Chapter 4
... When ___________ react, they often __________ the one electron needed to have eight valence electrons, a filled outer energy level. ...
... When ___________ react, they often __________ the one electron needed to have eight valence electrons, a filled outer energy level. ...
D. - Taylor County Schools
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
POGIL: Periodic Table Trends
... b. Why does Hydrogen fit into this group? c. Why does Hydrogen NOT fit into this group? (Hint: Why does it make sense that European Periodic Tables show H in both Group 1 and 17?) ...
... b. Why does Hydrogen fit into this group? c. Why does Hydrogen NOT fit into this group? (Hint: Why does it make sense that European Periodic Tables show H in both Group 1 and 17?) ...
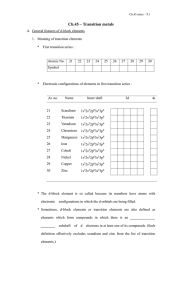
Chapter 5 – The Periodic Law 5-1 History of the Periodic Table A
... 3. His first periodic table was published in ___________. a. He placed _________________, __ (atomic mass _________), after ____________________, ___ (atomic mass _________). It allowed him to place _______________________ in a group of elements with which it shares similar _________________________ ...
... 3. His first periodic table was published in ___________. a. He placed _________________, __ (atomic mass _________), after ____________________, ___ (atomic mass _________). It allowed him to place _______________________ in a group of elements with which it shares similar _________________________ ...
Ch. 6 SG answers
... d. Alkali Metals __D__ 5. The more distinctive property of the noble gases is that they are a. metallic c. metalloids b. reactive d. largely unreactive __C___ 6. Lithium, the first element in Group 1, has an atomic number of 3. The second element in this group has an atomic number a. 4 c. 11 b. 10 d ...
... d. Alkali Metals __D__ 5. The more distinctive property of the noble gases is that they are a. metallic c. metalloids b. reactive d. largely unreactive __C___ 6. Lithium, the first element in Group 1, has an atomic number of 3. The second element in this group has an atomic number a. 4 c. 11 b. 10 d ...
UNIT 6- The Periodic Table CP Chemistry_CLASS NOTES.pptx
... have a single electron in their outermost level. They have 1 valence electron. ...
... have a single electron in their outermost level. They have 1 valence electron. ...
period
... Note that both hydrogen (H) and potassium (K) have just 1 electron in their outermost shell. Note also that these elements are both found in the 1st column of the periodic table. This is not a coincidence! ...
... Note that both hydrogen (H) and potassium (K) have just 1 electron in their outermost shell. Note also that these elements are both found in the 1st column of the periodic table. This is not a coincidence! ...
THE PERIODIC TABLE and PERIODIC LAW
... 1. Definition---a vertical column of elements on the Periodic Table --also called a “Family” 2. Valence electrons and group number---each element within a group has the same number of valence electrons --In general, the group number is equal to the number of valence electrons --For group numbers gre ...
... 1. Definition---a vertical column of elements on the Periodic Table --also called a “Family” 2. Valence electrons and group number---each element within a group has the same number of valence electrons --In general, the group number is equal to the number of valence electrons --For group numbers gre ...
Ch 5 power point
... atoms of A lose electrons easily. It is most likely to be an s-block metal because ionization energies increase across the periods. • Element B has a very high ionization energy which means that atoms of B have difficulty losing electrons. Therefore element B would most likely lie at the end of a p ...
... atoms of A lose electrons easily. It is most likely to be an s-block metal because ionization energies increase across the periods. • Element B has a very high ionization energy which means that atoms of B have difficulty losing electrons. Therefore element B would most likely lie at the end of a p ...
Trends on the Periodic Table
... Atomic Radius DECREASES across the P.T. because there is more of a positive pull on the electrons. More of an attraction pulls the electrons a bit closer. (think about having four people pull on a rope versus five. Five people are able to pull harder and will therefore bring the rope closer) ...
... Atomic Radius DECREASES across the P.T. because there is more of a positive pull on the electrons. More of an attraction pulls the electrons a bit closer. (think about having four people pull on a rope versus five. Five people are able to pull harder and will therefore bring the rope closer) ...
Name Pre-Test : Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... 1. Atomic ________________________ refers to the arrangement and number of smaller particles in an atom. 2. The ________________________ is the center or core of an atom. 3. ________________________ are positively charged particles located in the nucleus. 4. Neutrons have a ________________________ ...
... 1. Atomic ________________________ refers to the arrangement and number of smaller particles in an atom. 2. The ________________________ is the center or core of an atom. 3. ________________________ are positively charged particles located in the nucleus. 4. Neutrons have a ________________________ ...
Graphing Periodic Trends – Ana Julia Silva
... and crashing down to zero. 4a) What is happening to the number of protons and the number of energy levels as you move across the periodic table from left to right? How and why does this affect atomic radius. As you move across the periodic table, the number of protons increases by one. This affects ...
... and crashing down to zero. 4a) What is happening to the number of protons and the number of energy levels as you move across the periodic table from left to right? How and why does this affect atomic radius. As you move across the periodic table, the number of protons increases by one. This affects ...
Review of Periodic Trends
... 11. As one moves from left to right ( → ) within a period across the periodic table, the electronegativity of the elements encountered tends to: A. ...
... 11. As one moves from left to right ( → ) within a period across the periodic table, the electronegativity of the elements encountered tends to: A. ...
STUDY GUIDE – CHAPTER 1 ATOMS AND ELEMENTS 1
... Because all elements situated in the same group have the same number of valence electrons, they display similar chemical properties. They are therefore, also called “families”. Some groups of the periodic table display very district characteristic and are given special names. Group 1 - ALKALI METALS ...
... Because all elements situated in the same group have the same number of valence electrons, they display similar chemical properties. They are therefore, also called “families”. Some groups of the periodic table display very district characteristic and are given special names. Group 1 - ALKALI METALS ...
Document
... series, the atomic radii actually ____________again. At the beginning of the series, the increase in __________ _______________ with atomic number pulls in the electron cloud, resulting in a reduction of atomic size. Since electrons are added to an inner d subshell across the series, this adds to th ...
... series, the atomic radii actually ____________again. At the beginning of the series, the increase in __________ _______________ with atomic number pulls in the electron cloud, resulting in a reduction of atomic size. Since electrons are added to an inner d subshell across the series, this adds to th ...
Naming Compounds Essential Question
... In order to write a formula or name a compound, you need to understand relationships among the elements as shown by their position on the Periodic Table. 1. Metals are on the __________ and have the following characteristics: a. __________ oxidation numbers (the apparent charge on an atom in a compo ...
... In order to write a formula or name a compound, you need to understand relationships among the elements as shown by their position on the Periodic Table. 1. Metals are on the __________ and have the following characteristics: a. __________ oxidation numbers (the apparent charge on an atom in a compo ...
Unit 6 Chemical Equations and Reactions Balancing Equations
... Single Replacement- a metal will replace a less active metal in an ionic compound OR a nonmetal will replace a less active nonmetal. Double Replacement- the metals in ionic compounds switch places. Combustion- an organic compound containing carbon, hydrogen and sometimes oxygen reacts with oxygen ga ...
... Single Replacement- a metal will replace a less active metal in an ionic compound OR a nonmetal will replace a less active nonmetal. Double Replacement- the metals in ionic compounds switch places. Combustion- an organic compound containing carbon, hydrogen and sometimes oxygen reacts with oxygen ga ...
C1a Revision notes - Calthorpe Park Moodle
... contains very reactive metals such as sodium - Na - while group 7 contains very reactive non-metals such as chlorine - Cl. Note that you will never find a compound in the periodic table, because these consist of two or more different elements joined together by chemical bonds. Reactions and compound ...
... contains very reactive metals such as sodium - Na - while group 7 contains very reactive non-metals such as chlorine - Cl. Note that you will never find a compound in the periodic table, because these consist of two or more different elements joined together by chemical bonds. Reactions and compound ...
Scandium and Yttrium - Mercyhurst University
... reaction.4 At room temperature, scandium metal turns a light yellow or pink color in air.1 It is not obvious what is causing the color as Sc3+ would be expected to be colorless (white) due to the lack of d-electrons. Purification and Properties The most interesting thing about these two elements is ...
... reaction.4 At room temperature, scandium metal turns a light yellow or pink color in air.1 It is not obvious what is causing the color as Sc3+ would be expected to be colorless (white) due to the lack of d-electrons. Purification and Properties The most interesting thing about these two elements is ...
ionization energy
... particle) it becomes positively charged because it now has less negative charges than it originally had. When they lose these electrons they will end up with a smaller radius than when they were atoms. Group I or all those elements in the first column, except hydrogen, will all have similar properti ...
... particle) it becomes positively charged because it now has less negative charges than it originally had. When they lose these electrons they will end up with a smaller radius than when they were atoms. Group I or all those elements in the first column, except hydrogen, will all have similar properti ...
Name
... d. Alkali Metals _____ 5. The more distinctive property of the noble gases is that they are a. metallic c. metalloids b. reactive d. largely unreactive _____ 6. Lithium, the first element in Group 1, has an atomic number of 3. The second element in this group has an atomic number a. 4 c. 11 b. 10 d. ...
... d. Alkali Metals _____ 5. The more distinctive property of the noble gases is that they are a. metallic c. metalloids b. reactive d. largely unreactive _____ 6. Lithium, the first element in Group 1, has an atomic number of 3. The second element in this group has an atomic number a. 4 c. 11 b. 10 d. ...
The Modern Periodic Table
... • These elements form part of the actinide series in which the 5f orbitals are being filled. • The transuranium elements do not occur in nature. They are classified as artificial elments because they can only be generated in a laboratory by using sophisticated equipment. • Today, elements with atomi ...
... • These elements form part of the actinide series in which the 5f orbitals are being filled. • The transuranium elements do not occur in nature. They are classified as artificial elments because they can only be generated in a laboratory by using sophisticated equipment. • Today, elements with atomi ...
Practice Packet Unit: 5 Periodic Table
... The Periodic Table is a list of all the known elements. It is organized by increasing atomic number. There are two main groups on the periodic table: metals and nonmetals. The left side of the table contains elements with the greatest metallic properties. As you move from the left to the right, the ...
... The Periodic Table is a list of all the known elements. It is organized by increasing atomic number. There are two main groups on the periodic table: metals and nonmetals. The left side of the table contains elements with the greatest metallic properties. As you move from the left to the right, the ...