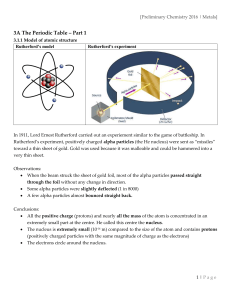
Physical Science
... Each row in the table of elements is a period. • Hydrogen, the first element in Period 1, has one electron in its first energy level. • Lithium, the first element in Period 2, has one electron in its second energy level. • Sodium, the first element in Period 3, has one electron in its third energy l ...
... Each row in the table of elements is a period. • Hydrogen, the first element in Period 1, has one electron in its first energy level. • Lithium, the first element in Period 2, has one electron in its second energy level. • Sodium, the first element in Period 3, has one electron in its third energy l ...
Flexbook - What is Matter?
... matter if the atoms are in groups, as in P4 or S8 , or isolated, as in Na. As long as there is only one kind of atom, the substance is an element. Elements cannot be chemically broken down into anything smaller and still retain the properties of the element. For example, an atom of iron can be smash ...
... matter if the atoms are in groups, as in P4 or S8 , or isolated, as in Na. As long as there is only one kind of atom, the substance is an element. Elements cannot be chemically broken down into anything smaller and still retain the properties of the element. For example, an atom of iron can be smash ...
Document
... Which family of elements tend to be at the top of the peaks? Which family of elements tend to be at the bottom of the “valleys”? Arrange the following atoms in order of increasing ionization energy: lithium, oxygen, magnesium, strontium, and chlorine. Explain your order. ...
... Which family of elements tend to be at the top of the peaks? Which family of elements tend to be at the bottom of the “valleys”? Arrange the following atoms in order of increasing ionization energy: lithium, oxygen, magnesium, strontium, and chlorine. Explain your order. ...
WS #10 - Atomic Theory and Periodic Table
... electrons more strongly. This atom has therefore acquired an extra share of negative charge and begins to resemble a negative ion. The other atom correspondingly begins to resemble a positive ion. The extent to which this sharing of an electron pair is unequal is indicated by the percentage ionic ch ...
... electrons more strongly. This atom has therefore acquired an extra share of negative charge and begins to resemble a negative ion. The other atom correspondingly begins to resemble a positive ion. The extent to which this sharing of an electron pair is unequal is indicated by the percentage ionic ch ...
Alexandre-Emile Béguyer de Chancourtois
... When going down Group VII, the atomic size of the halogens increases. Hence, the outermost occupied shell becomes further away from the nucleus. Therefore, the electrostatic force of attraction between the nucleus and the valence electrons decreases as the atomic size increases. It is harder for the ...
... When going down Group VII, the atomic size of the halogens increases. Hence, the outermost occupied shell becomes further away from the nucleus. Therefore, the electrostatic force of attraction between the nucleus and the valence electrons decreases as the atomic size increases. It is harder for the ...
(halogens group) 4-write down the electronic configuration
... 4-The density of pure water in solid state is………... a-less than its density in liquid state b- equal to its density in liquid state c- equal to its density in gaseous state d- greater than its density in liquid state 5-The density of pure water in solid state is ……… liquid state a-less than b- equal ...
... 4-The density of pure water in solid state is………... a-less than its density in liquid state b- equal to its density in liquid state c- equal to its density in gaseous state d- greater than its density in liquid state 5-The density of pure water in solid state is ……… liquid state a-less than b- equal ...
Unit 13
... C Many properties of the elements change in a predictable way as you move through the periodic table. These systematic variations are called periodic trends. Î The atomic radius is the distance from the center of an atom’s nucleus to its outermost electron. C Atoms get larger going down a group. (ie ...
... C Many properties of the elements change in a predictable way as you move through the periodic table. These systematic variations are called periodic trends. Î The atomic radius is the distance from the center of an atom’s nucleus to its outermost electron. C Atoms get larger going down a group. (ie ...
The Periodic Table
... – Also very reactive, so not found as pure elements in nature – Not as reactive as group 1 – Have 2 valence electrons ...
... – Also very reactive, so not found as pure elements in nature – Not as reactive as group 1 – Have 2 valence electrons ...
Periodic Properties of Elements
... Metals with more than one oxidation states exhibit more metallic behavior in their lower oxidation states - they acts as a reducing agent; An element with more than one oxidation state is a strong oxidizing agent when in its highest oxidation state. Trends Across the Periodic Among The Second Pe ...
... Metals with more than one oxidation states exhibit more metallic behavior in their lower oxidation states - they acts as a reducing agent; An element with more than one oxidation state is a strong oxidizing agent when in its highest oxidation state. Trends Across the Periodic Among The Second Pe ...
Atoms, Elements, and the Periodic Table Spring Packet
... period (or row) in the periodic table? (Example: Na Ar) ...
... period (or row) in the periodic table? (Example: Na Ar) ...
Students should be able to describe
... There are about 100 different elements. Elements are shown in the periodic table. Compounds are formed from elements by chemical reactions. Chemical reactions always involve the formation of one or more new substances, and often involve a detectable energy change. Compounds contain two or more eleme ...
... There are about 100 different elements. Elements are shown in the periodic table. Compounds are formed from elements by chemical reactions. Chemical reactions always involve the formation of one or more new substances, and often involve a detectable energy change. Compounds contain two or more eleme ...
Organic Functional Groups: Halocarbons
... Halocarbon Uses • Halocarbons are not naturally occurring • Their most important use is to build large organic molecules – their ability to substitute for hydrogen is matched by their ability to be removed! • Many industrial uses of halocarbons have been limited because of their toxicity, but they ...
... Halocarbon Uses • Halocarbons are not naturally occurring • Their most important use is to build large organic molecules – their ability to substitute for hydrogen is matched by their ability to be removed! • Many industrial uses of halocarbons have been limited because of their toxicity, but they ...
The Periodic Table
... used atomic number instead of mass. Periodic law: properties of elements are periodic functions of atomic numbers. ...
... used atomic number instead of mass. Periodic law: properties of elements are periodic functions of atomic numbers. ...
Our modern Periodic Table
... b) Attempts focused on grouping elements with similar properties c) In 1867, Dimitri Mendeleev found patterns in the elements and organized them into a table d) The resulting table had holes for elements not yet discovered ...
... b) Attempts focused on grouping elements with similar properties c) In 1867, Dimitri Mendeleev found patterns in the elements and organized them into a table d) The resulting table had holes for elements not yet discovered ...
Elements of Chemistry The Periodic Table ES14 - rdt-maps-lab
... to fill in the bottom of each card with the following information: • Number of protons, electrons, and neutrons • A model of an atom of that element • Number of electron shells in the atom • Number of valence electrons 4. Next, ask each group to arrange their cards in order using the following rules ...
... to fill in the bottom of each card with the following information: • Number of protons, electrons, and neutrons • A model of an atom of that element • Number of electron shells in the atom • Number of valence electrons 4. Next, ask each group to arrange their cards in order using the following rules ...
Unit 9 Chemical Equations and Reactions Balancing Equations Notes
... OR a nonmetal will replace a less active nonmetal. Double Replacement- the metals in ionic compounds _________________ places. Combustion- an ____________________ compound containing carbon, hydrogen and sometimes oxygen reacts with oxygen gas to form carbon dioxide and water. ...
... OR a nonmetal will replace a less active nonmetal. Double Replacement- the metals in ionic compounds _________________ places. Combustion- an ____________________ compound containing carbon, hydrogen and sometimes oxygen reacts with oxygen gas to form carbon dioxide and water. ...
Year 10 Chemistry File
... • Negative ions are also called ANIONS • Positive ions keep their same name. • Negative ions change the end of their name. O2- S2- Cl- all end in -ide ...
... • Negative ions are also called ANIONS • Positive ions keep their same name. • Negative ions change the end of their name. O2- S2- Cl- all end in -ide ...
Chemistry 1 Chapter 4, The Periodic Table
... valence electrons and are very reactive • they are never found in nature as pure elements because they are so reactive they are always combined with other elements as compounds •group 2 – alkaline-earth metals, they have 2 valence electrons, they must lose 2 electrons to have a stable configuration, ...
... valence electrons and are very reactive • they are never found in nature as pure elements because they are so reactive they are always combined with other elements as compounds •group 2 – alkaline-earth metals, they have 2 valence electrons, they must lose 2 electrons to have a stable configuration, ...
The Periodic Table
... Metals tend to lose their outer “valence” electrons because they are large (low electronegativity). Non-metals tend to attract electrons because they are small (high electronegativity). ...
... Metals tend to lose their outer “valence” electrons because they are large (low electronegativity). Non-metals tend to attract electrons because they are small (high electronegativity). ...
Biology - Mr. Julien`s Homepage
... 2. Biological, chemical, and physical properties of matter result from the ability of atoms to form bonds from electrostatic forces between electrons and protons and between atoms and molecules. As a basis for understanding this concept: g.*Students know how electronegativity and ionization energy r ...
... 2. Biological, chemical, and physical properties of matter result from the ability of atoms to form bonds from electrostatic forces between electrons and protons and between atoms and molecules. As a basis for understanding this concept: g.*Students know how electronegativity and ionization energy r ...
SCH 3U - Norbraten
... a) From your observations, what physical properties do the elements in each of your groups have in common? b) From your observations, what chemical properties do the elements in each of your groups have in common? 3. Is the solution that is produced when a metal reacts with water acidic or basic? 4. ...
... a) From your observations, what physical properties do the elements in each of your groups have in common? b) From your observations, what chemical properties do the elements in each of your groups have in common? 3. Is the solution that is produced when a metal reacts with water acidic or basic? 4. ...
Chemistry 4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table NEED TO
... The elements in Group 0 of the periodic table are called the noble gases. They are unreactive and do not easily form molecules because their atoms have stable arrangements of electrons. The noble gases have eight electrons in their outer energy level, except for helium, which has only two electrons. ...
... The elements in Group 0 of the periodic table are called the noble gases. They are unreactive and do not easily form molecules because their atoms have stable arrangements of electrons. The noble gases have eight electrons in their outer energy level, except for helium, which has only two electrons. ...
File - Lenora Henderson`s Flipped Chemistry Classroom
... increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their physical and chemical properties Elements that are in the same group have similar chemical and physical properties ...
... increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their physical and chemical properties Elements that are in the same group have similar chemical and physical properties ...
Homework Packet - Chemistry from AZ
... horizontal rows called periods are numbered 1 to 7; elements in the same period have the same number of principle energy levels (PEL’s) or shells vertical columns called groups or families, are numbered 1 to 18; elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons and therefore have ...
... horizontal rows called periods are numbered 1 to 7; elements in the same period have the same number of principle energy levels (PEL’s) or shells vertical columns called groups or families, are numbered 1 to 18; elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons and therefore have ...