oil (triolein) 3 oleates ...
... - TGs that have 3 saturated fatty acid groups are solid at room temp. - TGs with unsaturated groups tend to be liquids at room temp. Olive oil (triolein) 3 oleates ...
File
... Both are ‘prokaryotic’ and have a single strand of genetic information floating in the cytoplasm. There is no organized ‘nucleus’. Bacteria – are the oldest and most abundant group of living organisms. Some have fossil records! Some lived in harshest conditions (like our early Earth). Cyanobacteria ...
... Both are ‘prokaryotic’ and have a single strand of genetic information floating in the cytoplasm. There is no organized ‘nucleus’. Bacteria – are the oldest and most abundant group of living organisms. Some have fossil records! Some lived in harshest conditions (like our early Earth). Cyanobacteria ...
Lipids_Notes
... Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an even number of carbons ranging from 14 to 22. Fatty acids have a characteristically long chain of carbon and hydrogen atoms forming a hydrocarbon tail. The tails determine many of their properties including insolubility in water as they are hydropho ...
... Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an even number of carbons ranging from 14 to 22. Fatty acids have a characteristically long chain of carbon and hydrogen atoms forming a hydrocarbon tail. The tails determine many of their properties including insolubility in water as they are hydropho ...
Document
... What is the major role of fat in our diets? a. to add fiber b. to provide energy c. to create structural material d. to synthesize hemoglobin e. I dont know ...
... What is the major role of fat in our diets? a. to add fiber b. to provide energy c. to create structural material d. to synthesize hemoglobin e. I dont know ...
Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
... salts with soaps Synthetic detergents are alkylbenzene sulfonates that dissolve dirt like soaps but do not form scums with Mg+2 and Ca+2 . ...
... salts with soaps Synthetic detergents are alkylbenzene sulfonates that dissolve dirt like soaps but do not form scums with Mg+2 and Ca+2 . ...
PowerPoint slide presentation
... polyenoic fatty acids in phosphatidylcholine (PC) and cardiolipin (CL). Decrease Viable biomass (total PLFA) 4. Cell lysis ~ high diglyceride/PLFA ratio. ...
... polyenoic fatty acids in phosphatidylcholine (PC) and cardiolipin (CL). Decrease Viable biomass (total PLFA) 4. Cell lysis ~ high diglyceride/PLFA ratio. ...
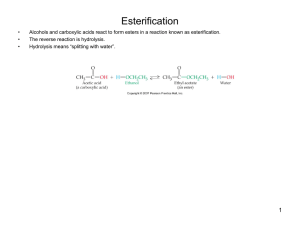
Esterification
... 3 fatty acids form an ester bond to glycerol; fatty acids in nature are part of triglycerides and are fats or oils. – Fats are from animal sources. They are solid at room temperature due to the stronger IFAs that form when the carbon chains stack together. – Oils are from plant sources. They are liq ...
... 3 fatty acids form an ester bond to glycerol; fatty acids in nature are part of triglycerides and are fats or oils. – Fats are from animal sources. They are solid at room temperature due to the stronger IFAs that form when the carbon chains stack together. – Oils are from plant sources. They are liq ...
Phospholipid-derived fatty acids
Phospholipid-derived fatty acids (PLFA) are widely used in microbial ecology as chemotaxonomic markers of bacteria and other organisms. Phospholipids are the primary lipids composing cellular membranes. Phospholipids can be saponified, which releases the fatty acids contained in their diglyceride tail. Once the phospholipids of an unknown sample are saponified, the composition of the resulting PLFA can be compared to the PLFA of known organisms to determine the identity of the sample organism. PLFA analysis may be combined with other techniques, such as stable isotope probing to determine which microbes are metabolically active in a sample. PLFA analysis was pioneered by D.C. White, MD, PhD, at the University of Tennessee, in the early to mid 1980s.