Lecture 3
... Folds in polypeptide that form a more stable structure, often involving hydrogen bonding between R groups There are two types of secondary structure: Helical structure called an alpha helix (α-helix) (region of polypeptide chain coils around itself Pleated sheet (β sheet(: two parts of polypeptide c ...
... Folds in polypeptide that form a more stable structure, often involving hydrogen bonding between R groups There are two types of secondary structure: Helical structure called an alpha helix (α-helix) (region of polypeptide chain coils around itself Pleated sheet (β sheet(: two parts of polypeptide c ...
Biology Top 105
... individual still only inherits two) • Ex. Blood Type (IA,IB, i) type A = IAIA or IAi type B = IBIB or IBi ...
... individual still only inherits two) • Ex. Blood Type (IA,IB, i) type A = IAIA or IAi type B = IBIB or IBi ...
Biology-CST Test 1 Two students were testing the amount of
... A protein molecules arranged in two layers with polar areas forming the outside of the membrane. B two layers of lipids organized with the nonpolar tails forming the interior of the membrane. C lipid molecules positioned between two carbohydrate layers. D protein molecules with polar and nonpolar ta ...
... A protein molecules arranged in two layers with polar areas forming the outside of the membrane. B two layers of lipids organized with the nonpolar tails forming the interior of the membrane. C lipid molecules positioned between two carbohydrate layers. D protein molecules with polar and nonpolar ta ...
slides
... • Given two strings (of same set of characters) find a sequence of reversals of substrings that will transform one to other • Biologist are interested in shortest such sequence • Which makes the algorithm more challenging, and it is one of the most studied problem in algorithmic bioinformatics !!! ...
... • Given two strings (of same set of characters) find a sequence of reversals of substrings that will transform one to other • Biologist are interested in shortest such sequence • Which makes the algorithm more challenging, and it is one of the most studied problem in algorithmic bioinformatics !!! ...
What elements am I made of?
... So what is a macromolecule? A very large molecule, such as a polymer or carbohydrate, consisting of many smaller structural units linked together. ...
... So what is a macromolecule? A very large molecule, such as a polymer or carbohydrate, consisting of many smaller structural units linked together. ...
HW and review worksheet
... b cells can tell the two apart c usually one is biologically active while the other is not B. Polymers 1. Large molecules made by linking many individual building blocks together in long chains. Four types – carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids 2. The building block subunits are called mon ...
... b cells can tell the two apart c usually one is biologically active while the other is not B. Polymers 1. Large molecules made by linking many individual building blocks together in long chains. Four types – carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids 2. The building block subunits are called mon ...
Guide 1406 Ch, 1-5
... Tetra valence, hydrocarbon, the functional groups Polysaccharides important in an organism Types of diabetes, insulin, glycogen where produced, functions Cholesterol in the blood, how to control levels Compare the # of electrons, protons neutrons atomic wt Define a cell, DNA Gene, organism, science, ...
... Tetra valence, hydrocarbon, the functional groups Polysaccharides important in an organism Types of diabetes, insulin, glycogen where produced, functions Cholesterol in the blood, how to control levels Compare the # of electrons, protons neutrons atomic wt Define a cell, DNA Gene, organism, science, ...
Chapter 1 • Lesson 3
... usually oils. Waxes are produced by both animals and plants. Waxes are made up of long-chain fatty acids attached to an alcohol molecule. Lipids have two main functions. They are used for long-term energy storage, and they insulate and waterproof the organism. For example, cutin and other waxes coat ...
... usually oils. Waxes are produced by both animals and plants. Waxes are made up of long-chain fatty acids attached to an alcohol molecule. Lipids have two main functions. They are used for long-term energy storage, and they insulate and waterproof the organism. For example, cutin and other waxes coat ...
How are biomolecules made?
... Inorganic compounds- Can have one or the other, but do not contain both carbon and hydrogen atoms ...
... Inorganic compounds- Can have one or the other, but do not contain both carbon and hydrogen atoms ...
What is Life? Project PART 6: The molecules of life
... The fatty end of these molecules will not dissolve in water, but the glycerol end will. For this reason when you drop lipids in water, they form little balls, with the glycerol ends touching the water, and the fatty ends in the middle. The plasma membrane, as well as other membranes in the cell, is ...
... The fatty end of these molecules will not dissolve in water, but the glycerol end will. For this reason when you drop lipids in water, they form little balls, with the glycerol ends touching the water, and the fatty ends in the middle. The plasma membrane, as well as other membranes in the cell, is ...
Proteins and Nucleic Acids
... order determines the structure of specific proteins. Every cell in the body contains this information. There are many different types of ...
... order determines the structure of specific proteins. Every cell in the body contains this information. There are many different types of ...
Eötvös Loránd Science University Faculty of Sciences Department of
... 3. Terminology and landmarks in gene technology. Basics of molecular cloning:, vectors, inserts, ligation, amplification, selection. 4. DNA modifying enzymes and their application. Design of recombinant DNA constructs. 5. DNA introduction into cells (transformation, infection, electroporation). Elec ...
... 3. Terminology and landmarks in gene technology. Basics of molecular cloning:, vectors, inserts, ligation, amplification, selection. 4. DNA modifying enzymes and their application. Design of recombinant DNA constructs. 5. DNA introduction into cells (transformation, infection, electroporation). Elec ...
Protein synthesis - Teachnet UK-home
... 3. What are the four bases of DNA called? 4. How many bases make up the code for one amino acid? This site will help you remember: - BBC Education - AS Guru - Biology - Genes and Genetics - Structure of DNA - Nucleotides ...
... 3. What are the four bases of DNA called? 4. How many bases make up the code for one amino acid? This site will help you remember: - BBC Education - AS Guru - Biology - Genes and Genetics - Structure of DNA - Nucleotides ...
Biology - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... Share similarities among a fundamental set of genes, and replicate this genetic information when reproducing ...
... Share similarities among a fundamental set of genes, and replicate this genetic information when reproducing ...
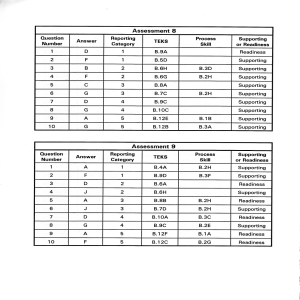
Assessment 8 Assessment I
... of the nucleotides, which make up a DNA molecule, was discovered in 1919 by Phoebus Levene. Levene discovered that nucleotides consisted of three parts. What are the three parts of every nucleotide? ...
... of the nucleotides, which make up a DNA molecule, was discovered in 1919 by Phoebus Levene. Levene discovered that nucleotides consisted of three parts. What are the three parts of every nucleotide? ...
Molecular Models Concept Map
... Word Bank: Amino acids, animals, carbohydrates, DNA, disaccharide, fructose, glucose, glycogen, isoleucine, leucine, lipids, monosaccharide, nucleic acids, phospholipids, plants, polypeptides, polysaccharides, proteins, RNA, saturated, serine, starch, steroids, sucrose, triglycerol, unsaturated ...
... Word Bank: Amino acids, animals, carbohydrates, DNA, disaccharide, fructose, glucose, glycogen, isoleucine, leucine, lipids, monosaccharide, nucleic acids, phospholipids, plants, polypeptides, polysaccharides, proteins, RNA, saturated, serine, starch, steroids, sucrose, triglycerol, unsaturated ...
Biochemistry Review
... 56. How does our body use the protein we eat? Breaks the proteins apart into the individual amino acids and then uses those amino acids to build new proteins according to the directions of the DNA 57. What is the bond between amino acids called? Peptide bond 58. Recognize picture 59. Each individual ...
... 56. How does our body use the protein we eat? Breaks the proteins apart into the individual amino acids and then uses those amino acids to build new proteins according to the directions of the DNA 57. What is the bond between amino acids called? Peptide bond 58. Recognize picture 59. Each individual ...
The Chemistry of Life
... In this unit we reviewed the structure of atoms. We investigated four biomolecules needed for life Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic acids We learned that enzymes help to speed up reactions in body cells. Understand that chemical reactions are needed for life’s processes, from t ...
... In this unit we reviewed the structure of atoms. We investigated four biomolecules needed for life Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic acids We learned that enzymes help to speed up reactions in body cells. Understand that chemical reactions are needed for life’s processes, from t ...
CHEMISTRY LIST OF TOPICS 1. Nature of chemistry (matter, mass
... 9. Hydrocarbons (IUPAC nomenclature, special properties of carbon, alkanes, alkenes and alkynes series, aromatic hydrocarbons, reactions of hydrocarbons); 10. Derivatives of hydrocarbons (nomenclature, alkyl - halides, alcohols, phenols, quinones, ethers, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, carbox ...
... 9. Hydrocarbons (IUPAC nomenclature, special properties of carbon, alkanes, alkenes and alkynes series, aromatic hydrocarbons, reactions of hydrocarbons); 10. Derivatives of hydrocarbons (nomenclature, alkyl - halides, alcohols, phenols, quinones, ethers, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, carbox ...
Biochemistry of Cells
... Substitution of one amino acid for another in hemoglobin causes sickle-cell disease ...
... Substitution of one amino acid for another in hemoglobin causes sickle-cell disease ...
VGCSE Health and Social Care Unit 2
... Three fatty acid chains become attached to a glycerol molecule which has 3 OH groups attached to its 3 carbons. This is called a condensation reaction because 3 water molecules are formed from 3 OH groups from the fatty acids chains and 3 H atoms from the glycerol. The bond between the fatty acid ch ...
... Three fatty acid chains become attached to a glycerol molecule which has 3 OH groups attached to its 3 carbons. This is called a condensation reaction because 3 water molecules are formed from 3 OH groups from the fatty acids chains and 3 H atoms from the glycerol. The bond between the fatty acid ch ...