Biochemistry of Cells - Lakewood City Schools
... Proteins are polymers made of monomers called amino acids All proteins are made of 20 different amino acids linked in different orders Proteins are used to build cells, act as hormones & enzymes, and do much of the work in a cell ...
... Proteins are polymers made of monomers called amino acids All proteins are made of 20 different amino acids linked in different orders Proteins are used to build cells, act as hormones & enzymes, and do much of the work in a cell ...
Biochemistry of Cells
... The nature and arrangement of amino acids in the active site make it specific for only one type of substrate. ...
... The nature and arrangement of amino acids in the active site make it specific for only one type of substrate. ...
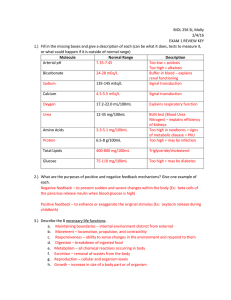
Exam 1 Review KEY
... 14.) Define each of the structural levels of proteins. Primary – single strand of amino acids Secondary – 3D arrangement (alpha helix or beta sheet) Tertiary – overall molecular structure/secondary pieces that have come together Quaternary – 2+ polypeptides come together 15.) When DNA polymerase cre ...
... 14.) Define each of the structural levels of proteins. Primary – single strand of amino acids Secondary – 3D arrangement (alpha helix or beta sheet) Tertiary – overall molecular structure/secondary pieces that have come together Quaternary – 2+ polypeptides come together 15.) When DNA polymerase cre ...
4 Types Biological Molecules in plants and animals
... catalysts for chemical reactions in living things. Thousands of chemical reactions are going on in your body EACH SECOND. Sugar does not turn into water and carbon dioxide by itself. Outside the body, this reaction would need a flame. How does the body do this at a lower temperature? Enzymes allow y ...
... catalysts for chemical reactions in living things. Thousands of chemical reactions are going on in your body EACH SECOND. Sugar does not turn into water and carbon dioxide by itself. Outside the body, this reaction would need a flame. How does the body do this at a lower temperature? Enzymes allow y ...
Chapter 11
... Enzymes allow your body to initiate chemical reactions at low temperature and to control the rate of reactions. Catalyst – a chemical that allows a reaction to have a much lower activation energy than it normally would The body controls the rate of reactions by regulating the amount of enzymes produ ...
... Enzymes allow your body to initiate chemical reactions at low temperature and to control the rate of reactions. Catalyst – a chemical that allows a reaction to have a much lower activation energy than it normally would The body controls the rate of reactions by regulating the amount of enzymes produ ...
Chemistry of Life notes
... Below is a dehydration synthesis reaction of two amino acids: - highlight the atoms that become the water molecule ...
... Below is a dehydration synthesis reaction of two amino acids: - highlight the atoms that become the water molecule ...
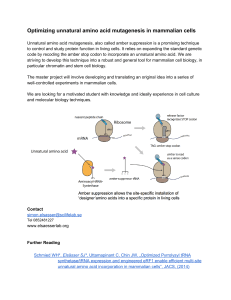
Optimizing unnatural amino acid mutagenesis in mammalian cells
... Unnatural amino acid mutagenesis, also called amber suppression is a promising technique to control and study protein function in living cells. It relies on expanding the standard genetic code by recoding the amber stop codon to incorporate an unnatural amino acid. We are striving to develop this ...
... Unnatural amino acid mutagenesis, also called amber suppression is a promising technique to control and study protein function in living cells. It relies on expanding the standard genetic code by recoding the amber stop codon to incorporate an unnatural amino acid. We are striving to develop this ...
BIO 220 Chapter 8 lecture outline Vocabulary Central dogma of
... 2. What is the central dogma of biology? Who proposed this theory? 3. What is the difference between the terms genotype and phenotype? Are bacteria typically diploid or haploid? What do diploid and haploid mean? 4. How many chromosomes does the typical bacterial cell have? In what form do these chro ...
... 2. What is the central dogma of biology? Who proposed this theory? 3. What is the difference between the terms genotype and phenotype? Are bacteria typically diploid or haploid? What do diploid and haploid mean? 4. How many chromosomes does the typical bacterial cell have? In what form do these chro ...
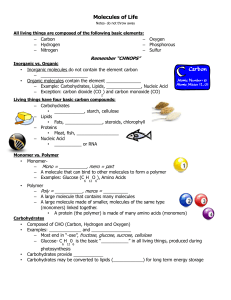
Molecules of Life---Whoa! - Rimac-Science-Web
... Carbon atoms have four valence electrons, allowing them to form strong covalent bonds with many other elements, including hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur, and nitrogen. ...
... Carbon atoms have four valence electrons, allowing them to form strong covalent bonds with many other elements, including hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur, and nitrogen. ...
Building Macromolecules Notes
... One important group of proteins - enzymes help control chemical reactions by acting as catalysts. Catalysts speed up reactions by lowering activation energy. ...
... One important group of proteins - enzymes help control chemical reactions by acting as catalysts. Catalysts speed up reactions by lowering activation energy. ...
Lesson 27 - Leavell Science Home
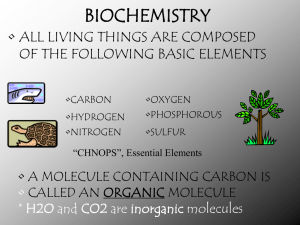
... Carbon is especially important because one carbon atom can make covalent bonds with four other atoms, resulting in the formation of very stable and complex structures. Carbon is in all living things, as well as in the remains of living things. Molecules containing carbon are called organic molecules ...
... Carbon is especially important because one carbon atom can make covalent bonds with four other atoms, resulting in the formation of very stable and complex structures. Carbon is in all living things, as well as in the remains of living things. Molecules containing carbon are called organic molecules ...
File
... 1. Unsaturated fats- Have a Carbon to Carbon Double bond (C=C) 2. Saturated fats- Do not have a C=C ...
... 1. Unsaturated fats- Have a Carbon to Carbon Double bond (C=C) 2. Saturated fats- Do not have a C=C ...
File
... Are Made Up Of: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen Monomer / subunit: _____________________ consisting of An amino group Carboxyl group R group There are exactly 20 different amino acids. Think of them like beads on a strand. Which beads you put on and in which order determines the necklace ...
... Are Made Up Of: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen Monomer / subunit: _____________________ consisting of An amino group Carboxyl group R group There are exactly 20 different amino acids. Think of them like beads on a strand. Which beads you put on and in which order determines the necklace ...
Worksheet Lesson 5: The discovery of DNA`s
... Worksheet Lesson 5: The discovery of DNA's structure We can't credit just one scientist with the discovery of the structure of DNA. It was the work of many different scientists who built on the work of others before them. In this activity you will be finding out about some of these scientists and th ...
... Worksheet Lesson 5: The discovery of DNA's structure We can't credit just one scientist with the discovery of the structure of DNA. It was the work of many different scientists who built on the work of others before them. In this activity you will be finding out about some of these scientists and th ...
Lesson 2: DNA Transcription and Translation Introduction This
... DNA transcription occurs in the nucleus. Messenger RNA (mRNA) makes a complimentary strand to the section of DNA coding for the protein. In mRNA, adenine compliments with uracil instead of thymine, the compliment in DNA. The messenger RNA carries the complimentary strand out of the nucleus to the ri ...
... DNA transcription occurs in the nucleus. Messenger RNA (mRNA) makes a complimentary strand to the section of DNA coding for the protein. In mRNA, adenine compliments with uracil instead of thymine, the compliment in DNA. The messenger RNA carries the complimentary strand out of the nucleus to the ri ...
Chapter 2, section 2
... • The protein that binds to oxygen to deliver and release oxygen throughout the body: ...
... • The protein that binds to oxygen to deliver and release oxygen throughout the body: ...
Chemical Composition of Living Cells
... There are four general classes of macromolecules within living cells: nucleic acids, proteins, polysaccharides, and lipids. These compounds, which have molecular weights ranging from 1 x 103 to 1 x 106, are created through polymerization of building blocks that have molecular weights in the range of ...
... There are four general classes of macromolecules within living cells: nucleic acids, proteins, polysaccharides, and lipids. These compounds, which have molecular weights ranging from 1 x 103 to 1 x 106, are created through polymerization of building blocks that have molecular weights in the range of ...
amino acids - El Camino College
... Macromolecules • form the living organisms • have: – a carbon core base – the core has attached groups of atoms called functional groups which confer specific chemical properties ...
... Macromolecules • form the living organisms • have: – a carbon core base – the core has attached groups of atoms called functional groups which confer specific chemical properties ...
CHAPTER 9 DNA: The Genetic Material ACROSS
... that enables a bacterium to build the proteins needed for lactose metabolism only when lactose is present. Some of the genes determine whether or not other genes will be expressed; the other genes code for enzymes that break down lactose. 37. Eukaryotic cells contain more DNA than prokaryotic cells. ...
... that enables a bacterium to build the proteins needed for lactose metabolism only when lactose is present. Some of the genes determine whether or not other genes will be expressed; the other genes code for enzymes that break down lactose. 37. Eukaryotic cells contain more DNA than prokaryotic cells. ...
SBI 4U biochem 1
... • Primary Structure: the sequence of amino acids connected together through peptide bonds • Secondary Structure: coil-like alpha helix shapes and folded beta sheets due to hydrogen bonds • Tertiary Structure: 3D shapes of proteins • Quaternary Structure: multiple polypeptide chains arranged together ...
... • Primary Structure: the sequence of amino acids connected together through peptide bonds • Secondary Structure: coil-like alpha helix shapes and folded beta sheets due to hydrogen bonds • Tertiary Structure: 3D shapes of proteins • Quaternary Structure: multiple polypeptide chains arranged together ...
Molecules of Life
... – A large molecule that contains many molecules – A large molecule made of smaller, molecules of the same type (monomers) linked together. • A protein (the polymer) is made of many amino acids (monomers) ...
... – A large molecule that contains many molecules – A large molecule made of smaller, molecules of the same type (monomers) linked together. • A protein (the polymer) is made of many amino acids (monomers) ...
Molecules of Life
... – A large molecule that contains many molecules – A large molecule made of smaller, molecules of the same type (monomers) linked together. • A protein (the polymer) is made of many amino acids (monomers) ...
... – A large molecule that contains many molecules – A large molecule made of smaller, molecules of the same type (monomers) linked together. • A protein (the polymer) is made of many amino acids (monomers) ...
Here
... carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen. Other elements are found in proteins in very small amounts. Protein molecules are constructed from building blocks called amino acids. There are twenty different kinds of amino acids. As amino acids are joined to each other with special covalent peptide bonds, ...
... carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen. Other elements are found in proteins in very small amounts. Protein molecules are constructed from building blocks called amino acids. There are twenty different kinds of amino acids. As amino acids are joined to each other with special covalent peptide bonds, ...
Living Environment Regents Review
... Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the air. Too much carbon dioxide chloroplasts will cause the Earth to heat up Animals can (the greenhouse effect). eat the sugar made to use as energy ...
... Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the air. Too much carbon dioxide chloroplasts will cause the Earth to heat up Animals can (the greenhouse effect). eat the sugar made to use as energy ...